
A ladder 5m long is leaning against a wall. The bottom of the ladder is pulled along the ground away from the wall, at the rate of 2m/sec. How fast its height on the wall decreasing when the foot of the ladder is 4m away from the wall.
\[\begin{align}
& \text{A}.\text{ }\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ m}/\text{sec} \\
& \text{B}.\text{ }\dfrac{8}{3}\text{ m}/\text{sec} \\
& \text{C}.\text{ }\dfrac{10}{3}\text{ m}/\text{sec} \\
& \text{D}.\text{ }\dfrac{6}{3}\text{ m}/\text{sec} \\
\end{align}\]
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: First, we will draw the figure and will get a right-angled triangle. Assume height as y, then, by Pythagoras theorem, find the solution between the height of the wall and distance from the wall. Converting the equation in a single variable differentiate the equation with respect to time, because this gives the desired rate at which the height on the wall is changing. Then, substitute x=4m to get the rate of decrease of height.
Complete step by step answer:
A ladder that is 5m long is leaning against a wall and the bottom of the ladder is being pulled, we need to find at which rate the height on the wall is decreasing. We will have a condition like this:
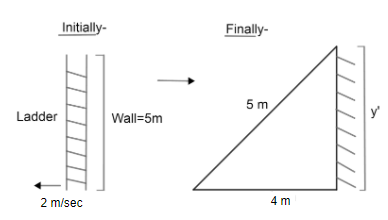
Suppose, the height on the wall is 'y' when the ladder is 4m away from the wall.
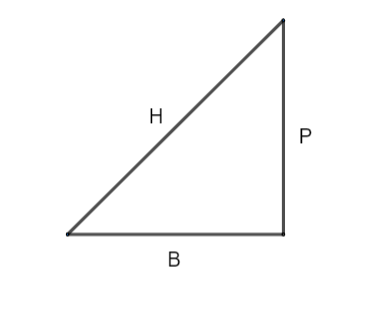
By Pythagoras theorem,
\[{{H}^{2}}={{P}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}}\]
As per the question, at any time ’t’ the figure would be:
\[\begin{align}
& {{5}^{2}}={{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}} \\
& {{y}^{2}}={{5}^{2}}-{{x}^{2}} \\
& {{y}^{2}}=25-{{x}^{2}} \\
& y=\sqrt{25-{{x}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}\]
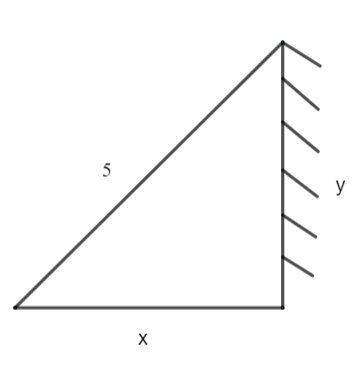
Now, we have the relation of height on the wall y and distance from the wall x in one variable .i.e.
\[y=\sqrt{25-{{x}^{2}}}\]
But, the question is asking about rate of change of height on wall that is \[\dfrac{dy}{dt}\]
Therefore, differentiating 'y' with respect to time ’t’.
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{dy}{dt}=\dfrac{d}{dt}\left( \sqrt{25-{{x}^{2}}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dt}=\dfrac{-x}{\sqrt{25-{{x}^{2}}}}\times \dfrac{dx}{dt} \\
\end{align}\]
It is given that, rate of change of the distance from wall i.e. \[\dfrac{dx}{dt}\] is 2 m/sec.
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dt}=\dfrac{-2x}{\left( \sqrt{25-{{x}^{2}}} \right)}\]
We need to find the rate of change of height on the wall when the bottom of the ladder is at a distance 4m away from the wall. So, put x=4m.
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dt}=\dfrac{-2\times 4}{\left( \sqrt{25-4\times 4} \right)}=\dfrac{-8}{\sqrt{9}}=\dfrac{-8}{3}\]
Hence, the height of the ladder on the wall is decreasing at the rate of \[\dfrac{8}{3}m/sec\]
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note:
Students must be very clear and specific for using Pythagoras theorem at right place because it will convert the two-variable problems into a single one. Students must also be aware of all the differentiation rules and formulas. Here, we have differentiated y and x with respect to time, so as to get the rate of decrease of height in m/sec. Sometimes students forget this and differentiate with y with respect to x, this will not lead them to the right answer as there won't be a term indicating the rate of decrease.
Complete step by step answer:
A ladder that is 5m long is leaning against a wall and the bottom of the ladder is being pulled, we need to find at which rate the height on the wall is decreasing. We will have a condition like this:

Suppose, the height on the wall is 'y' when the ladder is 4m away from the wall.
By Pythagoras theorem,
\[{{H}^{2}}={{P}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}}\]

As per the question, at any time ’t’ the figure would be:
\[\begin{align}
& {{5}^{2}}={{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}} \\
& {{y}^{2}}={{5}^{2}}-{{x}^{2}} \\
& {{y}^{2}}=25-{{x}^{2}} \\
& y=\sqrt{25-{{x}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}\]

Now, we have the relation of height on the wall y and distance from the wall x in one variable .i.e.
\[y=\sqrt{25-{{x}^{2}}}\]
But, the question is asking about rate of change of height on wall that is \[\dfrac{dy}{dt}\]
Therefore, differentiating 'y' with respect to time ’t’.
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{dy}{dt}=\dfrac{d}{dt}\left( \sqrt{25-{{x}^{2}}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dt}=\dfrac{-x}{\sqrt{25-{{x}^{2}}}}\times \dfrac{dx}{dt} \\
\end{align}\]
It is given that, rate of change of the distance from wall i.e. \[\dfrac{dx}{dt}\] is 2 m/sec.
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dt}=\dfrac{-2x}{\left( \sqrt{25-{{x}^{2}}} \right)}\]
We need to find the rate of change of height on the wall when the bottom of the ladder is at a distance 4m away from the wall. So, put x=4m.
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dt}=\dfrac{-2\times 4}{\left( \sqrt{25-4\times 4} \right)}=\dfrac{-8}{\sqrt{9}}=\dfrac{-8}{3}\]
Hence, the height of the ladder on the wall is decreasing at the rate of \[\dfrac{8}{3}m/sec\]
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note:
Students must be very clear and specific for using Pythagoras theorem at right place because it will convert the two-variable problems into a single one. Students must also be aware of all the differentiation rules and formulas. Here, we have differentiated y and x with respect to time, so as to get the rate of decrease of height in m/sec. Sometimes students forget this and differentiate with y with respect to x, this will not lead them to the right answer as there won't be a term indicating the rate of decrease.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




