
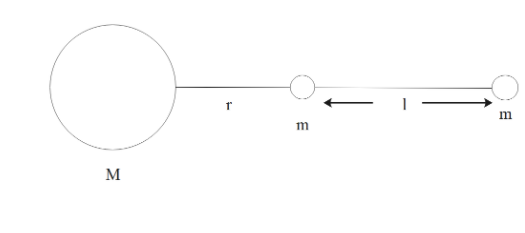
A large spherical mass M is fixed at one position and two identical point masses m are kept on a line passing through the centre of M. The point masses are connected by a rigid massless rod of length l and this assembly is free to move along the line connecting them. All three masses interact only through their mutual gravitational interaction. When the point mass nearer to M is at a distance r=3l from M, the tension in the rod is zero for $m=k(\dfrac{M}{288})$. The value of k is.

Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: Let us first find the force of gravitation acting on both the masses due to the presence of the bigger mass. As, the tension in the rod is zero when the mass nearer to M is at some fin item distance, the force acting on the left side and right side of the rod must be equal or add up to zero. Therefore, equalize the two forces and we can find the mass.
Complete step by step answer:
It is given that two masses are present beside the bigger mass M. The rod is massless so we don’t have to worry about that. Next, the length of the rod is l, given and the distance between bigger mass M and smaller mass m is given as r.
Now,
The force acting on the left mass m will be,
$\begin{align}
& {{F}_{1}}=\dfrac{GMm}{{{r}^{2}}}-\dfrac{G{{m}^{2}}}{{{l}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow r=3l; \\
& \Rightarrow {{F}_{1}}=\dfrac{GMm}{9{{l}^{2}}}-\dfrac{G{{m}^{2}}}{{{l}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}$
Similarly, the force acting on the right mass will be then,
${{F}_{2}}=\dfrac{GMm}{{{(4l)}^{2}}}+\dfrac{G{{m}^{2}}}{{{l}^{2}}}$
As the two forces are equal to zero when the tension acting in the rod is zero,
The force on the left mass must be equal to the force acting on the right mass,
$\begin{align}
& {{F}_{1}}={{F}_{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{GMm}{{{r}^{2}}}-\dfrac{G{{m}^{2}}}{{{l}^{2}}}=\dfrac{GMm}{{{(4l)}^{2}}}+\dfrac{G{{m}^{2}}}{{{l}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{7GMm}{144{{l}^{2}}}=\dfrac{2G{{m}^{2}}}{{{l}^{2}}} \\
& \therefore m=\dfrac{7M}{288} \\
\end{align}$
Comparing the mass m obtained with the given mass in the question, we can say that the value of k is 7.
Note: In the above question, the first thing to be noticed is the mass of the rod, it is massless or negligible here. We don’t have to consider it during the force calculation. As every mass has some finite force acting on it, there will be some gravitational force acted by the rod too, so the calculations will be changed too. Every object that has mass will have energy in it.
Complete step by step answer:
It is given that two masses are present beside the bigger mass M. The rod is massless so we don’t have to worry about that. Next, the length of the rod is l, given and the distance between bigger mass M and smaller mass m is given as r.
Now,
The force acting on the left mass m will be,
$\begin{align}
& {{F}_{1}}=\dfrac{GMm}{{{r}^{2}}}-\dfrac{G{{m}^{2}}}{{{l}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow r=3l; \\
& \Rightarrow {{F}_{1}}=\dfrac{GMm}{9{{l}^{2}}}-\dfrac{G{{m}^{2}}}{{{l}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}$
Similarly, the force acting on the right mass will be then,
${{F}_{2}}=\dfrac{GMm}{{{(4l)}^{2}}}+\dfrac{G{{m}^{2}}}{{{l}^{2}}}$
As the two forces are equal to zero when the tension acting in the rod is zero,
The force on the left mass must be equal to the force acting on the right mass,
$\begin{align}
& {{F}_{1}}={{F}_{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{GMm}{{{r}^{2}}}-\dfrac{G{{m}^{2}}}{{{l}^{2}}}=\dfrac{GMm}{{{(4l)}^{2}}}+\dfrac{G{{m}^{2}}}{{{l}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{7GMm}{144{{l}^{2}}}=\dfrac{2G{{m}^{2}}}{{{l}^{2}}} \\
& \therefore m=\dfrac{7M}{288} \\
\end{align}$
Comparing the mass m obtained with the given mass in the question, we can say that the value of k is 7.
Note: In the above question, the first thing to be noticed is the mass of the rod, it is massless or negligible here. We don’t have to consider it during the force calculation. As every mass has some finite force acting on it, there will be some gravitational force acted by the rod too, so the calculations will be changed too. Every object that has mass will have energy in it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




