
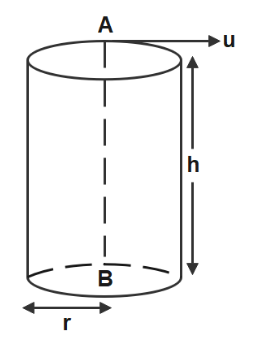
A hollow vertical cylinder of radius $r$ and height $h$ has a smooth internal surface. A small particle is placed in contact with the inner side of the upper rim, at point A, and given a horizontal speed $u$, tangential to the rim. It leaves the lower rim at point B, vertically below A. If $n$ is an integer then-
A. ${\text{ }}n = \dfrac{u}{{2\pi r}}\sqrt {\dfrac{{2h}}{g}} $
B. ${\text{ }}n = \dfrac{h}{{2\pi r}}$
C. ${\text{ }}n = \dfrac{{2\pi r}}{h}$
D. ${\text{ }}n = \dfrac{u}{{2gh}}$

Answer
497.4k+ views
Hint:In order to solve the question, we will first take the vertical motion into account using the second law of motion we will find the time and then we will take the horizontal motion into for which we substitute the value of time into the relation between time, horizontal distance and the horizontal velocity
Formula used:
$S = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
Where, $S$ is the distance, $a$ is the acceleration, $u$ is the velocity and $t$ is time.
Complete step by step answer:
In the question we are given a hollow vertical cylinder which has a smooth internal surface. A small particle is placed in contact with the inner side of the upper rim, at point A, and given a horizontal speed, tangential to the rim. It leaves the lower rim at point B, vertically below A.$n$ is the number of rotations of the particle and we have to find the value of $n$.
Radius of hollow vertical cylinder = $r$
Height of hollow vertical cylinder of hollow vertical cylinder = $h$
Horizontal speed = $u$
In the vertical direction the velocity is zero. Using the second equation of motion we will find the height of the cylinder which the particle travels.
Second equation of motion
$S = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
S is the height “h”
a is the acceleration which in this case g
vertical velocity = 0
substituting the values of a, g, u
$h = (0)t + \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$
Hence height is $h = \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$
Now we will find the value of t
Taking 2 and g on the other side
$t = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2h}}{g}}$
Now we will see the motion in the horizontal direction.
Horizontal speed = $u$
Radius is $r$ so the each rotation cover a circumference of $2\pi r$ and the number of turns is $n$ so the total distance in vertical direction is $n \times 2\pi r$.Using the formula
$d = ut$
Where d = $n \times 2\pi r$
We get
$n \times 2\pi r = ut$
Now substituting the value of $$t = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2h}}{g}} $$
$n \times 2\pi r = u\sqrt {\dfrac{{2h}}{g}} $
Solving for n and we get
$\therefore n = \dfrac{u}{{2\pi r}}\sqrt {\dfrac{{2h}}{g}} $$
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note:Many of the students will make the mistake by not taking the horizontal and the vertical motion separately as well as the only the time is the physical quantity which is constant either it is vertical motion or it is horizontal motion so which makes substituting the value of time will be the easiest way to find the other physical quantities.
Formula used:
$S = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
Where, $S$ is the distance, $a$ is the acceleration, $u$ is the velocity and $t$ is time.
Complete step by step answer:
In the question we are given a hollow vertical cylinder which has a smooth internal surface. A small particle is placed in contact with the inner side of the upper rim, at point A, and given a horizontal speed, tangential to the rim. It leaves the lower rim at point B, vertically below A.$n$ is the number of rotations of the particle and we have to find the value of $n$.
Radius of hollow vertical cylinder = $r$
Height of hollow vertical cylinder of hollow vertical cylinder = $h$
Horizontal speed = $u$
In the vertical direction the velocity is zero. Using the second equation of motion we will find the height of the cylinder which the particle travels.
Second equation of motion
$S = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
S is the height “h”
a is the acceleration which in this case g
vertical velocity = 0
substituting the values of a, g, u
$h = (0)t + \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$
Hence height is $h = \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$
Now we will find the value of t
Taking 2 and g on the other side
$t = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2h}}{g}}$
Now we will see the motion in the horizontal direction.
Horizontal speed = $u$
Radius is $r$ so the each rotation cover a circumference of $2\pi r$ and the number of turns is $n$ so the total distance in vertical direction is $n \times 2\pi r$.Using the formula
$d = ut$
Where d = $n \times 2\pi r$
We get
$n \times 2\pi r = ut$
Now substituting the value of $$t = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2h}}{g}} $$
$n \times 2\pi r = u\sqrt {\dfrac{{2h}}{g}} $
Solving for n and we get
$\therefore n = \dfrac{u}{{2\pi r}}\sqrt {\dfrac{{2h}}{g}} $$
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note:Many of the students will make the mistake by not taking the horizontal and the vertical motion separately as well as the only the time is the physical quantity which is constant either it is vertical motion or it is horizontal motion so which makes substituting the value of time will be the easiest way to find the other physical quantities.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




