
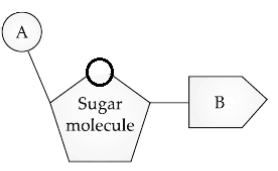
A. Identify the picture given.
B. What do ‘A’ and ‘B’ indicate?

Answer
498k+ views
Hint: Nucleic acid is a type of macromolecule that may be present in all organisms and viruses. The information a cell needs to produce proteins is encoded in deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a similar kind of nucleic acid that participates in protein synthesis in many molecular forms. Nucleic acids are one of the most important biomolecules present in the living system.
Complete answer:
Let us answer this question as follows:
A. The picture is representing the structure of a typical ‘nucleotide’.
Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA), which are responsible for storing and transmitting genetic information.
They also serve as chemical energy transporters in cells, as cofactors for enzymes, and as secondary messengers.
A nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar, and a phosphate group make up nucleotides.
In RNA the five carbon sugars are ribose and in DNA it is deoxyribose.
B. ‘A’ indicates phosphate group and ‘B’ indicates ‘nitrogenous base’.
The phosphate group in a nucleotide is bound by a phosphoester bond with the fifth carbon of the sugar molecule.
The nitrogenous base in a nucleotide is bound to the sugar molecule by forming the N-glycosidic linkage with the first carbon of sugar.
Note:
A nucleoside is a five-carbon sugar that is either ribose or deoxyribose and is made up of a pyrimidine (cytosine, thymine, or uracil) or a purine (adenine or guanine). A nucleotide is made up of a nucleoside and a phosphate group. Biosynthetic precursors of glucose and amino acid metabolism, as well as ammonia and carbon dioxide, are utilised in de novo nucleotide synthesis.
Complete answer:
Let us answer this question as follows:
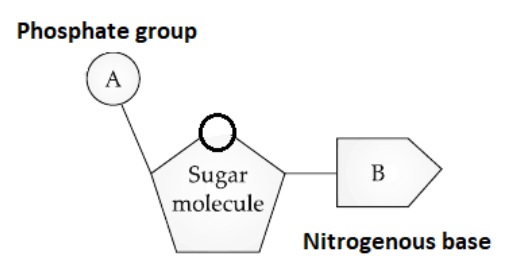
A. The picture is representing the structure of a typical ‘nucleotide’.
Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA), which are responsible for storing and transmitting genetic information.
They also serve as chemical energy transporters in cells, as cofactors for enzymes, and as secondary messengers.
A nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar, and a phosphate group make up nucleotides.
In RNA the five carbon sugars are ribose and in DNA it is deoxyribose.
B. ‘A’ indicates phosphate group and ‘B’ indicates ‘nitrogenous base’.
The phosphate group in a nucleotide is bound by a phosphoester bond with the fifth carbon of the sugar molecule.
The nitrogenous base in a nucleotide is bound to the sugar molecule by forming the N-glycosidic linkage with the first carbon of sugar.

Note:
A nucleoside is a five-carbon sugar that is either ribose or deoxyribose and is made up of a pyrimidine (cytosine, thymine, or uracil) or a purine (adenine or guanine). A nucleotide is made up of a nucleoside and a phosphate group. Biosynthetic precursors of glucose and amino acid metabolism, as well as ammonia and carbon dioxide, are utilised in de novo nucleotide synthesis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




