
A frictionless track ABCD ends in a circular loop of radius 2 cm. A body slides down the track from point A which is at height h. The minimum value of h for a body to complete one loop is,
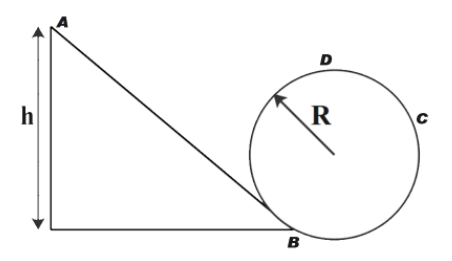
A. 3 cm
B. 5 cm
C. 10/3 cm
D. 4 cm

Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: In this question we have been asked to calculate the height required for a body to complete one loop of radius 2 cm. Now, we know that the energy will be conserved for the body at two points. Therefore, we shall be using the energy conversion formula to calculate the height required. We know that potential energy at the datum plane is zero and the final kinetic energy is zero.
Complete answer:
To calculate the velocity required for a body to complete one loop, consider the circle with radius R, having a body with mass m on its circumference as shown.
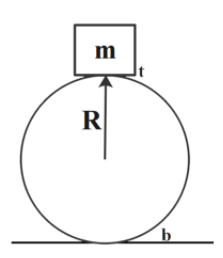
Now, from energy conservation between the top point and the bottom point
We get,
\[{{(PE+KE)}_{t}}=K{{E}_{b}}\] …………… (since the potential at datum is zero)
\[2mgr+\dfrac{1}{2}mgr=\dfrac{1}{2}{{v}^{2}}\]
Here v is the velocity required to complete one loop from the bottom point
Therefore,
\[v=\sqrt{5gr}\] …………… (1)
Now, applying the energy conservation for given condition,
We get,
\[mgh=\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}\]
Therefore,
\[v=\sqrt{2gh}\] …………….. (2)
Now, from (1) and (2)
We get,
\[\sqrt{5gr}=\sqrt{2gh}\]
It is given that radius r of the circular track is 2 cm
Therefore, on solving
We get,
\[h=5cm\]
Therefore, the correct answer is option B.
Note: Potential energy is the amount of energy stored in an object due to change in its vertical position. The potential energy is passive energy which has the potential to do work. The energy that a body possesses due to its motion is known as kinetic energy. The kinetic energy of the object depends on the velocity and mass of the object.
Complete answer:
To calculate the velocity required for a body to complete one loop, consider the circle with radius R, having a body with mass m on its circumference as shown.

Now, from energy conservation between the top point and the bottom point
We get,
\[{{(PE+KE)}_{t}}=K{{E}_{b}}\] …………… (since the potential at datum is zero)
\[2mgr+\dfrac{1}{2}mgr=\dfrac{1}{2}{{v}^{2}}\]
Here v is the velocity required to complete one loop from the bottom point
Therefore,
\[v=\sqrt{5gr}\] …………… (1)
Now, applying the energy conservation for given condition,
We get,
\[mgh=\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}\]
Therefore,
\[v=\sqrt{2gh}\] …………….. (2)
Now, from (1) and (2)
We get,
\[\sqrt{5gr}=\sqrt{2gh}\]
It is given that radius r of the circular track is 2 cm
Therefore, on solving
We get,
\[h=5cm\]
Therefore, the correct answer is option B.
Note: Potential energy is the amount of energy stored in an object due to change in its vertical position. The potential energy is passive energy which has the potential to do work. The energy that a body possesses due to its motion is known as kinetic energy. The kinetic energy of the object depends on the velocity and mass of the object.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




