
A hollow cone is cut by a plane parallel to its base and the upper portion is removed. If the curved surface area of the remaining is \[\dfrac{8}{9}\] of the curved surface area of the whole cone, find the ratio of line segments into which the cone’s altitude is divided by the plane.
Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: We solve this problem by using the formula of the curved surface area of the cone.
We have the formula for the curved surface area of the cone as
\[A=2\pi rl\]
Where \[r\] is the radius of the cone and \[l\] is the slant height of the cone.
We assume that the ratio of heights of the original cone to the removed cone as \[k:1\] to find the value of \[k\] by using the given condition of the curved surface area of the cones so that we can find the ratio of altitude that the plane divided the cone.
Complete step by step answer:
We are given that the plane parallel to the base of the cone cuts the cone into two parts.
Let us take the rough figure of the cone before and after cutting as follows.
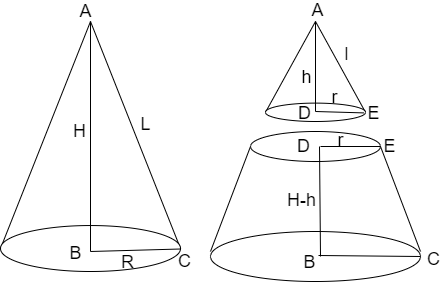
We are asked to find the ratio of altitude that the plane divided the cone that the ratio of \[h\] to \[H-h\]
Let us assume that the ratio of altitude of the original cone to the removed cone as \[k:1\]
By converting the above statement into a mathematical equation then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{H}{h}=\dfrac{k}{1} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{h}{H}=\dfrac{1}{k} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, let us consider the triangles \[\Delta ABC\] and \[\Delta ADE\]
Here, we can see that there are three conditions with respect to the angles of two triangles as
(1) \[\angle BAC=\angle DAE\left( \because \text{common angle} \right)\]
(2) \[\angle ABC=\angle ADE\left( \because AB,AD\text{ are altitudes} \right)\]
(3) \[\angle ACB=\angle AED\left( \because DE\parallel BC \right)\]
We know that if three angles of two triangles are equal then the triangles are similar.
By using the above condition we can say that triangles \[\Delta ABC\] and \[\Delta ADE\] are similar.
We know that if two triangles are similar then the corresponding sides are in proportion.
By using the above condition to triangles \[\Delta ABC\] and \[\Delta ADE\] we get
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{AD}{AB}=\dfrac{DE}{BC}=\dfrac{AE}{AC}\]
By substituting the required values in the above equation then we get
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{h}{H}=\dfrac{r}{R}=\dfrac{l}{L}=\dfrac{1}{k}...........equation(i)\]
We know that the formula for a curved surface area of the cone as
\[A=2\pi rl\]
Where \[r\] is the radius of the cone and \[l\] is the slant height of the cone.
We are given that the curved surface area of the remaining after removing the smaller cone is \[\dfrac{8}{9}\] of the curved surface area of the whole cone
We can rewrite the statement as that the curved surface area of the small cone is \[\dfrac{1}{9}\] of the curved surface area of the whole cone.
By converting the above statement into mathematical equation by using the formula of curved surface area of the cone then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \pi rl=\dfrac{1}{9}\left( \pi RL \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{r}{R} \right)\left( \dfrac{l}{L} \right)=\dfrac{1}{9} \\
\end{align}\]
By substituting the required values form equation (i) then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{1}{k} \right)\left( \dfrac{1}{k} \right)=\dfrac{1}{9} \\
& \Rightarrow {{k}^{2}}=9 \\
& \Rightarrow k=3 \\
\end{align}\]
By substituting the value of \[k\] in equation (i) having heights then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{h}{H}=\dfrac{1}{3} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{H}{h}=3 \\
\end{align}\]
Now, by subtracting by 1 on both sides then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{H}{h}-1=3-1 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{H-h}{h}=2 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{h}{H-h}=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, we can conclude that the required ratio is \[1:2\]
Note:
We need to note that the given condition that is the curved surface area of the remaining after removing the smaller cone is \[\dfrac{8}{9}\] of the curved surface area of the whole cone
Here, the remaining refers to the frustum of the cone.
Converting this statement to a mathematical equation will take the complex problem that is it gives some cubic equation in one variable.
So, to solve easily we use the curved surface area of the cone that is removed.
We have the formula for the curved surface area of the cone as
\[A=2\pi rl\]
Where \[r\] is the radius of the cone and \[l\] is the slant height of the cone.
We assume that the ratio of heights of the original cone to the removed cone as \[k:1\] to find the value of \[k\] by using the given condition of the curved surface area of the cones so that we can find the ratio of altitude that the plane divided the cone.
Complete step by step answer:
We are given that the plane parallel to the base of the cone cuts the cone into two parts.
Let us take the rough figure of the cone before and after cutting as follows.

We are asked to find the ratio of altitude that the plane divided the cone that the ratio of \[h\] to \[H-h\]
Let us assume that the ratio of altitude of the original cone to the removed cone as \[k:1\]
By converting the above statement into a mathematical equation then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{H}{h}=\dfrac{k}{1} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{h}{H}=\dfrac{1}{k} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, let us consider the triangles \[\Delta ABC\] and \[\Delta ADE\]
Here, we can see that there are three conditions with respect to the angles of two triangles as
(1) \[\angle BAC=\angle DAE\left( \because \text{common angle} \right)\]
(2) \[\angle ABC=\angle ADE\left( \because AB,AD\text{ are altitudes} \right)\]
(3) \[\angle ACB=\angle AED\left( \because DE\parallel BC \right)\]
We know that if three angles of two triangles are equal then the triangles are similar.
By using the above condition we can say that triangles \[\Delta ABC\] and \[\Delta ADE\] are similar.
We know that if two triangles are similar then the corresponding sides are in proportion.
By using the above condition to triangles \[\Delta ABC\] and \[\Delta ADE\] we get
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{AD}{AB}=\dfrac{DE}{BC}=\dfrac{AE}{AC}\]
By substituting the required values in the above equation then we get
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{h}{H}=\dfrac{r}{R}=\dfrac{l}{L}=\dfrac{1}{k}...........equation(i)\]
We know that the formula for a curved surface area of the cone as
\[A=2\pi rl\]
Where \[r\] is the radius of the cone and \[l\] is the slant height of the cone.
We are given that the curved surface area of the remaining after removing the smaller cone is \[\dfrac{8}{9}\] of the curved surface area of the whole cone
We can rewrite the statement as that the curved surface area of the small cone is \[\dfrac{1}{9}\] of the curved surface area of the whole cone.
By converting the above statement into mathematical equation by using the formula of curved surface area of the cone then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \pi rl=\dfrac{1}{9}\left( \pi RL \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{r}{R} \right)\left( \dfrac{l}{L} \right)=\dfrac{1}{9} \\
\end{align}\]
By substituting the required values form equation (i) then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{1}{k} \right)\left( \dfrac{1}{k} \right)=\dfrac{1}{9} \\
& \Rightarrow {{k}^{2}}=9 \\
& \Rightarrow k=3 \\
\end{align}\]
By substituting the value of \[k\] in equation (i) having heights then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{h}{H}=\dfrac{1}{3} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{H}{h}=3 \\
\end{align}\]
Now, by subtracting by 1 on both sides then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{H}{h}-1=3-1 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{H-h}{h}=2 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{h}{H-h}=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, we can conclude that the required ratio is \[1:2\]
Note:
We need to note that the given condition that is the curved surface area of the remaining after removing the smaller cone is \[\dfrac{8}{9}\] of the curved surface area of the whole cone
Here, the remaining refers to the frustum of the cone.
Converting this statement to a mathematical equation will take the complex problem that is it gives some cubic equation in one variable.
So, to solve easily we use the curved surface area of the cone that is removed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




