
What is a functional group? Give examples of four different functional groups.
Answer
564.6k+ views
Hint: Organic chemistry is the study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carbon-containing compounds which include not only hydrocarbons but also compounds with any number of other elements including hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, etc. In organic chemistry, functional groups are substituents in a molecule that impart certain characteristics to the molecule and are responsible for certain chemical reactions. Similar functional groups undergo the same type of reactions regardless of what molecule they are a part of and this helps us to predict the chemical reactions of a compound and design methods of chemical synthesis.
Complete step by step answer:
Functional Group-A functional group is a substituent group of atoms in a molecule that gives a distinct characteristic to it and gives the same chemical reactions independent of what molecule it is attached to.
Example of four different functional groups:
Hydroxyl group-This group contains oxygen and a hydrogen atom bonded together. The class of organic compounds that contain hydroxyl groups in it are termed as alcohols.
$R - OH$
Carbonyl group-This group contains a carbon atom bonded to an oxygen atom by a double bond. The compounds containing the carbonyl group can be aldehydes or ketones. If at least one substituent in the compound is hydrogen then it is an aldehydic group and if neither substituent is hydrogen then it is a ketonic group.
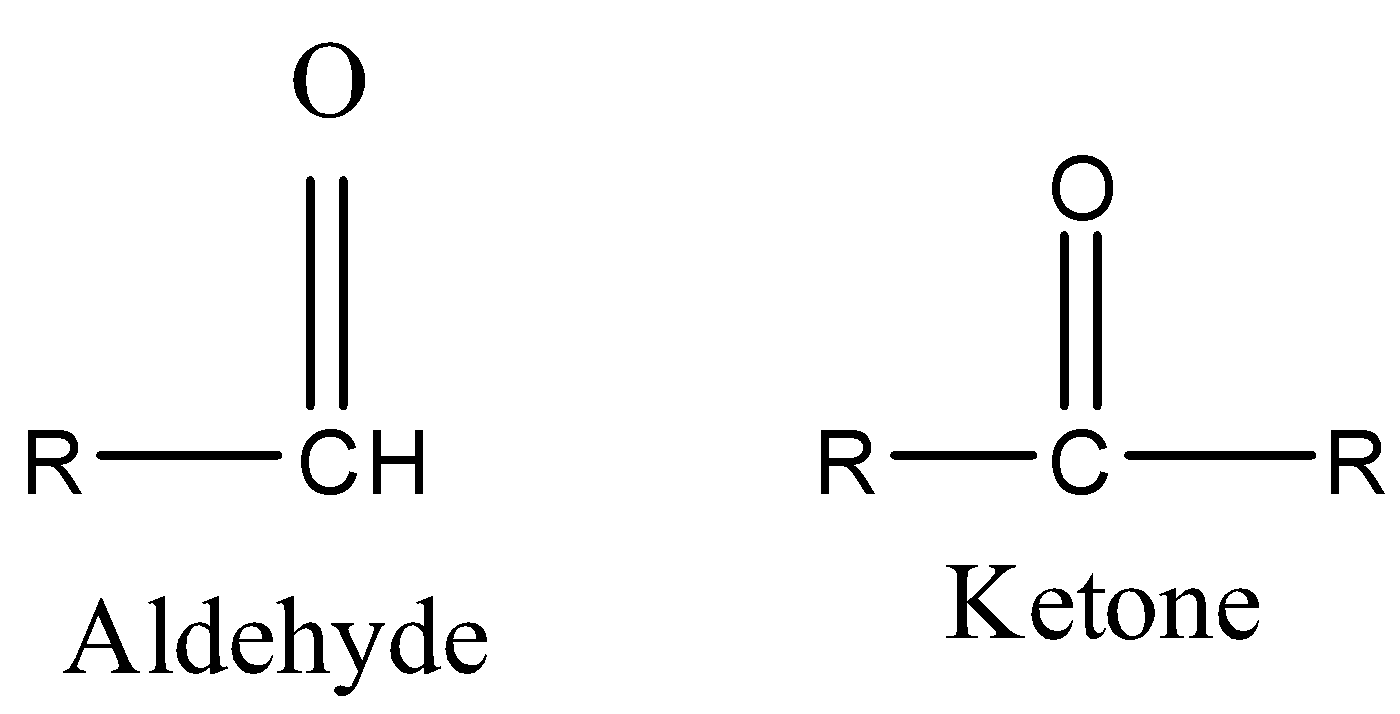
Amine group-An amine group is a derivative of ammonia in which one, two, or three hydrogen atoms are replaced by hydrocarbon groups. Amines are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary by the number of hydrocarbon groups attached to the nitrogen atom.
$R - N{H_2}$ (primary amine)
Carboxylic Acid group- It is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group attached to an R-group where R-group is an alkyl group.
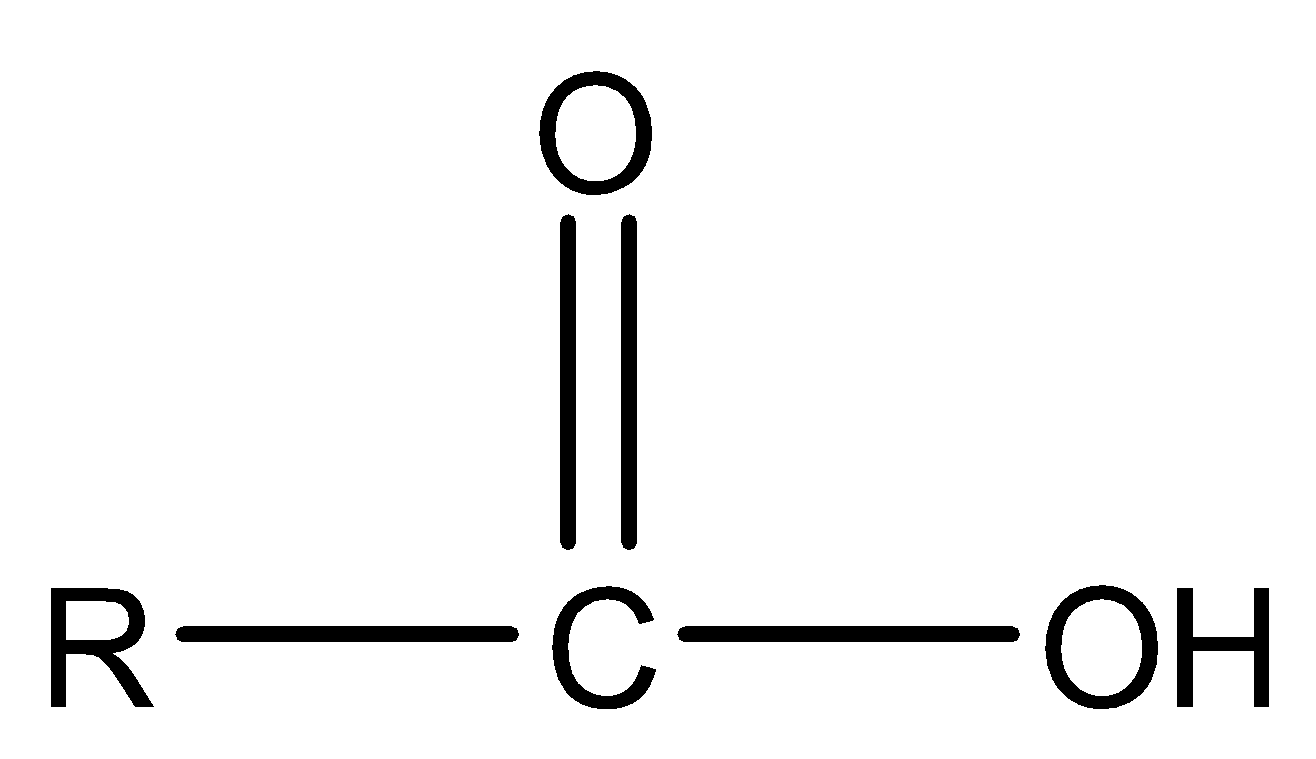
Note: Functional groups can always be interconverted into one another through different chemical reactions. Atoms of functional groups are linked to one another through covalent bonds. Functional group binding to a central atom in a coordination compound is called a ligand.
Complete step by step answer:
Functional Group-A functional group is a substituent group of atoms in a molecule that gives a distinct characteristic to it and gives the same chemical reactions independent of what molecule it is attached to.
Example of four different functional groups:
Hydroxyl group-This group contains oxygen and a hydrogen atom bonded together. The class of organic compounds that contain hydroxyl groups in it are termed as alcohols.
$R - OH$
Carbonyl group-This group contains a carbon atom bonded to an oxygen atom by a double bond. The compounds containing the carbonyl group can be aldehydes or ketones. If at least one substituent in the compound is hydrogen then it is an aldehydic group and if neither substituent is hydrogen then it is a ketonic group.

Amine group-An amine group is a derivative of ammonia in which one, two, or three hydrogen atoms are replaced by hydrocarbon groups. Amines are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary by the number of hydrocarbon groups attached to the nitrogen atom.
$R - N{H_2}$ (primary amine)
Carboxylic Acid group- It is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group attached to an R-group where R-group is an alkyl group.

Note: Functional groups can always be interconverted into one another through different chemical reactions. Atoms of functional groups are linked to one another through covalent bonds. Functional group binding to a central atom in a coordination compound is called a ligand.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




