
(a) in the above reaction is:
$HCONHR\xrightarrow[Pyridine]{POCl_3}\left ( a \right )+H_2O$
(1) ${\rm{RCH}} = {\rm{NOH}}$
(2) ${\rm{R}} - {\rm{N}} = {\rm{C}} = {\rm{O}}$
(3) ${\rm{R}} - {\rm{C}} \equiv {\rm{N}}$
(4) $R - \mathop {\rm{N}}\limits^ + \equiv \mathop {\rm{C}}\limits^ - $
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: We know that amide is a functional group which contains an acyl group (R-C=O) linked to a nitrogen atom. Simply we can say that amide is formed by replacing one hydrogen atom of ammonia by an acyl group.
Complete step by step solution:
Let’s understand the types of amide in detail. There are three types of amide, that is, primary amide, secondary amide and tertiary amide.
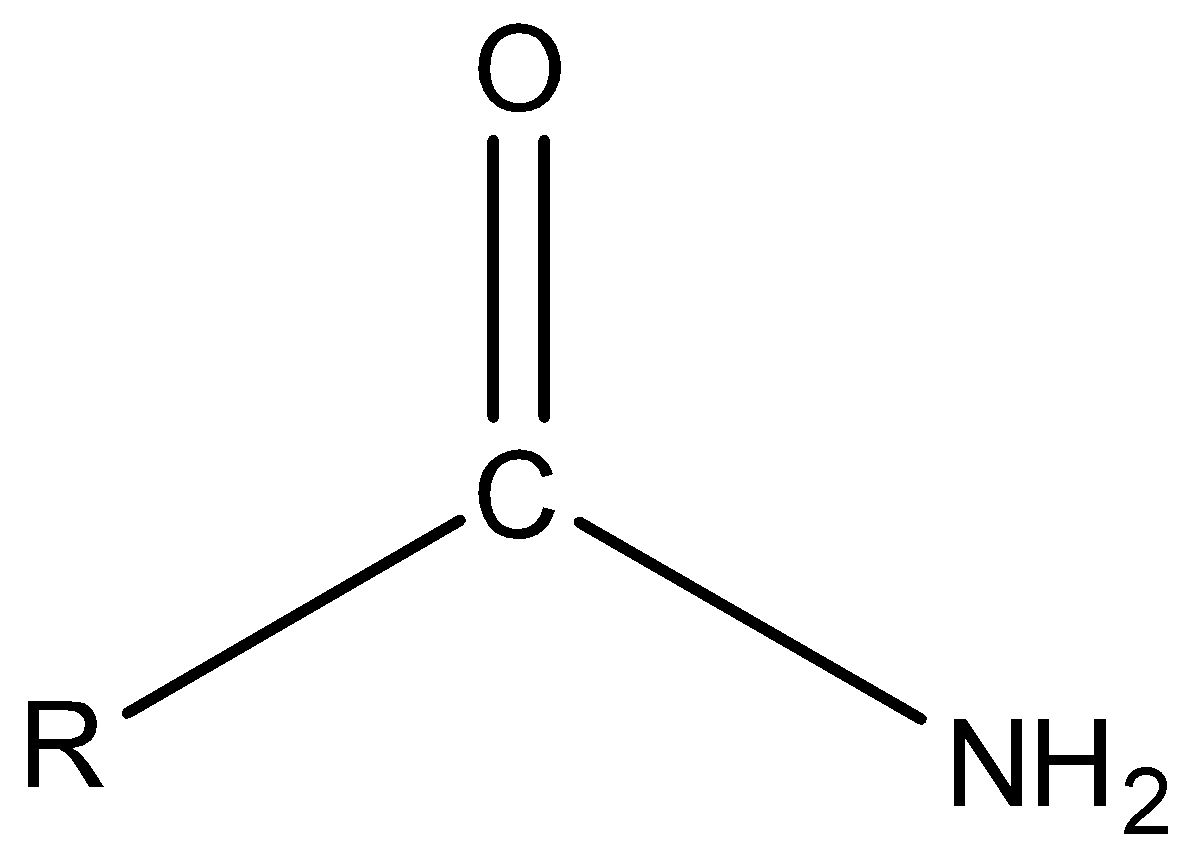
Primary amide is the amide in which N atom is bonded to only one carbon atom.
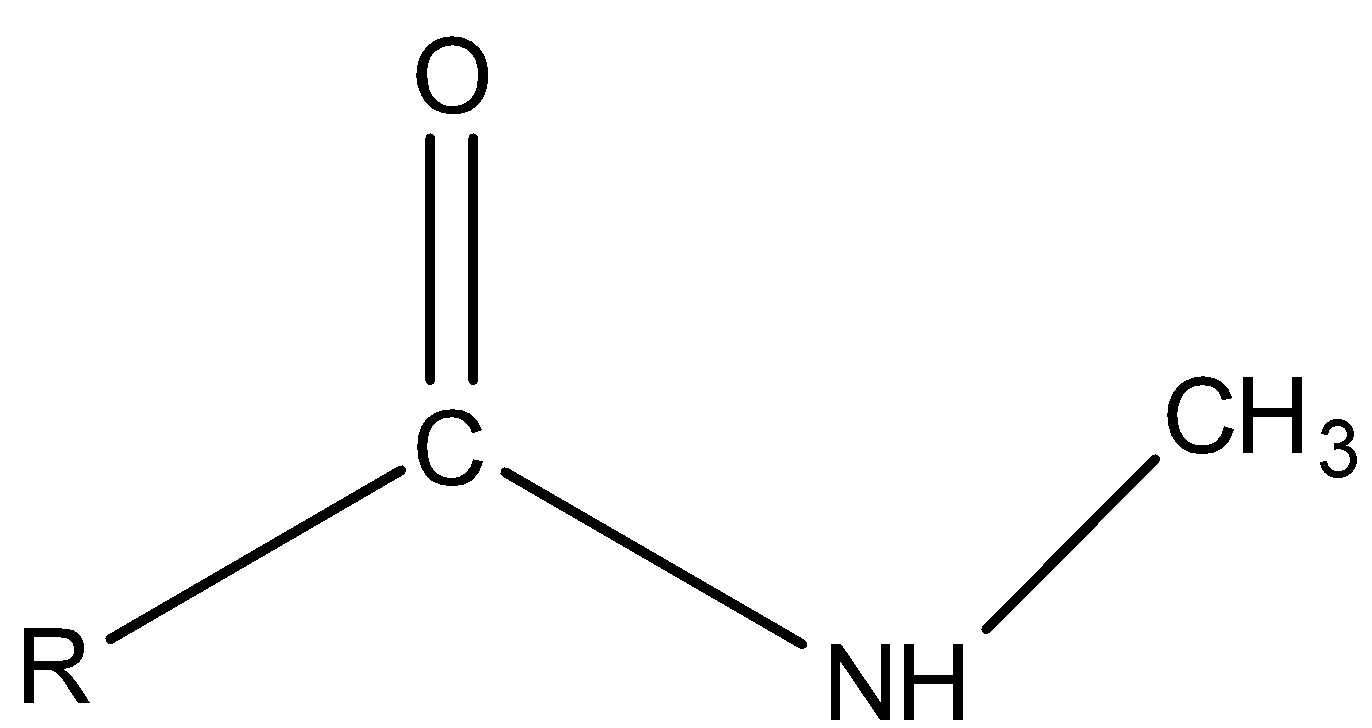
Secondary amide is the amide in which N atom is bonded to two carbon atoms.
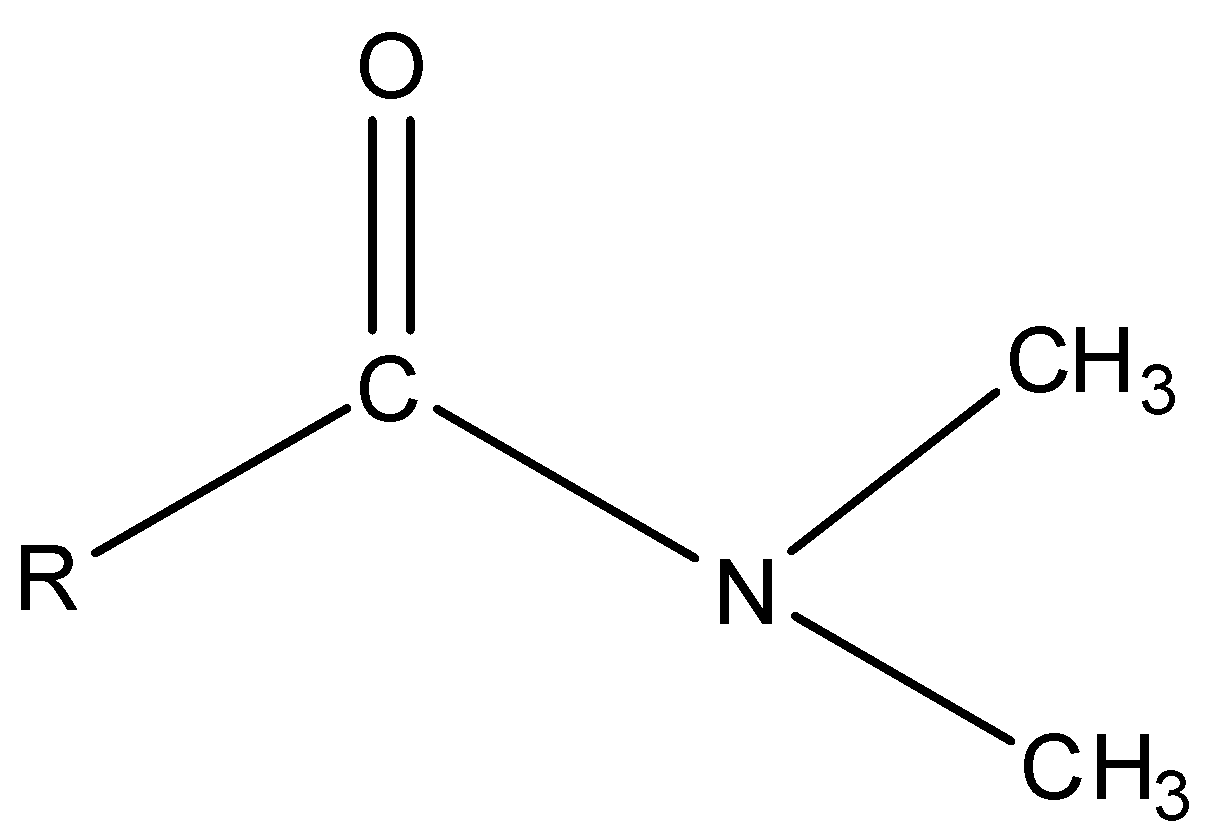
Tertiary amide is the amide in which N atom is bonded to three carbon atoms.
Let’s discuss the reagent POCl3. A primary amide can be converted to a nitrile using POCl3 . POCl3 is a dehydrating agent that removes water from the amide.
Now, come to the question. Here, a secondary amide is given which reacts with POCl3 in presence of pyridine. One product formed in the reaction is water and we have to find the other product.
Let’s discuss the mechanism of the reaction.
${\rm{POC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{3}}} \to {\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{3}}} + \left[ {\rm{O}} \right]$
Now, oxygen abstracts hydrogen from amide.
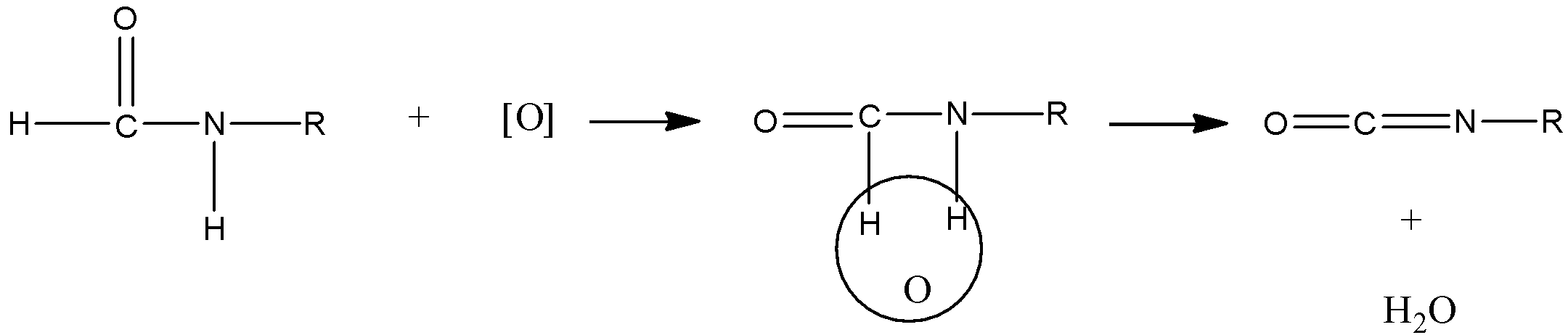
Therefore, (a) of the reaction is ${\rm{R}} - {\rm{N}} = {\rm{C}} = {\rm{O}}$.
So, the correct answer is Option 2.
Note: Primary amine can be synthesized by reacting amide with bromine in presence of aqueous ethanolic solution of sodium hydroxide. This reaction is known as Hoffmann bromamide reaction.

In this reaction, an acyl or aryl group migrates from carbonyl carbon of the amide to the nitrogen atom. The amine formed in the reaction possesses one less carbon atom than the amide.
Complete step by step solution:
Let’s understand the types of amide in detail. There are three types of amide, that is, primary amide, secondary amide and tertiary amide.
Primary amide is the amide in which N atom is bonded to only one carbon atom.

Secondary amide is the amide in which N atom is bonded to two carbon atoms.

Tertiary amide is the amide in which N atom is bonded to three carbon atoms.

Let’s discuss the reagent POCl3. A primary amide can be converted to a nitrile using POCl3 . POCl3 is a dehydrating agent that removes water from the amide.
Now, come to the question. Here, a secondary amide is given which reacts with POCl3 in presence of pyridine. One product formed in the reaction is water and we have to find the other product.
Let’s discuss the mechanism of the reaction.
${\rm{POC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{3}}} \to {\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{3}}} + \left[ {\rm{O}} \right]$
Now, oxygen abstracts hydrogen from amide.

Therefore, (a) of the reaction is ${\rm{R}} - {\rm{N}} = {\rm{C}} = {\rm{O}}$.
So, the correct answer is Option 2.
Note: Primary amine can be synthesized by reacting amide with bromine in presence of aqueous ethanolic solution of sodium hydroxide. This reaction is known as Hoffmann bromamide reaction.

In this reaction, an acyl or aryl group migrates from carbonyl carbon of the amide to the nitrogen atom. The amine formed in the reaction possesses one less carbon atom than the amide.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




