
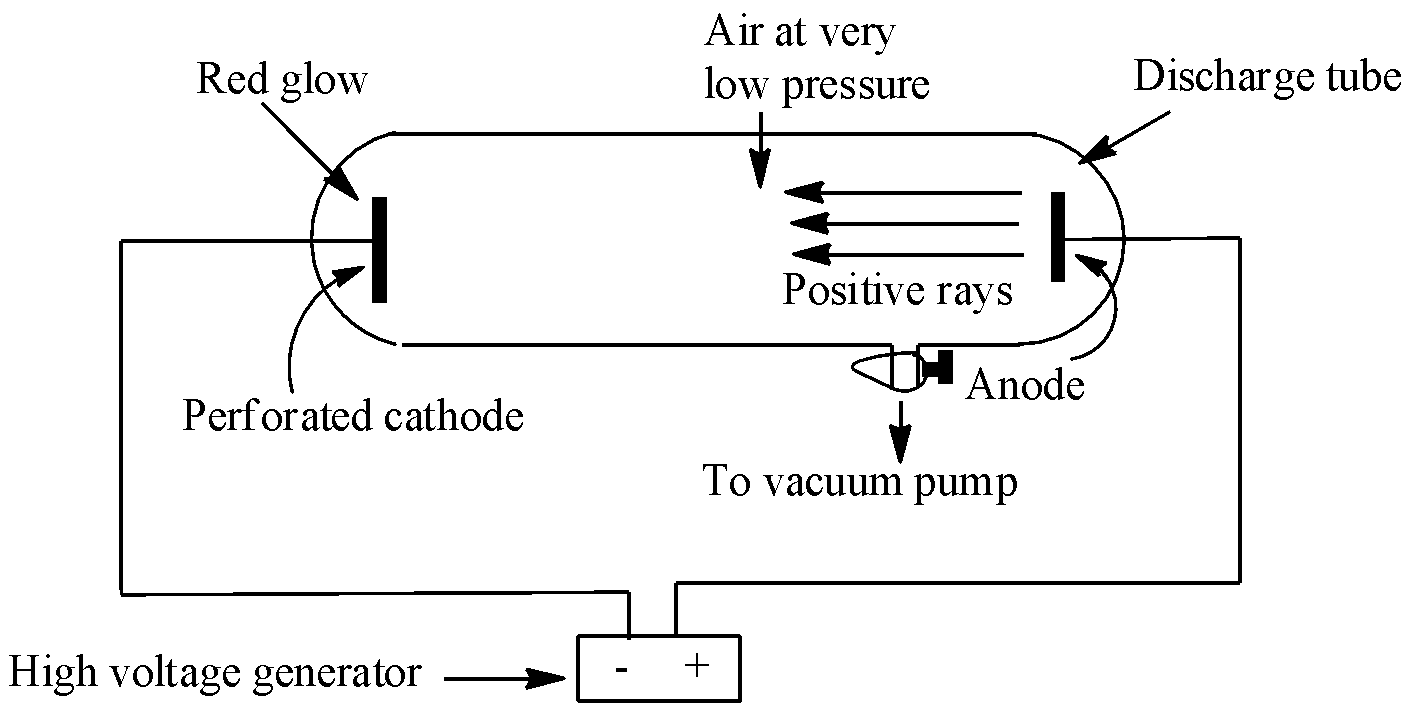
When a high voltage of about 10000 volts is applied to a discharge tube having a perforated cathode and containing air at very low pressure of about 0.001 mm of mercury, a faint red glow is observed behind the cathode. What were the conclusions of this experiment?
i. Anode rays are positively charged.
ii. Since these rays are formed at the anode, they are known as anode rays.
iii. The experiment led to the discovery of electrons.
iv. The experiment led to discovery of protons.
A) i, ii and iii
B) ii, iii and iv
C) i, ii and iv
D) i, iii, and iv

Answer
594.3k+ views
Hint: Refer to the Goldstein experiment of canal rays. Goldstein was the early investigator of discharge tubes and also the discoverer of the canal rays, also called anode rays. During his experiment, he found that in addition to cathode rays, there were also another set of rays that were travelling from the anode towards the cathode.
Complete step by step answer:
The given data of an experiment is the same as that of the canal ray experiment performed by the German scientist Eugen Goldstein in 1886. This experiment led to the discovery of protons. This discovery happened just after the discovery of electrons. In the experiment, Goldstein applied high voltage across a discharge tube which had a perforated cathode. When the voltage was increased to several thousand volts, a faint luminous ray or a faint red glow was observed from the holes behind the cathode. These rays were moving in the opposite direction of cathode rays (carrying electrons) and were named canal rays, also called anode rays (carrying positive charge particles). This discovery of anode rays led to the discovery of protons (positively charged particles).
Therefore, following conclusions were made:
i. Anode rays are positively charged.
ii. Since these rays are formed at the anode, they are known as anode rays.
iii. The experiment led to discovery of protons.
Thus, option (C) is correct.
Note: Goldstein also took his own investigations of discharge tubes and cathode rays. He discovered several important properties of cathode rays, which later contributed to the discovery of electrons. Cathode rays travel from negatively charged cathode towards the positively charged anode while anode rays travel in the opposite direction.
Complete step by step answer:
The given data of an experiment is the same as that of the canal ray experiment performed by the German scientist Eugen Goldstein in 1886. This experiment led to the discovery of protons. This discovery happened just after the discovery of electrons. In the experiment, Goldstein applied high voltage across a discharge tube which had a perforated cathode. When the voltage was increased to several thousand volts, a faint luminous ray or a faint red glow was observed from the holes behind the cathode. These rays were moving in the opposite direction of cathode rays (carrying electrons) and were named canal rays, also called anode rays (carrying positive charge particles). This discovery of anode rays led to the discovery of protons (positively charged particles).
Therefore, following conclusions were made:
i. Anode rays are positively charged.
ii. Since these rays are formed at the anode, they are known as anode rays.
iii. The experiment led to discovery of protons.
Thus, option (C) is correct.
Note: Goldstein also took his own investigations of discharge tubes and cathode rays. He discovered several important properties of cathode rays, which later contributed to the discovery of electrons. Cathode rays travel from negatively charged cathode towards the positively charged anode while anode rays travel in the opposite direction.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction




