
A line forms a triangle of area $54\sqrt 3 $ sq. with coordinate axes. Find the equation of the line if \[ \bot \] from origin to the line makes an angle of \[60^\circ \] with x-axis.
Answer
523.6k+ views
Hint: As mentioned in the question the line forms a triangle with coordinate axes which clearly means that the triangle will be a right-angled triangle. The Area of the triangle is also given so we need to calculate the height and base to form the required equation.
Complete step-by-step answer:
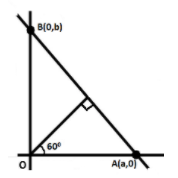
In the question, it is given that a line forms a triangle of area $54\sqrt 3 $ sq. with coordinate axes,
So, let us take a line \[AB\] as shown in figure which forms a triangle of area $54\sqrt 3 $ sq. with coordinate axes.
Since, we can see that point \[A\] lies on x-axis, therefore the y-coordinate of \[A\] will be \[0\]
So, \[A = \left( {a,0} \right)\]
Also, we can see that point \[B\] lies on y-axis, therefore the x-coordinate of \[B\] will be \[0\]
So, \[B = \left( {0,b} \right)\]
As we know, area of a triangle \[ = \dfrac{1}{2} \times height \times base\]
Now, in \[\vartriangle AOB\] , height \[ = b\] and base \[ = a\]
Area of \[\vartriangle AOB = \dfrac{1}{2} \times b \times a\]
And Area of \[\vartriangle AOB\] = $54\sqrt 3 $
Therefore, \[54\sqrt 3 = \dfrac{1}{2}ab\]
Or, \[ab = 108\sqrt 3 \] --- \[\left( 1 \right)\]
Now, the perpendicular drawn from the origin to the line makes an angle of \[60^\circ \] with x-axis as shown in figure.
Let the length of the perpendicular drawn from origin to line be \[P\] .
Also, we know that in a right-angled triangle, \[\cos \theta = \dfrac{{Base}}{{Hypotenuse}}\]
\[\cos 60^\circ = \dfrac{P}{a}\] and \[\cos 60^\circ = \dfrac{1}{2}\]
Or, \[a = \dfrac{P}{{\cos 60^\circ }} = 2P\]
And, \[\cos 30^\circ = \dfrac{P}{b}\] and \[\cos 30^\circ = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}\]
Or, \[b = \dfrac{P}{{\cos 30^\circ }} = \dfrac{{2P}}{{\sqrt 3 }}\]
Now, put values of \[a\] and \[b\] in equation \[\left( 1 \right)\] ,
\[2P \times \dfrac{{2P}}{{\sqrt 3 }} = 108\sqrt 3 \]
Or, \[\dfrac{{4{P^2}}}{{\sqrt 3 }} = 108\sqrt 3 \]
Or, \[{P^2} = 108 \times 3\]
\[P = \pm 18\]
But we can only take \[P = 18\] because the triangle is in the\[{1^{st}}\] quadrant.
So, \[P = 18\]
And, \[a = 2P = 36\] , \[b = \dfrac{{2P}}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{{36}}{{\sqrt 3 }} = 12\sqrt 3 \]
The intercept form of the equation of the straight line is \[\dfrac{x}{a} + \dfrac{y}{b} = 1\]
So, the equation of the line becomes \[\dfrac{x}{{36}} + \dfrac{y}{{12\sqrt 3 }} = 1\]
Hence, the equation of line comes out to be \[x + \sqrt 3 y - 36 = 0\]
Note: Few key points used in this question which needs to be remembered are- the points where
line cuts the coordinate axes are called intercepts, area of right-angled triangle is \[\dfrac{1}{2} \times height \times base\]
, and the intercept form of the equation of the straight line is \[\dfrac{x}{a} + \dfrac{y}{b} = 1\]
Complete step-by-step answer:

In the question, it is given that a line forms a triangle of area $54\sqrt 3 $ sq. with coordinate axes,
So, let us take a line \[AB\] as shown in figure which forms a triangle of area $54\sqrt 3 $ sq. with coordinate axes.
Since, we can see that point \[A\] lies on x-axis, therefore the y-coordinate of \[A\] will be \[0\]
So, \[A = \left( {a,0} \right)\]
Also, we can see that point \[B\] lies on y-axis, therefore the x-coordinate of \[B\] will be \[0\]
So, \[B = \left( {0,b} \right)\]
As we know, area of a triangle \[ = \dfrac{1}{2} \times height \times base\]
Now, in \[\vartriangle AOB\] , height \[ = b\] and base \[ = a\]
Area of \[\vartriangle AOB = \dfrac{1}{2} \times b \times a\]
And Area of \[\vartriangle AOB\] = $54\sqrt 3 $
Therefore, \[54\sqrt 3 = \dfrac{1}{2}ab\]
Or, \[ab = 108\sqrt 3 \] --- \[\left( 1 \right)\]
Now, the perpendicular drawn from the origin to the line makes an angle of \[60^\circ \] with x-axis as shown in figure.
Let the length of the perpendicular drawn from origin to line be \[P\] .
Also, we know that in a right-angled triangle, \[\cos \theta = \dfrac{{Base}}{{Hypotenuse}}\]
\[\cos 60^\circ = \dfrac{P}{a}\] and \[\cos 60^\circ = \dfrac{1}{2}\]
Or, \[a = \dfrac{P}{{\cos 60^\circ }} = 2P\]
And, \[\cos 30^\circ = \dfrac{P}{b}\] and \[\cos 30^\circ = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}\]
Or, \[b = \dfrac{P}{{\cos 30^\circ }} = \dfrac{{2P}}{{\sqrt 3 }}\]
Now, put values of \[a\] and \[b\] in equation \[\left( 1 \right)\] ,
\[2P \times \dfrac{{2P}}{{\sqrt 3 }} = 108\sqrt 3 \]
Or, \[\dfrac{{4{P^2}}}{{\sqrt 3 }} = 108\sqrt 3 \]
Or, \[{P^2} = 108 \times 3\]
\[P = \pm 18\]
But we can only take \[P = 18\] because the triangle is in the\[{1^{st}}\] quadrant.
So, \[P = 18\]
And, \[a = 2P = 36\] , \[b = \dfrac{{2P}}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{{36}}{{\sqrt 3 }} = 12\sqrt 3 \]
The intercept form of the equation of the straight line is \[\dfrac{x}{a} + \dfrac{y}{b} = 1\]
So, the equation of the line becomes \[\dfrac{x}{{36}} + \dfrac{y}{{12\sqrt 3 }} = 1\]
Hence, the equation of line comes out to be \[x + \sqrt 3 y - 36 = 0\]
Note: Few key points used in this question which needs to be remembered are- the points where
line cuts the coordinate axes are called intercepts, area of right-angled triangle is \[\dfrac{1}{2} \times height \times base\]
, and the intercept form of the equation of the straight line is \[\dfrac{x}{a} + \dfrac{y}{b} = 1\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




