
A ladder of length 6 m makes an angle of 45 degrees with the floor while leaning against one wall of a room. If the foot of the ladder is kept fixed on the floor and it is made to lean against the opposite wall of the room, it makes an angle of 60 degree with the floor. Find the distance between these two walls of the room.
Answer
597.6k+ views
Hint: We will use the trigonometric formula $\cos \theta =\dfrac{base}{hypotenuse}$ to find the distance between the two walls. Now, we know that the values of $\cos 45{}^\circ =\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$ and $\cos 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{1}{2}$. So, we will find the distance from the first wall to the ladder foot by forming the equation, $\cos 45{}^\circ =\dfrac{6m}{\left( \text{distance between foot of ladder and wall} \right)}$ and again to find the distance from the second wall to the ladder we will use the equation, $\cos 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{6m}{\left( \text{distance between foot of ladder and wall} \right)}$ to get the required answer.
Complete step by step solution:
It is given in the question that a ladder of length 6 m makes an angle of 45 degrees with the floor while leaning against one wall of a room and it makes an angle of 60 degrees with the floor when the ladder is leaning against the opposite wall of the room and we have to find the distance between the walls of the room. We will first assume the first wall as AB and the second wall as CD and the foot of the ladder at E. We will now represent this as the figure below.
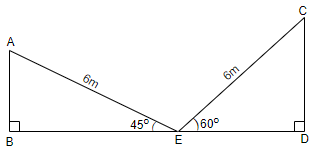
We know that $\cos \theta =\dfrac{base}{hypotenuse}$. Now, if we consider the triangle ABE, we have AE = hypotenuse, BE = base and $\cos \theta =\cos 45{}^\circ $. So, we can write the equation as,
$\cos 45{}^\circ =\dfrac{BE}{AE}$
Now, we have the values of AE = 6 m and $\cos 45{}^\circ =\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$, so substituting these values, we get,
$\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}=\dfrac{BE}{6}$
On cross multiplying both sides we get,
$\begin{align}
& BE\left( \sqrt{2} \right)=6 \\
& \Rightarrow BE=\dfrac{6}{\sqrt{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Rationalising the numerator and denominator by $\sqrt{2}$, we get,
$\begin{align}
& BE=\dfrac{6\sqrt{2}}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow BE=3\sqrt{2}m \\
\end{align}$
Now, if we take triangle CDE, we have,
$\cos 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{DE}{CE}$
We know that $\cos 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{1}{2}$ and CE = 6 m. So, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{DE}{6} \\
& \Rightarrow 2DE=6 \\
& \Rightarrow DE=\dfrac{6}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow DE=3m \\
\end{align}$
So, we will get the distance between the two walls as,
$\begin{align}
& BE+ED \\
& \Rightarrow 3\sqrt{2}+3 \\
& \Rightarrow 3\left( \sqrt{2}+1 \right)m \\
\end{align}$
Hence, we get the distance between the two walls of the room will be $3\left( \sqrt{2}+1 \right)m$.
Note: Many students get confused with the values of $\cos 60{}^\circ $ and $\cos 30{}^\circ $ and they wrongly take the value of $\cos 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$ and end up with a wrong answer. So, the students should remember the basic values of the standard trigonometric angles. They should remember the ratio of base and hypotenuse for $\cos \theta $ as the answer may change entirely if they write $\cos \theta =\dfrac{hypotenuse}{base}$.
Complete step by step solution:
It is given in the question that a ladder of length 6 m makes an angle of 45 degrees with the floor while leaning against one wall of a room and it makes an angle of 60 degrees with the floor when the ladder is leaning against the opposite wall of the room and we have to find the distance between the walls of the room. We will first assume the first wall as AB and the second wall as CD and the foot of the ladder at E. We will now represent this as the figure below.

We know that $\cos \theta =\dfrac{base}{hypotenuse}$. Now, if we consider the triangle ABE, we have AE = hypotenuse, BE = base and $\cos \theta =\cos 45{}^\circ $. So, we can write the equation as,
$\cos 45{}^\circ =\dfrac{BE}{AE}$
Now, we have the values of AE = 6 m and $\cos 45{}^\circ =\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$, so substituting these values, we get,
$\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}=\dfrac{BE}{6}$
On cross multiplying both sides we get,
$\begin{align}
& BE\left( \sqrt{2} \right)=6 \\
& \Rightarrow BE=\dfrac{6}{\sqrt{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Rationalising the numerator and denominator by $\sqrt{2}$, we get,
$\begin{align}
& BE=\dfrac{6\sqrt{2}}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow BE=3\sqrt{2}m \\
\end{align}$
Now, if we take triangle CDE, we have,
$\cos 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{DE}{CE}$
We know that $\cos 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{1}{2}$ and CE = 6 m. So, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{DE}{6} \\
& \Rightarrow 2DE=6 \\
& \Rightarrow DE=\dfrac{6}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow DE=3m \\
\end{align}$
So, we will get the distance between the two walls as,
$\begin{align}
& BE+ED \\
& \Rightarrow 3\sqrt{2}+3 \\
& \Rightarrow 3\left( \sqrt{2}+1 \right)m \\
\end{align}$
Hence, we get the distance between the two walls of the room will be $3\left( \sqrt{2}+1 \right)m$.
Note: Many students get confused with the values of $\cos 60{}^\circ $ and $\cos 30{}^\circ $ and they wrongly take the value of $\cos 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$ and end up with a wrong answer. So, the students should remember the basic values of the standard trigonometric angles. They should remember the ratio of base and hypotenuse for $\cos \theta $ as the answer may change entirely if they write $\cos \theta =\dfrac{hypotenuse}{base}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




