
A given object takes $n$ times as much time to slide down as ${{45}^{{}^\circ }}$ rough incline as it takes to slide down a perfectly smooth ${{45}^{{}^\circ }}$ incline. What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the object and the incline?
$\text{A}\text{. }\left( 1-\dfrac{1}{{{n}^{2}}} \right)$
$\text{B}\text{. }\dfrac{1}{1-{{n}^{2}}}$
$\text{C}\text{. }\sqrt{\left( 1-\dfrac{1}{{{n}^{2}}} \right)}$
$\text{D}\text{. }\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{1-{{n}^{2}}}}$
Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint: Kinetic friction is the force that acts on two surfaces when at least one of them is moving. The magnitude of this force depends on the coefficient of kinetic friction between the two materials. The coefficient of kinetic friction is the ratio of kinetic friction force and normal reaction force on the object.
Formula used:
Net force${{F}_{net}}=ma$
Displacement due to constant acceleration $s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}$
Complete step-by-step answer:
First, we assume that time taken by an object of mass $m$ to slide down on a smooth inclined plane is $t$ and a rough inclined plane is $t'$. Since the object takes $n$ times as much time to slide down rough incline as it takes to slide down a perfectly smooth incline, we have
$t'=nt$
Now we resolve the components acceleration in direction of motion and perpendicular to direction of motion.
For smooth incline, equation of motion:
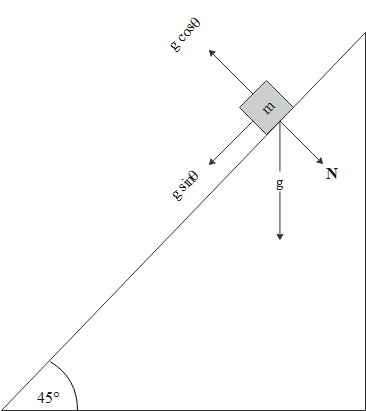
In direction perpendicular to direction of motion, the normal reaction $N$ when $\theta$ is the angle of inclination
$N=mg\cos \theta $
Along the direction of motion, net force ${{F}_{net}}$ when object accelerates with constant acceleration $a$
${{F}_{net}}=ma$
$mg\sin \theta =ma\Rightarrow a=g\sin \theta $
For rough incline, equation of motion:
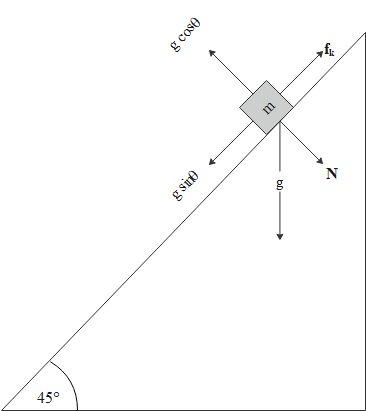
In direction perpendicular to direction of motion
$N=mg\cos \theta $
Along the direction of motion net force when object accelerates with acceleration $a'$ is
$F_{net}^{'}=ma'$
$mg\sin \theta -{{f}_{k}}=ma'$
Where kinetic friction ${{f}_{k}}=\mu N$
$\mu$ is the coefficient of kinetic friction.
$\Rightarrow {{f}_{k}}=\mu mg\cos \theta $
Therefore we get,
$a'=g(\sin \theta -\mu \cos \theta )$
Since distance travelled by object is same in both cases, we have
$s=s'$
$\left( g\sin \theta \right){{t}^{2}}=g(\sin \theta -\mu \cos \theta ){{(t')}^{2}}$
On simplifying this equation and substituting $t'=nt$ and $\theta=45^\circ$ we get
${{t}^{2}}=(1-\dfrac{\mu \cos {{45}^{{}^\circ }}}{\sin {{45}^{{}^\circ }}}){{(nt)}^{2}}$
On solving the above equation for coefficient of kinetic friction $\mu$ we get
$\mu =1-\dfrac{1}{{{n}^{2}}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Friction is a force that comes into play when two surfaces are in contact with each other when some force tries to move one body. Friction always opposes the motion of the body thus slowing it down.
Normal reaction force is the force exerted by a surface perpendicular to the surface of the object which is in contact with it.
Formula used:
Net force${{F}_{net}}=ma$
Displacement due to constant acceleration $s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}$
Complete step-by-step answer:
First, we assume that time taken by an object of mass $m$ to slide down on a smooth inclined plane is $t$ and a rough inclined plane is $t'$. Since the object takes $n$ times as much time to slide down rough incline as it takes to slide down a perfectly smooth incline, we have
$t'=nt$
Now we resolve the components acceleration in direction of motion and perpendicular to direction of motion.
For smooth incline, equation of motion:

In direction perpendicular to direction of motion, the normal reaction $N$ when $\theta$ is the angle of inclination
$N=mg\cos \theta $
Along the direction of motion, net force ${{F}_{net}}$ when object accelerates with constant acceleration $a$
${{F}_{net}}=ma$
$mg\sin \theta =ma\Rightarrow a=g\sin \theta $
For rough incline, equation of motion:

In direction perpendicular to direction of motion
$N=mg\cos \theta $
Along the direction of motion net force when object accelerates with acceleration $a'$ is
$F_{net}^{'}=ma'$
$mg\sin \theta -{{f}_{k}}=ma'$
Where kinetic friction ${{f}_{k}}=\mu N$
$\mu$ is the coefficient of kinetic friction.
$\Rightarrow {{f}_{k}}=\mu mg\cos \theta $
Therefore we get,
$a'=g(\sin \theta -\mu \cos \theta )$
Since distance travelled by object is same in both cases, we have
$s=s'$
$\left( g\sin \theta \right){{t}^{2}}=g(\sin \theta -\mu \cos \theta ){{(t')}^{2}}$
On simplifying this equation and substituting $t'=nt$ and $\theta=45^\circ$ we get
${{t}^{2}}=(1-\dfrac{\mu \cos {{45}^{{}^\circ }}}{\sin {{45}^{{}^\circ }}}){{(nt)}^{2}}$
On solving the above equation for coefficient of kinetic friction $\mu$ we get
$\mu =1-\dfrac{1}{{{n}^{2}}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Friction is a force that comes into play when two surfaces are in contact with each other when some force tries to move one body. Friction always opposes the motion of the body thus slowing it down.
Normal reaction force is the force exerted by a surface perpendicular to the surface of the object which is in contact with it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




