
A ladder of length $ L $ leans against a wall at an angle of $ \theta $ from the horizontal, as shown in figure. The normal force $ {F_N} $ applied from the ground on the ladder applies what torque about the ladders center of mass?
$ \left( A \right){F_N}\dfrac{L}{2} \\
\left( B \right){F_N}L\cos \theta \\
\left( C \right){F_N}L\sin \theta \\
\left( D \right){F_N}\dfrac{L}{2}\cos \theta \\ $

Answer
538.2k+ views
Hint :In order to solve this question, we are going to draw a figure showing all the forces that are present on the ladder at the different points in the vertical and the horizontal directions. Then, by defining the torque, we can calculate the torque on the ladder due to the forces acting on it.
The torque on the ladder is given as
$ \tau = {F_H} \times r $
Where $ {F_H} $ is the horizontal component of the force
And $ r $ is the perpendicular distance from the center of mass of the rod.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
First of all, we need to start off by drawing a free body diagram for this configuration of the ladder, which gives the different forces with directions that are acting on this.
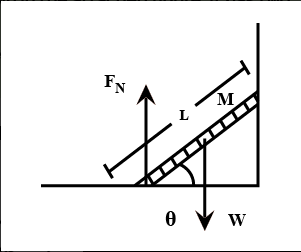
The direction of the normal force is shown in the figure above. The force $ {F_N} $ can be divided into two components, $ {F_N}\sin \theta $ the vertical component is along the ladder, and $ {F_N}\cos \theta $ the horizontal component is perpendicular to the ladder.
The torque about the ladder’s center of mass is given as:
$ \tau = {F_H} \times r $
Where $ {F_H} $ is the horizontal component of the force
And $ r $ is the perpendicular distance from the center of mass of the rod.
$ \tau = {F_N}\cos \theta \times \dfrac{L}{2} \\
\Rightarrow \tau = {F_N}\dfrac{L}{2}\cos \theta \\ $
Hence, option $ \left( D \right){F_N}\dfrac{L}{2}\cos \theta $ is the correct answer.
Note :
The torque is defined as the moment of the force that makes a rod or ladder to rotate. Mathematically, the torque is the product of the force and the perpendicular distance from the center of mass of the rod. Although the torque is unable to rotate the ladder completely but it may cause a display.
The torque on the ladder is given as
$ \tau = {F_H} \times r $
Where $ {F_H} $ is the horizontal component of the force
And $ r $ is the perpendicular distance from the center of mass of the rod.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
First of all, we need to start off by drawing a free body diagram for this configuration of the ladder, which gives the different forces with directions that are acting on this.

The direction of the normal force is shown in the figure above. The force $ {F_N} $ can be divided into two components, $ {F_N}\sin \theta $ the vertical component is along the ladder, and $ {F_N}\cos \theta $ the horizontal component is perpendicular to the ladder.
The torque about the ladder’s center of mass is given as:
$ \tau = {F_H} \times r $
Where $ {F_H} $ is the horizontal component of the force
And $ r $ is the perpendicular distance from the center of mass of the rod.
$ \tau = {F_N}\cos \theta \times \dfrac{L}{2} \\
\Rightarrow \tau = {F_N}\dfrac{L}{2}\cos \theta \\ $
Hence, option $ \left( D \right){F_N}\dfrac{L}{2}\cos \theta $ is the correct answer.
Note :
The torque is defined as the moment of the force that makes a rod or ladder to rotate. Mathematically, the torque is the product of the force and the perpendicular distance from the center of mass of the rod. Although the torque is unable to rotate the ladder completely but it may cause a display.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




