
A light thread is wound on a disk of mass \[m\] in and the other end of the thread is connected to a block of mass \[m\], which is placed on a rough ground as shown in diagram. Find the minimum value of coefficient of friction for which block remains at rest.
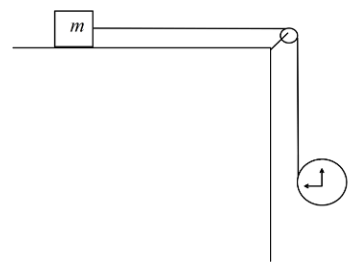
A. \[\dfrac{1}{3}\]
B. \[\dfrac{1}{4}\]
C. \[\dfrac{1}{2}\]
D. \[\dfrac{1}{5}\]

Answer
528.3k+ views
Hint:Write the equation of motion of the disk to find the tension in the string. For a disk rolling on a surface equation of motion will be, \[\tau = {I_{cm}}\alpha \] where, \[{I_{cm}} = \dfrac{{m{r^2}}}{2}\] is the moment of inertia along the axis passing through centre of mass \[\tau \] is the torque acting on the disk, \[\alpha \] is the angular acceleration. Then, find the equation of motion of the block and calculate the coefficient of friction.
Complete step by step answer:
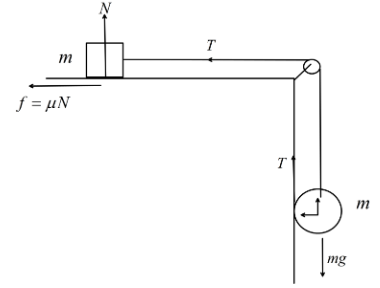
We know that for a body in rotational motion then the equation of motion can be written as, \[\tau = I\alpha \] where, \[I\] is the moment of inertia along the axis of rotation. \[\tau \] is the torque acting on the body, \[\alpha \] is the angular acceleration. Here, we have a circular disk of mass \[m\] which can roll along the vertical wall. So, the equation of motion can be written as, \[\tau = {I_{cm}}\alpha \] where, \[{I_{cm}} = \dfrac{{m{r^2}}}{2}\] is the moment of inertia along the axis passing through centre of mass.
Now, we know, angular acceleration is related to linear acceleration as,
\[{a_{cm}} = \alpha r\]
Hence, putting the values we have, \[\tau = \dfrac{{m{r^2}}}{2}\dfrac{{{a_{cm}}}}{r}\].
\[\tau = \dfrac{{mr{a_{cm}}}}{2}\]
Now, we can see that the tension acting on the string is producing the torque on the disk. Hence we can write, \[\tau = Tr\]
\[Tr = \dfrac{{mr{a_{cm}}}}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow T = \dfrac{{m{a_{cm}}}}{2}\]
Now, we can write the linear equation of motion of the disk as, \[mg - T = m{a_{cm}}\].
So, putting the value of tension we get,
\[mg = m{a_{cm}} + \dfrac{{m{a_{cm}}}}{2} = \dfrac{{3m{a_{cm}}}}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow g = \dfrac{{3{a_{cm}}}}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow {a_{cm}} = \dfrac{{2g}}{3}\].
So, tension of the string becomes, \[T = \dfrac{m}{2}\dfrac{{2g}}{3} = \dfrac{{mg}}{3}\]
Now, we can write the equation of motion of the block at equilibrium(at rest) as, \[T - \mu N = 0\] where, \[N = mg\].
So, pitting the value of tension we get,
\[\dfrac{{mg}}{3} - \mu mg = 0\].
On, simplifying we get, \[\mu = \dfrac{1}{3}\].
So, the minimum value of the coefficient of friction must be, \[\dfrac{1}{3}\].
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note: The frictional force on the block can be greater than \[\dfrac{1}{3}mg\] for keeping the block at rest. That means the coefficient of friction can be greater than \[\dfrac{1}{3}\] (\[\mu \geqslant \dfrac{1}{3}\] ) for the block to be at rest. Though, \[f = \dfrac{1}{3}mg\] will be just sufficient to keep the block at rest.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that for a body in rotational motion then the equation of motion can be written as, \[\tau = I\alpha \] where, \[I\] is the moment of inertia along the axis of rotation. \[\tau \] is the torque acting on the body, \[\alpha \] is the angular acceleration. Here, we have a circular disk of mass \[m\] which can roll along the vertical wall. So, the equation of motion can be written as, \[\tau = {I_{cm}}\alpha \] where, \[{I_{cm}} = \dfrac{{m{r^2}}}{2}\] is the moment of inertia along the axis passing through centre of mass.

Now, we know, angular acceleration is related to linear acceleration as,
\[{a_{cm}} = \alpha r\]
Hence, putting the values we have, \[\tau = \dfrac{{m{r^2}}}{2}\dfrac{{{a_{cm}}}}{r}\].
\[\tau = \dfrac{{mr{a_{cm}}}}{2}\]
Now, we can see that the tension acting on the string is producing the torque on the disk. Hence we can write, \[\tau = Tr\]
\[Tr = \dfrac{{mr{a_{cm}}}}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow T = \dfrac{{m{a_{cm}}}}{2}\]
Now, we can write the linear equation of motion of the disk as, \[mg - T = m{a_{cm}}\].
So, putting the value of tension we get,
\[mg = m{a_{cm}} + \dfrac{{m{a_{cm}}}}{2} = \dfrac{{3m{a_{cm}}}}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow g = \dfrac{{3{a_{cm}}}}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow {a_{cm}} = \dfrac{{2g}}{3}\].
So, tension of the string becomes, \[T = \dfrac{m}{2}\dfrac{{2g}}{3} = \dfrac{{mg}}{3}\]
Now, we can write the equation of motion of the block at equilibrium(at rest) as, \[T - \mu N = 0\] where, \[N = mg\].
So, pitting the value of tension we get,
\[\dfrac{{mg}}{3} - \mu mg = 0\].
On, simplifying we get, \[\mu = \dfrac{1}{3}\].
So, the minimum value of the coefficient of friction must be, \[\dfrac{1}{3}\].
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note: The frictional force on the block can be greater than \[\dfrac{1}{3}mg\] for keeping the block at rest. That means the coefficient of friction can be greater than \[\dfrac{1}{3}\] (\[\mu \geqslant \dfrac{1}{3}\] ) for the block to be at rest. Though, \[f = \dfrac{1}{3}mg\] will be just sufficient to keep the block at rest.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




