
Why is a golgi body like a post office?
Answer
487.5k+ views
Hint: The Golgi body is an organelle found in the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell. It is also known as Golgi apparatus, Golgi complex, and dictyosome. It bundles the macromolecules like lipids and proteins, which are synthesized inside the cell. Generally, proteins are synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum and are traveled to the Golgi body, where they are processed and sent throughout the cell.
Complete answer:
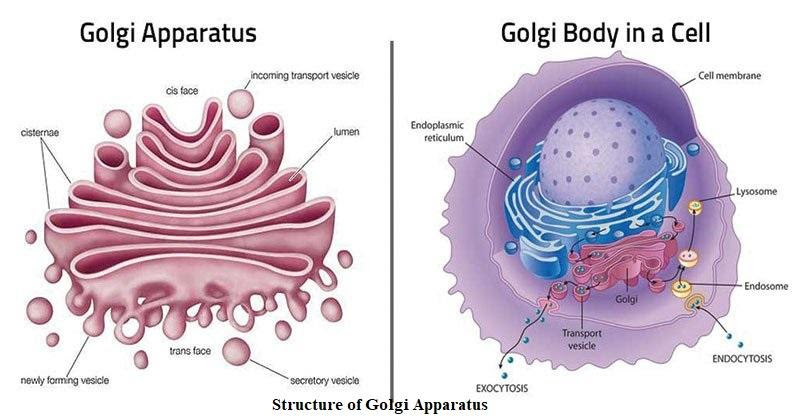
Fig: Structure and Location of Golgi Body in a Cell
The Golgi bodies aid in the translocation of vesicles to the final destination. They transport the materials to the destinations. The molecules are packaged in vesicles and the vesicles work like a shipping envelope for the cell.
The packaged vesicles move to the Golgi bodies. The Golgi bodies open the packages and modify the contents to their final forms and aid in the movement for their final destinations.
In a lot of ways, the Golgi bodies act as the shipping and receiving department of the cell. They package and sort the proteins and other biomolecules before they are sent to final destinations.
Assuming the cell as a city, the Golgi body acts as a post office. It is a stack of membranes, which package, sort, and deliver proteins to the region of the cell they require to go. The Golgi body is the post office of the cell as post offices pack, sort, and deliver mail similarly, Golgi bodies also work with proteins.
Note:
For survival, a cell has to make proteins, as proteins are essential for structure, movement, and energy production. The protein products need to be transported to the right location in the cell for fulfilling their functions. The proteins need to be sent out of the cell sometimes. But proteins are not able to move independently and that’s why they are transported through carrier vesicles arranged by Golgi bodies.
Complete answer:

Fig: Structure and Location of Golgi Body in a Cell
The Golgi bodies aid in the translocation of vesicles to the final destination. They transport the materials to the destinations. The molecules are packaged in vesicles and the vesicles work like a shipping envelope for the cell.
The packaged vesicles move to the Golgi bodies. The Golgi bodies open the packages and modify the contents to their final forms and aid in the movement for their final destinations.
In a lot of ways, the Golgi bodies act as the shipping and receiving department of the cell. They package and sort the proteins and other biomolecules before they are sent to final destinations.
Assuming the cell as a city, the Golgi body acts as a post office. It is a stack of membranes, which package, sort, and deliver proteins to the region of the cell they require to go. The Golgi body is the post office of the cell as post offices pack, sort, and deliver mail similarly, Golgi bodies also work with proteins.
Note:
For survival, a cell has to make proteins, as proteins are essential for structure, movement, and energy production. The protein products need to be transported to the right location in the cell for fulfilling their functions. The proteins need to be sent out of the cell sometimes. But proteins are not able to move independently and that’s why they are transported through carrier vesicles arranged by Golgi bodies.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




