
A ladder 20ft long leans against a vertical wall. The top end slides downwards at the rate of 2 ft per second. The rate at which the lower end moves on a horizontal floor when it is 12ft from the wall is:
$
A.\;\dfrac{8}{3} \\
B.\;\dfrac{6}{5} \\
C.\;\dfrac{3}{2} \\
D.\;\dfrac{{17}}{4} \\
$
Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint:Draw a diagram according to given information, it forms a right angled triangle. So, use Pythagoras theorem to make relationship between its sides. Try to apply differentiation concepts with the equation. Assume the needed velocity as ‘v’, find the distance travelled in same time ‘t’ by both ends of ladder. Substitute the values to get the value of ‘v’.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Diagram of the given question as below:
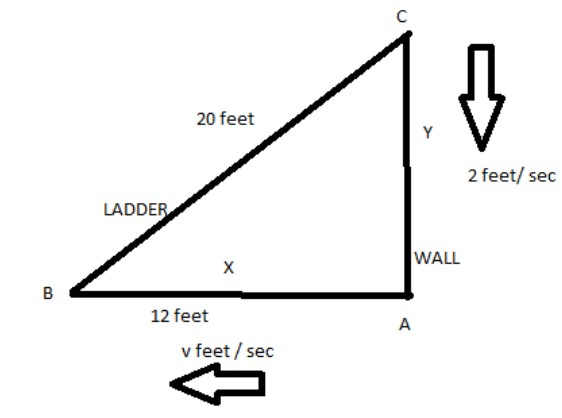
In the diagram, BC is the ladder and AC is the wall against which the ladder is leaning. Let us suppose that the horizontal speed of the ladder is v feet/sec whereas its vertical speed is given as 2 feet per second.
So, $\dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}} = v$ ….(1)
Also assume that,
AB = x feet
AC = y feet
So, vertical speed of the ladder will be, $\dfrac{{dy}}{{dt}} = - 2$ ….(2) ( It is negative due to decreasing in nature)
In $\vartriangle ABC$ applying the Pythagoras theorem, we have
$A{C^2} + A{B^2} = B{C^2}$
Substituting the values of AC and AB, in the above equation,
$
{y^2} + {x^2} = {20^{^2}} \\
\Rightarrow {y^2} + {x^2} = 400 \\
$ ….(3)
So, when x = 12 , then from equation (3), we get
\[
{y^2} + {12^2} = 400 \\
\Rightarrow {y^2} = 400 - 144 \\
\Rightarrow y = \sqrt {256} \\
\Rightarrow y = 16 \\
\]
Taking derivative of equation (3) both sides, we get
$2x\dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}} + 2y\dfrac{{dy}}{{dt}} = 0$ (Using derivative formulas with respect to time t).
Substituting the known values as well as terms from equations (1) and (2) in above equation, we have
$
2 \times 12 \times v - 2 \times 16 \times 2 = 0 \\
\Rightarrow v = \dfrac{{32}}{{12}} \\
\Rightarrow v = \dfrac{8}{3} \\
$
After solving the above equation we get the value of v as $\dfrac{8}{3}$.
$\therefore $ The rate at which the lower end moves on the horizontal floor will be $\dfrac{8}{3}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Pythagoras theorem is always useful in a right angled triangle. Rate of change of x with respect to time will give the speed of the object. Rate of change can be obtained by finding the derivative of the position variable with respect to time.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Diagram of the given question as below:

In the diagram, BC is the ladder and AC is the wall against which the ladder is leaning. Let us suppose that the horizontal speed of the ladder is v feet/sec whereas its vertical speed is given as 2 feet per second.
So, $\dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}} = v$ ….(1)
Also assume that,
AB = x feet
AC = y feet
So, vertical speed of the ladder will be, $\dfrac{{dy}}{{dt}} = - 2$ ….(2) ( It is negative due to decreasing in nature)
In $\vartriangle ABC$ applying the Pythagoras theorem, we have
$A{C^2} + A{B^2} = B{C^2}$
Substituting the values of AC and AB, in the above equation,
$
{y^2} + {x^2} = {20^{^2}} \\
\Rightarrow {y^2} + {x^2} = 400 \\
$ ….(3)
So, when x = 12 , then from equation (3), we get
\[
{y^2} + {12^2} = 400 \\
\Rightarrow {y^2} = 400 - 144 \\
\Rightarrow y = \sqrt {256} \\
\Rightarrow y = 16 \\
\]
Taking derivative of equation (3) both sides, we get
$2x\dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}} + 2y\dfrac{{dy}}{{dt}} = 0$ (Using derivative formulas with respect to time t).
Substituting the known values as well as terms from equations (1) and (2) in above equation, we have
$
2 \times 12 \times v - 2 \times 16 \times 2 = 0 \\
\Rightarrow v = \dfrac{{32}}{{12}} \\
\Rightarrow v = \dfrac{8}{3} \\
$
After solving the above equation we get the value of v as $\dfrac{8}{3}$.
$\therefore $ The rate at which the lower end moves on the horizontal floor will be $\dfrac{8}{3}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Pythagoras theorem is always useful in a right angled triangle. Rate of change of x with respect to time will give the speed of the object. Rate of change can be obtained by finding the derivative of the position variable with respect to time.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




