
A frictionless cart of mass M carries two other frictionless carts having masses $m_1\ and \ m_2$ connected by a string passing over a pulley as shown in figure. The horizontal force that must be applied on M so that $m_1\ and \ m_2$do not move relative to it will be:
$\text A. \quad (M+m_1+m_2)(m_2/m_1)g$
$\text B. \quad (M+m_1+m_2)(m_1/m_2)g$
$\text C. \quad (M+m_1)(m_2/m_1)g$
$\text D. \quad (M+m_2)(m_2/m_1)g$
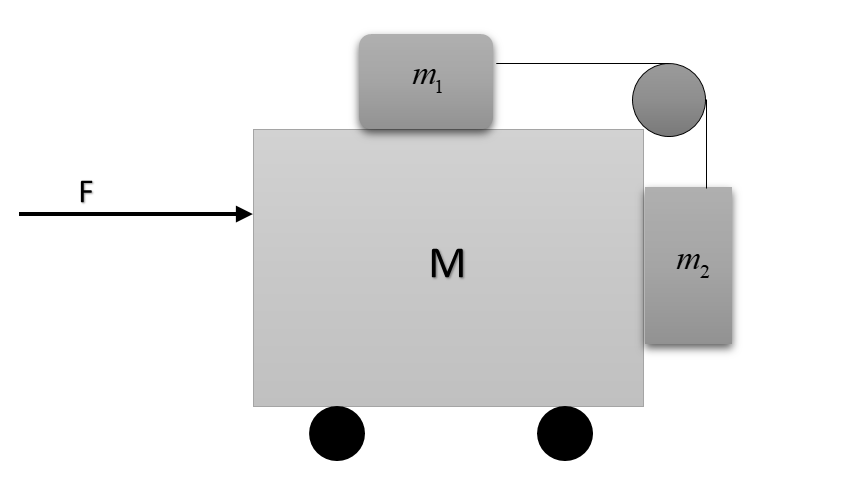

Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: The limitation of Newton's laws of motion is that they are valid only for inertial frames of reference. These are not valid for frame moving with some acceleration. Hence, to apply these laws, physicists suggested that we must apply an imaginary force on the system called a pseudo force which will act on the centre of mass of the body and has direction opposite to the motion of the frame.
Formula used: F = ma
Complete step by step answer:
The first and foremost thing is to draw the free body diagram of the system.
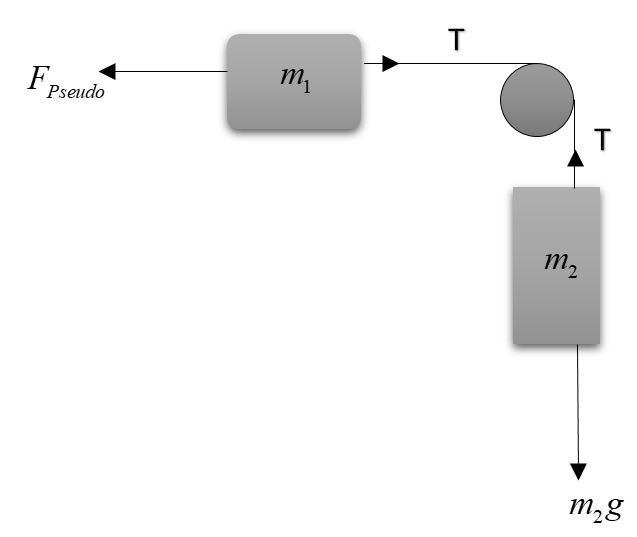
Here, we’ve shown only the important forces that will take us to the final result.
Concept used – We just have to reach that value so that the pseudo force on $m_1$ balances the weight of $m_2$.
Now, using ‘F’, we can write the equation as $F = m_T a$, where $m_T$ is the total mass of the system.
Thus, $F = (M+m_1 +m_2)a$
$\implies a = \dfrac{F}{M+m_1+m_2}$
Now, pseudo force acting of upper block will be:
$F_{Pseudo} = m_1 a = \dfrac{m_1 F}{M+m_1+m_2}$
This should balance the weight of $m_2$, hence:
$m_2 g = \dfrac{m_1 F}{M+m_1+m_2}$
$\implies F = (M+m_1+m_2)(m_2 /m_1) g$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: It must be noted that we’ve taken only contributing forces while making free body diagrams as showing all forces will create unnecessary calculations and confusions. On both the blocks, the weight is acting. But we’ve shown only the weight of $m_2$ as only it will contribute to the motion of blocks. Similarly pseudo force is acting on both the blocks, but we’ve shown it only for the upper block. In case friction, we have to take each and every force including normal reactions, contact forces, etc. and then analyze the situation properly.
Formula used: F = ma
Complete step by step answer:
The first and foremost thing is to draw the free body diagram of the system.

Here, we’ve shown only the important forces that will take us to the final result.
Concept used – We just have to reach that value so that the pseudo force on $m_1$ balances the weight of $m_2$.
Now, using ‘F’, we can write the equation as $F = m_T a$, where $m_T$ is the total mass of the system.
Thus, $F = (M+m_1 +m_2)a$
$\implies a = \dfrac{F}{M+m_1+m_2}$
Now, pseudo force acting of upper block will be:
$F_{Pseudo} = m_1 a = \dfrac{m_1 F}{M+m_1+m_2}$
This should balance the weight of $m_2$, hence:
$m_2 g = \dfrac{m_1 F}{M+m_1+m_2}$
$\implies F = (M+m_1+m_2)(m_2 /m_1) g$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: It must be noted that we’ve taken only contributing forces while making free body diagrams as showing all forces will create unnecessary calculations and confusions. On both the blocks, the weight is acting. But we’ve shown only the weight of $m_2$ as only it will contribute to the motion of blocks. Similarly pseudo force is acting on both the blocks, but we’ve shown it only for the upper block. In case friction, we have to take each and every force including normal reactions, contact forces, etc. and then analyze the situation properly.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




