
A line through origin meets the line \[2x = 3y + 13\] at the right angle at point\[Q\]. Find the absolute difference of coordinates of\[Q\].
Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint: In this problem, we need to find the slope of the line passing through the origin. Next, find the equation of the line passing through origin. Then, find the point of intersection of the two lines.
Complete step by step answer:
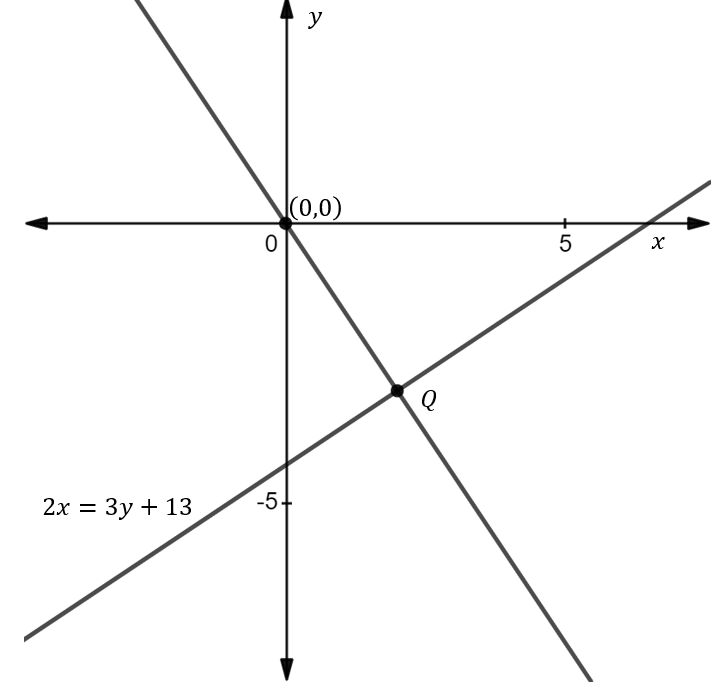
Rewrite, the given equation \[\left( {2x = 3y + 13} \right)\] of the line \[{L_1}\] in the form of \[y = mx + c\] as shown below.
\[
\,\,\,\,\,2x = 3y + 13 \\
\Rightarrow 3y = 2x - 13 \\
\Rightarrow y = \dfrac{2}{3}x - \dfrac{{13}}{3}\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,......\left( 1 \right) \\
\]
Compare, the above equation \[y = \dfrac{2}{3}x - \dfrac{{13}}{3}\] with \[y = mx + c\] to obtain the value of slope \[m\].
\[m = \dfrac{2}{3}\]
Let, the slope of another line \[{L_2} be {m_1}\].
As both the lines \[{L_1}\] and \[{L_2}\] intersect at right angle at point\[Q\],
\[
\,\,\,\,\,m \times {m_1} = - 1 \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{2}{3}{m_1} = - 1 \\
\Rightarrow {m_1} = - \dfrac{3}{2} \\
\]
The equation of line passing through point \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)\] having slope \[{m_1}\] is as follows:
\[y - {y_1} = {m_1}\left( {x - {x_1}} \right)\]
Since, the line \[{L_2}\] passes through the origin \[\left( {0,0} \right)\] and have slope \[- \dfrac{3}{2}\], substitute 0 for \[{x_1}\], 0 for \[{y_1}\] and \[- \dfrac{3}{2}\] for \[{m_1}\] in above equation.
\[
\,\,\,\,\,\,y - 0 = - \dfrac{3}{2}\left( {x - 0} \right) \\
\Rightarrow y = - \dfrac{3}{2}x \\
\Rightarrow 2y = - 3x \\
\Rightarrow 2y + 3x = 0\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,......\left( 2 \right) \\
\]
Now, the coordinate of the point \[Q\] is obtained by solving the equation (1) and (2).
From, equation (1) substitute, \[\dfrac{2}{3}x - \dfrac{{13}}{3}\] for \[y\] in equation (2).
\[
\,\,\,\,\,2\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}x - \dfrac{{13}}{3}} \right) + 3x = 0 \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{3}x - \dfrac{{26}}{3} + 3x = 0 \\
\Rightarrow 4x - 26 + 9x = 0 \\
\Rightarrow 13x = 26 \\
\Rightarrow x = 2 \\
\]
Substitute 2 for \[x\] in equation (1) to obtain the value of\[y\].
\[
\,\,\,\,\,\,y = \dfrac{2}{3}\left( 2 \right) - \dfrac{{13}}{3} \\
\Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{4 - 13}}{3} \\
\Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{ - 9}}{3} \\
y = - 3 \\
\]
Thus, the coordinate of the point \[Q\] is \[\left( {2, - 3} \right)\].
Note: When two lines intersect at right angles, the product of their slopes will be equal to -1. When two lines intersect each other, the intersection point is the solution of the two equations.
Complete step by step answer:

Rewrite, the given equation \[\left( {2x = 3y + 13} \right)\] of the line \[{L_1}\] in the form of \[y = mx + c\] as shown below.
\[
\,\,\,\,\,2x = 3y + 13 \\
\Rightarrow 3y = 2x - 13 \\
\Rightarrow y = \dfrac{2}{3}x - \dfrac{{13}}{3}\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,......\left( 1 \right) \\
\]
Compare, the above equation \[y = \dfrac{2}{3}x - \dfrac{{13}}{3}\] with \[y = mx + c\] to obtain the value of slope \[m\].
\[m = \dfrac{2}{3}\]
Let, the slope of another line \[{L_2} be {m_1}\].
As both the lines \[{L_1}\] and \[{L_2}\] intersect at right angle at point\[Q\],
\[
\,\,\,\,\,m \times {m_1} = - 1 \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{2}{3}{m_1} = - 1 \\
\Rightarrow {m_1} = - \dfrac{3}{2} \\
\]
The equation of line passing through point \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)\] having slope \[{m_1}\] is as follows:
\[y - {y_1} = {m_1}\left( {x - {x_1}} \right)\]
Since, the line \[{L_2}\] passes through the origin \[\left( {0,0} \right)\] and have slope \[- \dfrac{3}{2}\], substitute 0 for \[{x_1}\], 0 for \[{y_1}\] and \[- \dfrac{3}{2}\] for \[{m_1}\] in above equation.
\[
\,\,\,\,\,\,y - 0 = - \dfrac{3}{2}\left( {x - 0} \right) \\
\Rightarrow y = - \dfrac{3}{2}x \\
\Rightarrow 2y = - 3x \\
\Rightarrow 2y + 3x = 0\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,......\left( 2 \right) \\
\]
Now, the coordinate of the point \[Q\] is obtained by solving the equation (1) and (2).
From, equation (1) substitute, \[\dfrac{2}{3}x - \dfrac{{13}}{3}\] for \[y\] in equation (2).
\[
\,\,\,\,\,2\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}x - \dfrac{{13}}{3}} \right) + 3x = 0 \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{3}x - \dfrac{{26}}{3} + 3x = 0 \\
\Rightarrow 4x - 26 + 9x = 0 \\
\Rightarrow 13x = 26 \\
\Rightarrow x = 2 \\
\]
Substitute 2 for \[x\] in equation (1) to obtain the value of\[y\].
\[
\,\,\,\,\,\,y = \dfrac{2}{3}\left( 2 \right) - \dfrac{{13}}{3} \\
\Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{4 - 13}}{3} \\
\Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{ - 9}}{3} \\
y = - 3 \\
\]
Thus, the coordinate of the point \[Q\] is \[\left( {2, - 3} \right)\].
Note: When two lines intersect at right angles, the product of their slopes will be equal to -1. When two lines intersect each other, the intersection point is the solution of the two equations.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




