
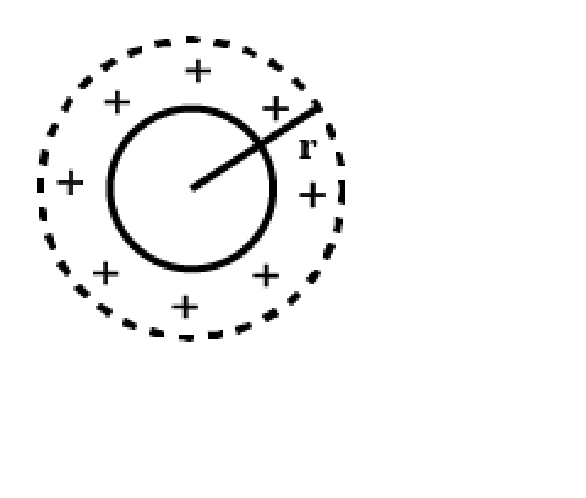
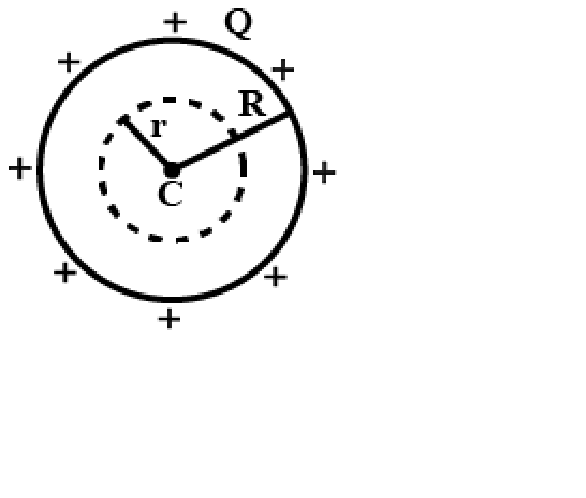
A hollow metal sphere of radius $R$ is uniformly charged. The electric field due to the sphere at a distance $r$ from the center.
A) Increases as $r$ increases for $r < R$ and for $r > R$ .
B) Zero as $r$ increases for $r < R$ , decreases as $r$ increases for $r > R$ .
C) Zero as $r$ increases for $r < R$ , increases as $r$ increases for $r > R$ .
D) Decreases as $r$ increases for $r < R$ and for $r > R$ .
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: We can use Gauss Law to solve this problem, because Gauss Law can be stated using the electric field. Charge is distributed over the surface of a hollow metal sphere. Take both the hollow metal sphere into consideration, i.e., inside, and outside, for getting the correct answer.
Formula used:
${{\phi }_{e}}=\oint{\overrightarrow{E}.\overrightarrow{dA}=\dfrac{Q}{{{\varepsilon }_{o}}}}$, where $E$ is the electric field,
$dA$ is a vector representing an infinitesimal element of area of the surface,
$Q$ is the total charge enclosed within volume, and
${{\varepsilon }_{o}}$ is the electric constant.
Complete answer:
According to Gauss Law, the net flux through any closed surface equals the total charge inside that surface divided by ${{\varepsilon }_{o}}$ . The equation for this law can be written as:
${{\phi }_{e}}=\oint{\overrightarrow{E}.\overrightarrow{dA}=\dfrac{{{Q}_{net}}}{{{\varepsilon }_{o}}}}$
For $rBy Gauss law,
\[{{\phi }_{e}}=\oint{{{\overrightarrow{E}}_{in}}.\overrightarrow{dA}=\dfrac{{{Q}_{net}}}{{{\varepsilon }_{o}}}=0\,(\because {{Q}_{net}}=0)}\]
$\Rightarrow {{E}_{in}}=0$
For $r>R$ (outside sphere):
By Gauss Law,
\[{{\phi }_{e}}=\oint{{{\overrightarrow{E}}_{o}}.\overrightarrow{dA}=\dfrac{{{q}_{en}}}{{{\varepsilon }_{o}}}}\]
Here, ${{q}_{en}}=Q\,and\,dA=4\pi {{r}^{2}}$
Substitute the value in the above equation, we get:
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{E}_{o}}\times 4\pi {{r}^{2}}=\dfrac{Q}{{{\varepsilon }_{o}}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{E}_{o}}\propto \dfrac{1}{{{r}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}$
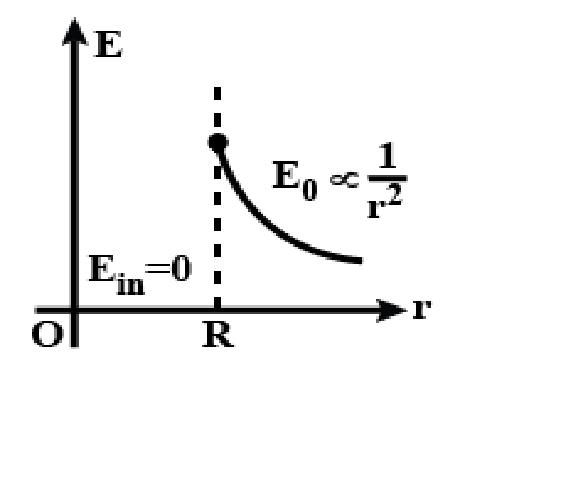
From the above solution, it is clear that the electric field is zero as $r$ increases for $r < R$ and decreases as $r$ increases for $r > R$.
Therefore, the correct answer is Option (B).
Note:
Substitute the value properly in both the condition to get the final relation. It is necessary to derive both the relations before marking the result, so that we can get the dependency of the electric field, which will help to reach a solution.
Formula used:
${{\phi }_{e}}=\oint{\overrightarrow{E}.\overrightarrow{dA}=\dfrac{Q}{{{\varepsilon }_{o}}}}$, where $E$ is the electric field,
$dA$ is a vector representing an infinitesimal element of area of the surface,
$Q$ is the total charge enclosed within volume, and
${{\varepsilon }_{o}}$ is the electric constant.
Complete answer:



According to Gauss Law, the net flux through any closed surface equals the total charge inside that surface divided by ${{\varepsilon }_{o}}$ . The equation for this law can be written as:
${{\phi }_{e}}=\oint{\overrightarrow{E}.\overrightarrow{dA}=\dfrac{{{Q}_{net}}}{{{\varepsilon }_{o}}}}$
For $r
\[{{\phi }_{e}}=\oint{{{\overrightarrow{E}}_{in}}.\overrightarrow{dA}=\dfrac{{{Q}_{net}}}{{{\varepsilon }_{o}}}=0\,(\because {{Q}_{net}}=0)}\]
$\Rightarrow {{E}_{in}}=0$
For $r>R$ (outside sphere):
By Gauss Law,
\[{{\phi }_{e}}=\oint{{{\overrightarrow{E}}_{o}}.\overrightarrow{dA}=\dfrac{{{q}_{en}}}{{{\varepsilon }_{o}}}}\]
Here, ${{q}_{en}}=Q\,and\,dA=4\pi {{r}^{2}}$
Substitute the value in the above equation, we get:
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{E}_{o}}\times 4\pi {{r}^{2}}=\dfrac{Q}{{{\varepsilon }_{o}}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{E}_{o}}\propto \dfrac{1}{{{r}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}$
From the above solution, it is clear that the electric field is zero as $r$ increases for $r < R$ and decreases as $r$ increases for $r > R$.
Therefore, the correct answer is Option (B).
Note:
Substitute the value properly in both the condition to get the final relation. It is necessary to derive both the relations before marking the result, so that we can get the dependency of the electric field, which will help to reach a solution.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




