
‘A’ is a carbide of ${3^{rd}}$ period element which forms amphoteric oxide in the below reaction. How D can be converted into B?
A. $Ni$
B. $Na/ether$
C. $Zn - Hg/HCl$
D. $LiAl{H_4}$

Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint: D can be converted to B by using the Clemmensen’s reduction. Clemmensen reduction is the reduction in which the reduction of aldehydes or ketones is done using zinc amalgam and concentrated hydrochloric acid.
Complete step by step answer:
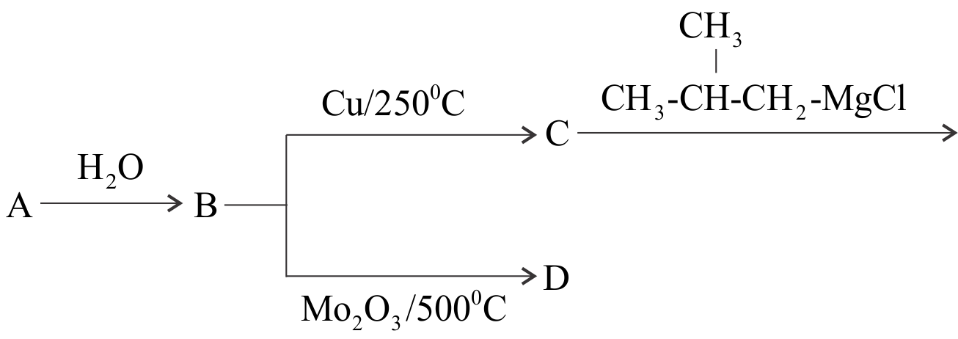
From the question, it is given that A is carbide in the reaction.
When the hydrolysis of metal carbide is done it gives methane. So, the element B is methane.
As given in question A is the element in the third period. We know that there are eight elements in the third period which are – sodium, magnesium, aluminium, silicon, phosphorus, sulphur, chlorine and argon.
So, let's take aluminium from the third period then the carbide A will be aluminium carbide whose molecular formula is $A{l_4}{C_3}$. Then, the reaction is –
$A{l_4}{C_3}\xrightarrow{{{H_2}O}}C{H_4}$
When methane B is oxidized with $M{o_2}{O_3}$ at the temperature of ${500^ \circ }C$ results in the formation of formaldehyde D. Therefore, the reaction is –
$C{H_4}\xrightarrow{{M{o_2}{O_3}/{{500}^ \circ }C}}HCHO$
As for the conversion from B to D we need to oxidize the compound B. Therefore, for the conversion from D to B we need to reduce D to form B. Reduction is the reverse process of oxidation.
Hence, this reduction process is known as Clemmensen’s reduction which can be defined as the reduction process in which aldehyde and ketone are reduced to alkanes in the presence of zinc amalgam and concentrated hydrochloric acid. So, the Clemmensen’s reduction is –
$HCHO\xrightarrow{{Zn - Hg/HCl}}C{H_4}$
From the reaction we conclude thatD can be converted into B by $Zn - Hg/HCl$.
Hence, the elements in the reaction in question are –
A – Aluminium carbide, $A{l_4}{C_3}$
B – Methane, $C{H_4}$
D – Formaldehyde, $HCHO$
So, Option D is correct.
Note: The hydrocarbons can be formed by the various process –
Hydrogenation
Addition
Substitution
Reduction
Decarboxylation
Complete step by step answer:
From the question, it is given that A is carbide in the reaction.
When the hydrolysis of metal carbide is done it gives methane. So, the element B is methane.
As given in question A is the element in the third period. We know that there are eight elements in the third period which are – sodium, magnesium, aluminium, silicon, phosphorus, sulphur, chlorine and argon.
So, let's take aluminium from the third period then the carbide A will be aluminium carbide whose molecular formula is $A{l_4}{C_3}$. Then, the reaction is –
$A{l_4}{C_3}\xrightarrow{{{H_2}O}}C{H_4}$
When methane B is oxidized with $M{o_2}{O_3}$ at the temperature of ${500^ \circ }C$ results in the formation of formaldehyde D. Therefore, the reaction is –
$C{H_4}\xrightarrow{{M{o_2}{O_3}/{{500}^ \circ }C}}HCHO$
As for the conversion from B to D we need to oxidize the compound B. Therefore, for the conversion from D to B we need to reduce D to form B. Reduction is the reverse process of oxidation.
Hence, this reduction process is known as Clemmensen’s reduction which can be defined as the reduction process in which aldehyde and ketone are reduced to alkanes in the presence of zinc amalgam and concentrated hydrochloric acid. So, the Clemmensen’s reduction is –
$HCHO\xrightarrow{{Zn - Hg/HCl}}C{H_4}$
From the reaction we conclude thatD can be converted into B by $Zn - Hg/HCl$.
Hence, the elements in the reaction in question are –
A – Aluminium carbide, $A{l_4}{C_3}$
B – Methane, $C{H_4}$
D – Formaldehyde, $HCHO$
So, Option D is correct.
Note: The hydrocarbons can be formed by the various process –
Hydrogenation
Addition
Substitution
Reduction
Decarboxylation
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




