
A hydrocarbon of molecular formula ${{C}_{7}}{{H}_{16}}$ upon monochlorination with $C{{l}_{2}}$ gives seven isomers. Predict the molecular structure of the hydrocarbon.
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint:A hydrocarbon is an organic compound formed by a number of Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen atoms in a certain proportion.
-The number of isomers of a structure gives the information about the number of equivalent atoms present in that molecule. Which means with each substitution of the functional groups, one isomer will be formed.
Complete answer:
The hydrocarbon here is n-heptane which upon free radical monochlorination with $C{{l}_{2}}$ in the presence of sunlight or UV gives seven different monochlorinated constitutional isomers as the product. The question says that there are seven isomers of the product, so this means there would be seven non identical sites where the chlorine could get attached and it would form a new compound with the same chemical formula but different structural formula. Equivalent carbons are the carbons which have the same resonance frequency of hydrogen-carbon bonds. For instance, in methane molecules, all the four hydrogens are equivalent. In case of ${{C}_{7}}{{H}_{16}}$, if it was a long straight chain hydrocarbon, the number of isomers would have been lesser, as the number of equivalent carbons in the structure would have been more. So, we need to think of a structure which has substitution of a methyl group. Then the longest chain would have six carbons, and the methyl group would be the seventh carbon atom. Suppose we substitute the third carbon of the hexane straight chain with methyl group, it will become $3-$methylhexane, now look at the structure given below, we can see that all the seven carbons are non-equivalent in nature as, if we substitute any hydrogen of two different carbons, with chlorine, we will get two different isomers from the same structure.
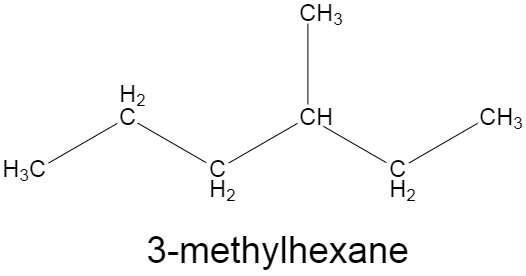
Similarly, since all the Carbon atoms in the given structure of $3-$methylhexane are not equivalent, a monochlorination reaction with $3-$methylhexane only, will give seven different constitutional isomers.
Thus, the correct answer is $3-$methylhexane.
Note:
-The number of isomers of the structure tells us about the number of non-equivalent carbons and substitution of hydrogens will lead to formation of isomers, one from each carbon.
-The molecular structure of a compound is the representation of the hydrocarbons where the bonds between the atoms are shown with lines.
-The number of isomers of a structure gives the information about the number of equivalent atoms present in that molecule. Which means with each substitution of the functional groups, one isomer will be formed.
Complete answer:
The hydrocarbon here is n-heptane which upon free radical monochlorination with $C{{l}_{2}}$ in the presence of sunlight or UV gives seven different monochlorinated constitutional isomers as the product. The question says that there are seven isomers of the product, so this means there would be seven non identical sites where the chlorine could get attached and it would form a new compound with the same chemical formula but different structural formula. Equivalent carbons are the carbons which have the same resonance frequency of hydrogen-carbon bonds. For instance, in methane molecules, all the four hydrogens are equivalent. In case of ${{C}_{7}}{{H}_{16}}$, if it was a long straight chain hydrocarbon, the number of isomers would have been lesser, as the number of equivalent carbons in the structure would have been more. So, we need to think of a structure which has substitution of a methyl group. Then the longest chain would have six carbons, and the methyl group would be the seventh carbon atom. Suppose we substitute the third carbon of the hexane straight chain with methyl group, it will become $3-$methylhexane, now look at the structure given below, we can see that all the seven carbons are non-equivalent in nature as, if we substitute any hydrogen of two different carbons, with chlorine, we will get two different isomers from the same structure.

Similarly, since all the Carbon atoms in the given structure of $3-$methylhexane are not equivalent, a monochlorination reaction with $3-$methylhexane only, will give seven different constitutional isomers.
Thus, the correct answer is $3-$methylhexane.
Note:
-The number of isomers of the structure tells us about the number of non-equivalent carbons and substitution of hydrogens will lead to formation of isomers, one from each carbon.
-The molecular structure of a compound is the representation of the hydrocarbons where the bonds between the atoms are shown with lines.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




