
A light string passing over a smooth light pulley connects two blocks of masses ${{\text{m}}_{\text{1}}}\text{ and }{{\text{m}}_{\text{2}}}$(vertically). . If the acceleration of the system is $\dfrac{g}{8}$ then, the ratio of their masses is
a) 8:1
b) 9:7
c) 4:3
d) 5:3
Answer
585k+ views
Hint: It is given in the question that ${{\text{m}}_{\text{2}}}$ is moving vertically upwards. Hence ${{\text{m}}_{\text{1}}}$ will move vertically downwards. Both the masses are connected to a common string and hence both of them will move with a common acceleration. Hence will draw the free body diagram of the above system and find the ratio of the masses and verify with the given options.
Complete step by step answer:
To begin with let us first draw the free body diagram and obtain the net force on each of the masses.
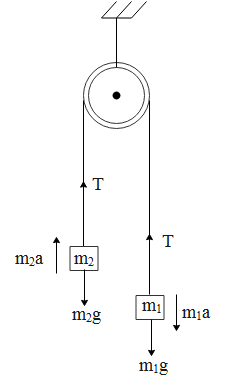
If we see the above free body diagram the mass ${{m}_{1}}$ moves downwards, while the mass ${{m}_{2}}$ moves upwards. Both of the masses move with common acceleration i.e. a. The net force on mass ${{m}_{1}}$is,
${{m}_{1}}a={{m}_{1}}g-T...(1)$ where g is the acceleration due to gravity and T is the tension in the rope. Similarly, the net force on ${{m}_{2}}$ is given by, ${{m}_{2}}a=T-{{m}_{2}}g...(2)$ where g is the acceleration due to gravity and T is the tension in the rope.
Adding both the equations 1 and 2 we get,
$\begin{align}
&\Rightarrow {{m}_{1}}a+{{m}_{2}}a={{m}_{1}}g-T+T-{{m}_{2}}g \\
& \Rightarrow a({{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}})=({{m}_{1}}-{{m}_{2}})g,\text{since a=g/8} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{g}{8}({{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}})=({{m}_{1}}-{{m}_{2}})g \\
&\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{m}_{1}}}{8}+\dfrac{{{m}_{2}}}{8}={{m}_{1}}-{{m}_{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{m}_{1}}\left( \dfrac{1}{8}-1 \right)=-{{m}_{2}}\left( 1+\dfrac{1}{8} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{m}_{1}}\left( -\dfrac{7}{8} \right)=-{{m}_{2}}\left( \dfrac{9}{8} \right) \\
& \dfrac{{{m}_{1}}}{{{m}_{2}}}=\dfrac{9}{7} \\
\end{align}$
Hence the correct answer to the above question is option b.
Note:
It is to be noted that the above thread is assumed to be mass less. Hence we can conclude that the tension at every point on the thread is constant. But in reality the thread also has mass, as a result the tension along the thread will be more at higher points from the point where the mass is attached to the thread.
Complete step by step answer:
To begin with let us first draw the free body diagram and obtain the net force on each of the masses.

If we see the above free body diagram the mass ${{m}_{1}}$ moves downwards, while the mass ${{m}_{2}}$ moves upwards. Both of the masses move with common acceleration i.e. a. The net force on mass ${{m}_{1}}$is,
${{m}_{1}}a={{m}_{1}}g-T...(1)$ where g is the acceleration due to gravity and T is the tension in the rope. Similarly, the net force on ${{m}_{2}}$ is given by, ${{m}_{2}}a=T-{{m}_{2}}g...(2)$ where g is the acceleration due to gravity and T is the tension in the rope.
Adding both the equations 1 and 2 we get,
$\begin{align}
&\Rightarrow {{m}_{1}}a+{{m}_{2}}a={{m}_{1}}g-T+T-{{m}_{2}}g \\
& \Rightarrow a({{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}})=({{m}_{1}}-{{m}_{2}})g,\text{since a=g/8} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{g}{8}({{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}})=({{m}_{1}}-{{m}_{2}})g \\
&\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{m}_{1}}}{8}+\dfrac{{{m}_{2}}}{8}={{m}_{1}}-{{m}_{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{m}_{1}}\left( \dfrac{1}{8}-1 \right)=-{{m}_{2}}\left( 1+\dfrac{1}{8} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{m}_{1}}\left( -\dfrac{7}{8} \right)=-{{m}_{2}}\left( \dfrac{9}{8} \right) \\
& \dfrac{{{m}_{1}}}{{{m}_{2}}}=\dfrac{9}{7} \\
\end{align}$
Hence the correct answer to the above question is option b.
Note:
It is to be noted that the above thread is assumed to be mass less. Hence we can conclude that the tension at every point on the thread is constant. But in reality the thread also has mass, as a result the tension along the thread will be more at higher points from the point where the mass is attached to the thread.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




