
What is A in the following reaction?
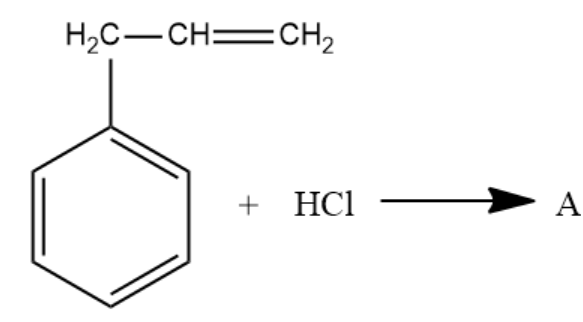

Answer
515.4k+ views
Hint: Remember to apply Markovnikov’s rule whenever a protic acid is added to an asymmetric alkene. The rule states that: In addition reactions involving unsymmetrical alkenes, the electron rich component of the reagent adds to the carbon atom with less number of hydrogen atoms bonded to it. The electron deficient component adds to the carbon with more hydrogen atoms bonded to it.
Complete answer:
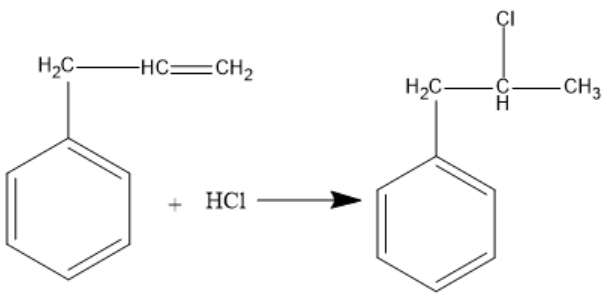
The given reaction proceeds with Markovnikov’s rule. First, electrophilic addition takes place and then nucleophilic attack occurs. According to Markovnikov’s rule, the electron rich component of the reagent adds to the carbon atom with less number of hydrogen atoms bonded to it. Nucleophilic part is the electron rich component of a reagent. Nucleophiles are chemical species which form bonds with electrophiles by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions which have a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. The nucleophile attaches to the carbon having less number of hydrogen atoms. $C{l^ - }$ is the nucleophile in the given reagent. The middle carbon has less number of hydrogens attached to it. So, the nucleophile attaches to the middle carbon. The reaction is given below:
Note:
While solving questions which involve addition of protic acids to unsymmetrical alkenes, we have to apply Markovnikov's rule and identify the nucleophilic part in the given reagent. Then, look for the carbon in the unsymmetrical alkene which has less number of hydrogens attached to it and attach the nucleophile to it.
Complete answer:
The given reaction proceeds with Markovnikov’s rule. First, electrophilic addition takes place and then nucleophilic attack occurs. According to Markovnikov’s rule, the electron rich component of the reagent adds to the carbon atom with less number of hydrogen atoms bonded to it. Nucleophilic part is the electron rich component of a reagent. Nucleophiles are chemical species which form bonds with electrophiles by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions which have a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. The nucleophile attaches to the carbon having less number of hydrogen atoms. $C{l^ - }$ is the nucleophile in the given reagent. The middle carbon has less number of hydrogens attached to it. So, the nucleophile attaches to the middle carbon. The reaction is given below:

Note:
While solving questions which involve addition of protic acids to unsymmetrical alkenes, we have to apply Markovnikov's rule and identify the nucleophilic part in the given reagent. Then, look for the carbon in the unsymmetrical alkene which has less number of hydrogens attached to it and attach the nucleophile to it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




