
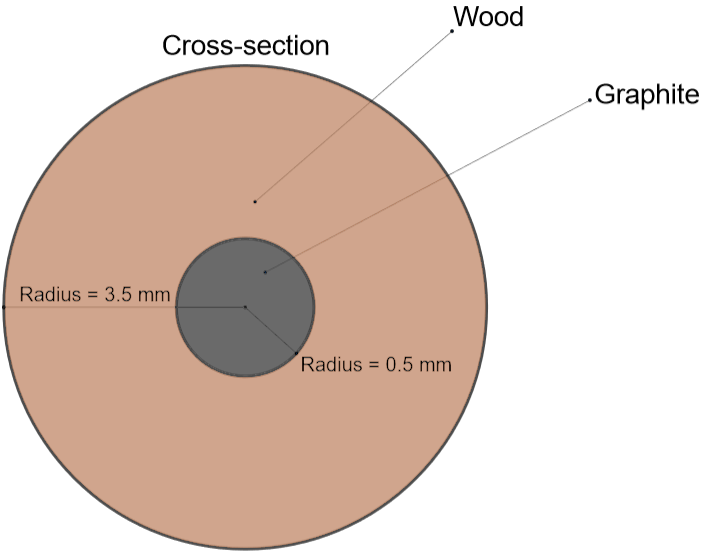
A lead pencil consists of a cylinder of wood with a solid cylinder of graphite filled in the interior. The diameter of the pencil is 7 mm and the diameter of graphite is 1 mm. If the length of the pencil is 14 cm. Find the volume of wood and that of graphite.
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: To solve this problem, we should know the formula for volume of a cylinder. The volume of a cylinder of height $h$ units and a radius of r units is given by volume \[=\pi {{r}^{2}}h\]. In the question, we are given a pencil of diameter 7 mm and length of 14 cm. The inner part of the pencil contains graphite of diameter 1 mm and length of graphite is equal to the length of pencil which is 14 cm. The graphite is a smaller cylinder with smaller dimensions. We can find the volume of graphite using the radius as $r=\dfrac{diameter}{2}=\dfrac{1}{2}=0.5mm$ and the height h as $h=length=14cm=140mm$ in the formula of volume stated above. We can also find the total volume of the pencil using the radius $r=\dfrac{7}{2}=3.5mm$ and height h as $h=length=14cm=140mm$. We can infer from the cross sectional view that the volume of wood can be calculated by subtracting the volume of graphite from the total volume of pencil.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that the volume of a cylinder of height $h$ units and a radius of r units is given by volume \[=\pi {{r}^{2}}h\]
We are given a cylindrical structure of pencil with dimensions as diameter = 7 mm and height = 14 cm. We have wood and graphite inside the pencil and the graphite is in the shape of a smaller cylinder with dimensions as diameter = 1 mm and height = 14 cm.
We will calculate the volume of the graphite and the total volume of the pencil using the volume of the cylinder formula as both of them are cylinders. For, calculating the volume of wood, we should note that the portion of pencil remaining after the graphite has occupied is wood. So, we can infer that the difference in the volumes of pencil and graphite gives the volume of wood.
Dimensions of graphite
$\text{height h}=\text{length}=14cm=14\times 10mm=140mm$
$\text{radius r}=\dfrac{\text{diameter}}{2}=\dfrac{1}{2}=0.5mm$
\[\begin{align}
& Volume=\pi {{r}^{2}}h \\
& =\pi {{\left( 0.5mm \right)}^{2}}140\ mm \\
& =\dfrac{22}{7}\times 0.25\times 140\ m{{m}^{3}} \\
& =110\ m{{m}^{3}} \\
\end{align}\]
Dimensions of pencil
$\text{height h}=\text{length}=14cm=14\times 10mm=140mm$
$\text{radius r}=\dfrac{\text{diameter}}{2}=\dfrac{7}{2}=3.5mm$
\[\begin{align}
& Volume=\pi {{r}^{2}}h \\
& =\pi {{\left( 3.5mm \right)}^{2}}140\ mm \\
& =\dfrac{22}{7}\times 12.25\times 140\ m{{m}^{3}} \\
& =5390\ m{{m}^{3}} \\
\end{align}\]
Volume of wood = Volume of pencil – Volume of graphite
Volume $=\left( 5390-110 \right)m{{m}^{3}}=5280m{{m}^{3}}$
$\therefore $ The volumes of wood and graphite are $5280m{{m}^{3}}$ and $110m{{m}^{3}}$ respectively.
Note: The students can make an error when it comes to units. The dimensions of diameter are in millimeter and height is in centimeter. If we substitute the values as they are given in the question, we get wrong answers. To nullify this mistake, it is always a good practice to write down all the quantities given in the question in the same units and then start solving the problem.
Complete step-by-step answer:

We know that the volume of a cylinder of height $h$ units and a radius of r units is given by volume \[=\pi {{r}^{2}}h\]
We are given a cylindrical structure of pencil with dimensions as diameter = 7 mm and height = 14 cm. We have wood and graphite inside the pencil and the graphite is in the shape of a smaller cylinder with dimensions as diameter = 1 mm and height = 14 cm.
We will calculate the volume of the graphite and the total volume of the pencil using the volume of the cylinder formula as both of them are cylinders. For, calculating the volume of wood, we should note that the portion of pencil remaining after the graphite has occupied is wood. So, we can infer that the difference in the volumes of pencil and graphite gives the volume of wood.
Dimensions of graphite
$\text{height h}=\text{length}=14cm=14\times 10mm=140mm$
$\text{radius r}=\dfrac{\text{diameter}}{2}=\dfrac{1}{2}=0.5mm$
\[\begin{align}
& Volume=\pi {{r}^{2}}h \\
& =\pi {{\left( 0.5mm \right)}^{2}}140\ mm \\
& =\dfrac{22}{7}\times 0.25\times 140\ m{{m}^{3}} \\
& =110\ m{{m}^{3}} \\
\end{align}\]
Dimensions of pencil
$\text{height h}=\text{length}=14cm=14\times 10mm=140mm$
$\text{radius r}=\dfrac{\text{diameter}}{2}=\dfrac{7}{2}=3.5mm$
\[\begin{align}
& Volume=\pi {{r}^{2}}h \\
& =\pi {{\left( 3.5mm \right)}^{2}}140\ mm \\
& =\dfrac{22}{7}\times 12.25\times 140\ m{{m}^{3}} \\
& =5390\ m{{m}^{3}} \\
\end{align}\]
Volume of wood = Volume of pencil – Volume of graphite
Volume $=\left( 5390-110 \right)m{{m}^{3}}=5280m{{m}^{3}}$
$\therefore $ The volumes of wood and graphite are $5280m{{m}^{3}}$ and $110m{{m}^{3}}$ respectively.
Note: The students can make an error when it comes to units. The dimensions of diameter are in millimeter and height is in centimeter. If we substitute the values as they are given in the question, we get wrong answers. To nullify this mistake, it is always a good practice to write down all the quantities given in the question in the same units and then start solving the problem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




