
A functional aspect of an ecosystem is:
(a) Producer, consumers, and abiotic environment
(b) Regulation of population
(c) Light, temperature, oxygen and carbon dioxide
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: An ecosystem is primarily composed of two basic components that interact with each other. Both these components are interdependent on each other and reason for each other’s existence.
Complete answer:
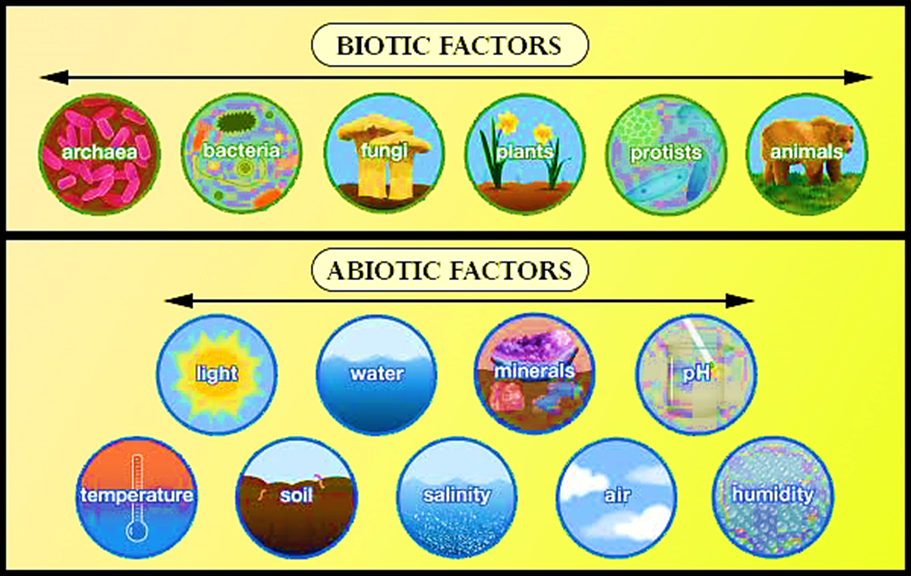
An ecosystem can be defined as a functional unit of nature, where interaction between living organisms takes place among themselves and also with the surrounding physical environment. Every ecosystem has nonliving or abiotic like temperature and living or biotic components like plants. The biotic components in an area are collectively referred to as a population. In a functional ecosystem, the population of an ecosystem is regulated through their interaction with the external factors or abiotic factors. The activities of a population, in turn, also affects its environment or abiotic components. Thus, a functional ecosystem regulates its environment efficiently.
Additional Information: Biotic components: They include autotrophs, heterotrophs, and decomposers. Autotrophs are the producers who can manufacture their food from simple inorganic substances by fixing energy. E.g. Green plants, algae, chemosynthetic bacteria, etc. Heterotrophs are the organisms that cannot synthesize the organic nutrients for themselves and thus depend on producers or other consumers for their survival.
Decomposers feed on dead organic matter.E.g. Fungi and bacteria.
Abiotic components: Temperature ranges in different parts of the earth. This has led to the presence of different climate zones such as tropical, subtropical, temperate, etc. Solar energy is an important source of light which provides heat as well the energy to the plants to carry out photosynthesis. Wind controls weather, transpiration, pollination, and dissemination of propagation. Humidity controls the formation of clouds, fog dew, etc. Precipitation may occur as rainfall, snow, dew which is again an important source of water refurbishing for groundwater, oceans in the water cycle.
So, the correct answer is ‘Regulation of population.’.’
Note: -Heterotrophs can be classified into herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, and detritivores based on their food source. Herbivores feed directly on producers. E.g. Cow. Carnivores feed on other animals. E.g Lion. Omnivores eat both plants and animals. E.g. Human beings. Detritivores eat detritus i.e. decomposing organic material. E.g. Earthworms.
-Both decomposers and detritivores derive nutrition from dead organic matter. The difference is that detritivores actually eat the organic matter but decomposers secrete enzymes for its breakdown and then absorb it.
Complete answer:
An ecosystem can be defined as a functional unit of nature, where interaction between living organisms takes place among themselves and also with the surrounding physical environment. Every ecosystem has nonliving or abiotic like temperature and living or biotic components like plants. The biotic components in an area are collectively referred to as a population. In a functional ecosystem, the population of an ecosystem is regulated through their interaction with the external factors or abiotic factors. The activities of a population, in turn, also affects its environment or abiotic components. Thus, a functional ecosystem regulates its environment efficiently.
Additional Information: Biotic components: They include autotrophs, heterotrophs, and decomposers. Autotrophs are the producers who can manufacture their food from simple inorganic substances by fixing energy. E.g. Green plants, algae, chemosynthetic bacteria, etc. Heterotrophs are the organisms that cannot synthesize the organic nutrients for themselves and thus depend on producers or other consumers for their survival.
Decomposers feed on dead organic matter.E.g. Fungi and bacteria.
Abiotic components: Temperature ranges in different parts of the earth. This has led to the presence of different climate zones such as tropical, subtropical, temperate, etc. Solar energy is an important source of light which provides heat as well the energy to the plants to carry out photosynthesis. Wind controls weather, transpiration, pollination, and dissemination of propagation. Humidity controls the formation of clouds, fog dew, etc. Precipitation may occur as rainfall, snow, dew which is again an important source of water refurbishing for groundwater, oceans in the water cycle.
So, the correct answer is ‘Regulation of population.’.’
Note: -Heterotrophs can be classified into herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, and detritivores based on their food source. Herbivores feed directly on producers. E.g. Cow. Carnivores feed on other animals. E.g Lion. Omnivores eat both plants and animals. E.g. Human beings. Detritivores eat detritus i.e. decomposing organic material. E.g. Earthworms.
-Both decomposers and detritivores derive nutrition from dead organic matter. The difference is that detritivores actually eat the organic matter but decomposers secrete enzymes for its breakdown and then absorb it.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




