
A line passing through the point \[P\left( 2,-3 \right)\] meets the lines $x-2y+7=0$ and $x+3y-3=0$ at the points A & B respectively. If P divides A & B externally in the ratio 3:2, then find the equation of the line?
Answer
572.7k+ views
Hint: We start solving the problem by assuming the slope of the line passing through the point \[P\left( 2,-3 \right)\]. We then find the equation of the line using the fact that the equation of the line passing through the point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ and having slope ‘m’ is $y-{{y}_{1}}=m\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)$. We then find the point of intersections A and B of the obtained line with the lines $x-2y+7=0$ and $x+3y-3=0$. We then use the section formula if the point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ divides the points $\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ and $\left( {{x}_{3}},{{y}_{3}} \right)$ externally in the ratio a:b, then $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)=\left( \dfrac{a{{x}_{3}}-b{{x}_{2}}}{a-b},\dfrac{a{{y}_{3}}-b{{y}_{2}}}{a-b} \right)$. We then make the necessary calculations to find the value of slope which later gives us the equation of the required line.
Complete step-by-step solution
According to the problem, we are given that a line passing through the point \[P\left( 2,-3 \right)\] meets the lines $x-2y+7=0$ and $x+3y-3=0$ at the points A & B respectively. We need to find the equation of the line if the point P divides the points A & B externally in the ratio 3:2.
Let us assume the slope of the line passing through the point \[P\left( 2,-3 \right)\] be ‘m’.
We know that the equation of the line passing through the point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ and having slope ‘m’ is $y-{{y}_{1}}=m\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)$.
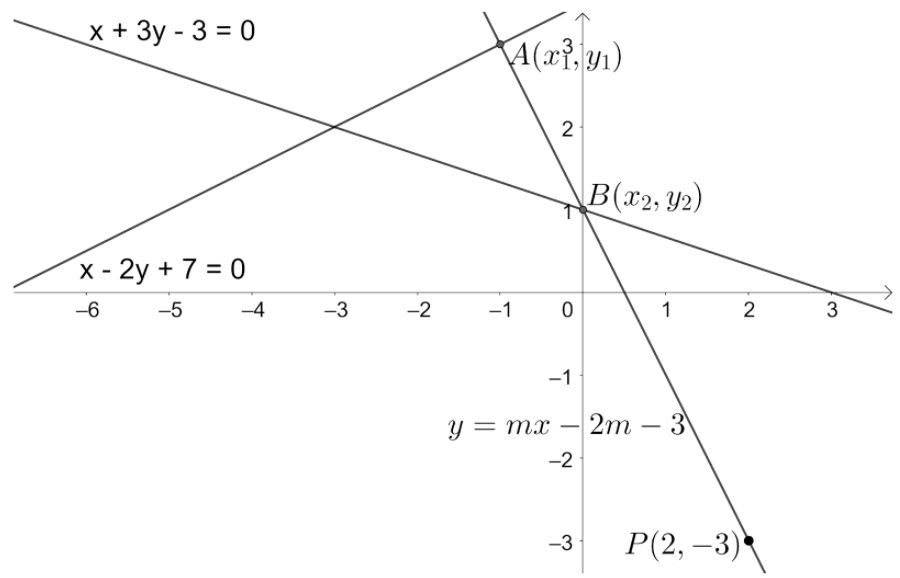
So, the equation of the line passing through the point \[P\left( 2,-3 \right)\] is $y+3=m\left( x-2 \right)$.
$\Rightarrow y+3=mx-2m$.
$\Rightarrow y=mx-2m-3$ ---(1).
Let us find the intersection point of this line with the line $x-2y+7=0$.
So, we have $x-2\left( mx-2m-3 \right)+7=0$.
$\Rightarrow x-2mx+4m+6+7=0$.
$\Rightarrow \left( 1-2m \right)x+4m+13=0$.
$\Rightarrow \left( 1-2m \right)x=-4m-13$.
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{4m+13}{2m-1}$. Let us substitute this in equation (1) to get y-coordinate.
So, we have $y=m\left( \dfrac{4m+13}{2m-1} \right)-2m-3$.
$\Rightarrow y=\left( \dfrac{4{{m}^{2}}+13m-\left( \left( 2m+3 \right)\left( 2m-1 \right) \right)}{2m-1} \right)$.
$\Rightarrow y=\left( \dfrac{4{{m}^{2}}+13m-\left( 4{{m}^{2}}+4m-3 \right)}{2m-1} \right)$.
$\Rightarrow y=\left( \dfrac{4{{m}^{2}}+13m-4{{m}^{2}}-4m+3}{2m-1} \right)$.
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{9m+3}{2m-1}$.
So, the intersection point of the lines $y=mx-2m-3$ and $x-2y+7=0$ is $A\left( \dfrac{4m+13}{2m-1},\dfrac{9m+3}{2m-1} \right)$ ---(2).
Let us find the intersection point of the line $y=mx-2m-3$ with the line $x+3y-3=0$.
So, we have $x+3\left( mx-2m-3 \right)-3=0$.
$\Rightarrow x+3mx-6m-9-3=0$.
$\Rightarrow \left( 1+3m \right)x-6m-12=0$.
$\Rightarrow \left( 1+3m \right)x=6m+12$.
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{6m+12}{1+3m}$. Let us substitute this in equation (1) to get y-coordinate.
So, we have $y=m\left( \dfrac{6m+12}{1+3m} \right)-2m-3$.
$\Rightarrow y=\left( \dfrac{6{{m}^{2}}+12m-\left( \left( 2m+3 \right)\left( 1+3m \right) \right)}{1+3m} \right)$.
$\Rightarrow y=\left( \dfrac{6{{m}^{2}}+12m-\left( 6{{m}^{2}}+11m+3 \right)}{1+3m} \right)$.
$\Rightarrow y=\left( \dfrac{6{{m}^{2}}+12m-6{{m}^{2}}-11m-3}{1+3m} \right)$.
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{m-3}{1+3m}$.
So, the intersection point of the lines $y=mx-2m-3$ and $x+3y-3=0$ is $B\left( \dfrac{6m+12}{1+3m},\dfrac{m-3}{1+3m} \right)$ ---(3).
Now, we have given that \[P\left( 2,-3 \right)\] divides the points $A\left( \dfrac{4m+13}{2m-1},\dfrac{9m+3}{2m-1} \right)$ and $B\left( \dfrac{6m+12}{1+3m},\dfrac{m-3}{1+3m} \right)$ internally in the ratio 3:2.
We know that if the point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ divides the points $\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ and $\left( {{x}_{3}},{{y}_{3}} \right)$ externally in the ratio a:b, then $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)=\left( \dfrac{a{{x}_{3}}-b{{x}_{2}}}{a-b},\dfrac{a{{y}_{3}}-b{{y}_{2}}}{a-b} \right)$.
So, we have $\left( 2,-3 \right)=\left( \dfrac{3\left( \dfrac{6m+12}{1+3m} \right)-2\left( \dfrac{4m+13}{2m-1} \right)}{3-2},\dfrac{3\left( \dfrac{m-3}{1+3m} \right)-2\left( \dfrac{9m+3}{2m-1} \right)}{3-2} \right)$.
$\Rightarrow \left( 2,-3 \right)=\left( \dfrac{\left( \dfrac{18m+36}{1+3m} \right)-\left( \dfrac{8m+26}{2m-1} \right)}{1},\dfrac{\left( \dfrac{3m-9}{1+3m} \right)-\left( \dfrac{18m+6}{2m-1} \right)}{1} \right)$.
$\Rightarrow \left( 2,-3 \right)=\left( \left( \dfrac{\left( \left( 18m+36 \right)\left( 2m-1 \right) \right)-\left( \left( 8m+26 \right)\left( 1+3m \right) \right)}{\left( 1+3m \right)\left( 2m-1 \right)} \right),\left( \dfrac{\left( \left( 3m-9 \right)\left( 2m-1 \right) \right)-\left( \left( 18m+6 \right)\left( 1+3m \right) \right)}{\left( 1+3m \right)\left( 2m-1 \right)} \right) \right)$.
\[\Rightarrow \left( 2,-3 \right)=\left( \left( \dfrac{\left( 36{{m}^{2}}+54m-36 \right)-\left( 24{{m}^{2}}+86m+26 \right)}{6{{m}^{2}}-m-1} \right),\left( \dfrac{\left( 6{{m}^{2}}-21m+9 \right)-\left( 54{{m}^{2}}+36m+6 \right)}{6{{m}^{2}}-m-1} \right) \right)\].
\[\Rightarrow \left( 2,-3 \right)=\left( \dfrac{12{{m}^{2}}-32m-62}{6{{m}^{2}}-m-1},\dfrac{-48{{m}^{2}}-57m+3}{6{{m}^{2}}-m-1} \right)\].
Comparing x-coordinates on both sides, we get \[2=\dfrac{12{{m}^{2}}-32m-62}{6{{m}^{2}}-m-1}\].
$\Rightarrow 12{{m}^{2}}-2m-2=12{{m}^{2}}-32m-62$.
$\Rightarrow -2m+32m=-62+2$.
$\Rightarrow 30m=-60$.
$\Rightarrow m=-2$. Let us substitute this in equation (1).
So, the equation of the line is $y=-2x-2\left( -2 \right)-3$.
$\Rightarrow y=-2x+4-3$.
$\Rightarrow y=-2x+1$.
$\Rightarrow 2x+y-1=0$.
$\therefore$ The required equation of the line is $2x+y-1=0$.
Note: We can see that the given problem contains a huge amount of calculation so, we need to perform each step carefully. Whenever we get this type of problem, we first assume the slope of the required line and then use the section formula for the intersection points. We should not confuse the section formula for internally dividing and externally dividing points while solving this type of point. Similarly, we can expect problems to find the equation of the line when the point P divides the points A and B internally.
Complete step-by-step solution
According to the problem, we are given that a line passing through the point \[P\left( 2,-3 \right)\] meets the lines $x-2y+7=0$ and $x+3y-3=0$ at the points A & B respectively. We need to find the equation of the line if the point P divides the points A & B externally in the ratio 3:2.
Let us assume the slope of the line passing through the point \[P\left( 2,-3 \right)\] be ‘m’.
We know that the equation of the line passing through the point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ and having slope ‘m’ is $y-{{y}_{1}}=m\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)$.

So, the equation of the line passing through the point \[P\left( 2,-3 \right)\] is $y+3=m\left( x-2 \right)$.
$\Rightarrow y+3=mx-2m$.
$\Rightarrow y=mx-2m-3$ ---(1).
Let us find the intersection point of this line with the line $x-2y+7=0$.
So, we have $x-2\left( mx-2m-3 \right)+7=0$.
$\Rightarrow x-2mx+4m+6+7=0$.
$\Rightarrow \left( 1-2m \right)x+4m+13=0$.
$\Rightarrow \left( 1-2m \right)x=-4m-13$.
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{4m+13}{2m-1}$. Let us substitute this in equation (1) to get y-coordinate.
So, we have $y=m\left( \dfrac{4m+13}{2m-1} \right)-2m-3$.
$\Rightarrow y=\left( \dfrac{4{{m}^{2}}+13m-\left( \left( 2m+3 \right)\left( 2m-1 \right) \right)}{2m-1} \right)$.
$\Rightarrow y=\left( \dfrac{4{{m}^{2}}+13m-\left( 4{{m}^{2}}+4m-3 \right)}{2m-1} \right)$.
$\Rightarrow y=\left( \dfrac{4{{m}^{2}}+13m-4{{m}^{2}}-4m+3}{2m-1} \right)$.
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{9m+3}{2m-1}$.
So, the intersection point of the lines $y=mx-2m-3$ and $x-2y+7=0$ is $A\left( \dfrac{4m+13}{2m-1},\dfrac{9m+3}{2m-1} \right)$ ---(2).
Let us find the intersection point of the line $y=mx-2m-3$ with the line $x+3y-3=0$.
So, we have $x+3\left( mx-2m-3 \right)-3=0$.
$\Rightarrow x+3mx-6m-9-3=0$.
$\Rightarrow \left( 1+3m \right)x-6m-12=0$.
$\Rightarrow \left( 1+3m \right)x=6m+12$.
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{6m+12}{1+3m}$. Let us substitute this in equation (1) to get y-coordinate.
So, we have $y=m\left( \dfrac{6m+12}{1+3m} \right)-2m-3$.
$\Rightarrow y=\left( \dfrac{6{{m}^{2}}+12m-\left( \left( 2m+3 \right)\left( 1+3m \right) \right)}{1+3m} \right)$.
$\Rightarrow y=\left( \dfrac{6{{m}^{2}}+12m-\left( 6{{m}^{2}}+11m+3 \right)}{1+3m} \right)$.
$\Rightarrow y=\left( \dfrac{6{{m}^{2}}+12m-6{{m}^{2}}-11m-3}{1+3m} \right)$.
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{m-3}{1+3m}$.
So, the intersection point of the lines $y=mx-2m-3$ and $x+3y-3=0$ is $B\left( \dfrac{6m+12}{1+3m},\dfrac{m-3}{1+3m} \right)$ ---(3).
Now, we have given that \[P\left( 2,-3 \right)\] divides the points $A\left( \dfrac{4m+13}{2m-1},\dfrac{9m+3}{2m-1} \right)$ and $B\left( \dfrac{6m+12}{1+3m},\dfrac{m-3}{1+3m} \right)$ internally in the ratio 3:2.
We know that if the point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ divides the points $\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ and $\left( {{x}_{3}},{{y}_{3}} \right)$ externally in the ratio a:b, then $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)=\left( \dfrac{a{{x}_{3}}-b{{x}_{2}}}{a-b},\dfrac{a{{y}_{3}}-b{{y}_{2}}}{a-b} \right)$.
So, we have $\left( 2,-3 \right)=\left( \dfrac{3\left( \dfrac{6m+12}{1+3m} \right)-2\left( \dfrac{4m+13}{2m-1} \right)}{3-2},\dfrac{3\left( \dfrac{m-3}{1+3m} \right)-2\left( \dfrac{9m+3}{2m-1} \right)}{3-2} \right)$.
$\Rightarrow \left( 2,-3 \right)=\left( \dfrac{\left( \dfrac{18m+36}{1+3m} \right)-\left( \dfrac{8m+26}{2m-1} \right)}{1},\dfrac{\left( \dfrac{3m-9}{1+3m} \right)-\left( \dfrac{18m+6}{2m-1} \right)}{1} \right)$.
$\Rightarrow \left( 2,-3 \right)=\left( \left( \dfrac{\left( \left( 18m+36 \right)\left( 2m-1 \right) \right)-\left( \left( 8m+26 \right)\left( 1+3m \right) \right)}{\left( 1+3m \right)\left( 2m-1 \right)} \right),\left( \dfrac{\left( \left( 3m-9 \right)\left( 2m-1 \right) \right)-\left( \left( 18m+6 \right)\left( 1+3m \right) \right)}{\left( 1+3m \right)\left( 2m-1 \right)} \right) \right)$.
\[\Rightarrow \left( 2,-3 \right)=\left( \left( \dfrac{\left( 36{{m}^{2}}+54m-36 \right)-\left( 24{{m}^{2}}+86m+26 \right)}{6{{m}^{2}}-m-1} \right),\left( \dfrac{\left( 6{{m}^{2}}-21m+9 \right)-\left( 54{{m}^{2}}+36m+6 \right)}{6{{m}^{2}}-m-1} \right) \right)\].
\[\Rightarrow \left( 2,-3 \right)=\left( \dfrac{12{{m}^{2}}-32m-62}{6{{m}^{2}}-m-1},\dfrac{-48{{m}^{2}}-57m+3}{6{{m}^{2}}-m-1} \right)\].
Comparing x-coordinates on both sides, we get \[2=\dfrac{12{{m}^{2}}-32m-62}{6{{m}^{2}}-m-1}\].
$\Rightarrow 12{{m}^{2}}-2m-2=12{{m}^{2}}-32m-62$.
$\Rightarrow -2m+32m=-62+2$.
$\Rightarrow 30m=-60$.
$\Rightarrow m=-2$. Let us substitute this in equation (1).
So, the equation of the line is $y=-2x-2\left( -2 \right)-3$.
$\Rightarrow y=-2x+4-3$.
$\Rightarrow y=-2x+1$.
$\Rightarrow 2x+y-1=0$.
$\therefore$ The required equation of the line is $2x+y-1=0$.
Note: We can see that the given problem contains a huge amount of calculation so, we need to perform each step carefully. Whenever we get this type of problem, we first assume the slope of the required line and then use the section formula for the intersection points. We should not confuse the section formula for internally dividing and externally dividing points while solving this type of point. Similarly, we can expect problems to find the equation of the line when the point P divides the points A and B internally.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




