
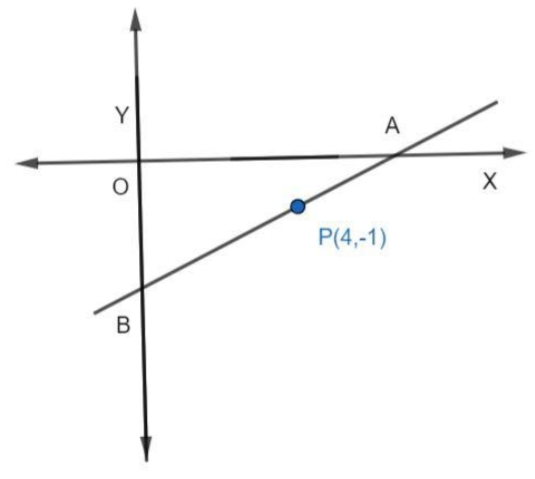
A line AB meets X-axis at A and Y-axis at B. P (4, -1) divides AB in the ratio 1:2. Find the coordinates of A and B.

Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint: Name the points of intersection of the line AB on the x and y axis. Recall the point on the x axis has y coordinate as zero and vice versa. Then, use section formula to find coordinates of A and B. It is given by \[(x,y)=\left( \dfrac{m{{x}_{2}}+n{{x}_{1}}}{m+n},\dfrac{m{{y}_{2}}+n{{y}_{1}}}{m+n} \right)\] .
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that the y-coordinate of the point that lies on the x-axis is zero, hence, the coordinate of A is (x, 0) for some x.
We know that the x-coordinate of the point that lies on the y-axis is zero, hence, the coordinate of B is (0, y) for some y.
Now, we have point P (4, -1) that divides the line segment joining the points A (0, y) and B (x, 0) in the ratio 1:2.

The section formula of a point P(x, y) that divides the line segment joining A \[({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})\] and B \[({{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}})\] in the ratio m:n is as follows:
\[(x,y)=\left( \dfrac{m{{x}_{2}}+n{{x}_{1}}}{m+n},\dfrac{m{{y}_{2}}+n{{y}_{1}}}{m+n} \right)..........(1)\]
We have P (4, -1), A (x, 0), B (0, y) and the ratio as 1:2. Substituting in equation (1), we have:
\[(4,-1)=\left( \dfrac{1(0)+2x}{1+2},\dfrac{1(y)+2(0)}{1+2} \right)\]
Simplifying we obtain:
\[(4,-1)=\left( \dfrac{2x}{3},\dfrac{y}{3} \right)...........(2)\]
We obtain two equations from equation (2).
\[\dfrac {2x}{3}=4........(3)\]
\[\dfrac {y}{3}=-1........(4)\]
From equation (3), we get the value of x as follows:
\[x=\dfrac{3}{2}\times 4\]
\[x=6\]
From equation (4), we get the value of y as follows:
\[y=3\times -1\]
\[y=-3\]
Hence, the coordinates of A and B are (6,0) and (0, -3) respectively.
Note: You may mistakenly write the coordinates of A as (0, y) and the coordinates of B as (x, 0) which is wrong. For a point on the x axis, the y coordinate is zero and vice versa. Any mistake in writing the section formula also should be avoided. You might interchange m and n in the numerator and write it as \[(x,y)=\left( \dfrac{n{{x}_{2}}+m{{x}_{1}}}{m+n},\dfrac{n{{y}_{2}}+m{{y}_{1}}}{m+n} \right)\] , this will give wrong answers.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that the y-coordinate of the point that lies on the x-axis is zero, hence, the coordinate of A is (x, 0) for some x.
We know that the x-coordinate of the point that lies on the y-axis is zero, hence, the coordinate of B is (0, y) for some y.
Now, we have point P (4, -1) that divides the line segment joining the points A (0, y) and B (x, 0) in the ratio 1:2.

The section formula of a point P(x, y) that divides the line segment joining A \[({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})\] and B \[({{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}})\] in the ratio m:n is as follows:
\[(x,y)=\left( \dfrac{m{{x}_{2}}+n{{x}_{1}}}{m+n},\dfrac{m{{y}_{2}}+n{{y}_{1}}}{m+n} \right)..........(1)\]
We have P (4, -1), A (x, 0), B (0, y) and the ratio as 1:2. Substituting in equation (1), we have:
\[(4,-1)=\left( \dfrac{1(0)+2x}{1+2},\dfrac{1(y)+2(0)}{1+2} \right)\]
Simplifying we obtain:
\[(4,-1)=\left( \dfrac{2x}{3},\dfrac{y}{3} \right)...........(2)\]
We obtain two equations from equation (2).
\[\dfrac {2x}{3}=4........(3)\]
\[\dfrac {y}{3}=-1........(4)\]
From equation (3), we get the value of x as follows:
\[x=\dfrac{3}{2}\times 4\]
\[x=6\]
From equation (4), we get the value of y as follows:
\[y=3\times -1\]
\[y=-3\]
Hence, the coordinates of A and B are (6,0) and (0, -3) respectively.
Note: You may mistakenly write the coordinates of A as (0, y) and the coordinates of B as (x, 0) which is wrong. For a point on the x axis, the y coordinate is zero and vice versa. Any mistake in writing the section formula also should be avoided. You might interchange m and n in the numerator and write it as \[(x,y)=\left( \dfrac{n{{x}_{2}}+m{{x}_{1}}}{m+n},\dfrac{n{{y}_{2}}+m{{y}_{1}}}{m+n} \right)\] , this will give wrong answers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




