
A force $F=k{{x}^{2}}$ acts on a particle at an angle of ${{60}^{\circ }}$ with the X-axis the work done in displacing the particle from ${{X}_{1}}$ to ${{X}_{2}}$will be-
Answer
559.5k+ views
Hint: given force is given by $F=k{{x}^{2}}$ so we can see that force is variable in terms of displacement of a particle so we need to integrate F over a small section of displacement dx from ${{X}_{1}}$ to ${{X}_{2}}$ to calculate total work done.
Formula used:
$W=\int_{{{x}_{1}}}^{{{x}_{2}}}{F.ds}$
Complete Step by step solution:
In the question the force is acting on the particle with an angle of ${{60}^{\circ }}$ so we have to its horizontal component by which particle is moving towards X-axis and it is given by,
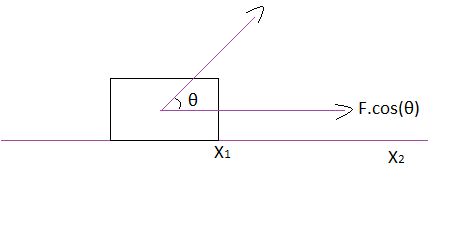
Given,$F=k{{x}^{2}}^{{}}$
Now total horizontal component of force is given by,
${{F}_{H}}=F\cdot \cos (\theta )=k{{x}^{2}}\cdot \cos ({{60}^{\circ }})=\dfrac{1}{2}k{{x}^{2}}$
$\cos ({{60}^{\circ }})=\dfrac{1}{2}$|
Now, work done = $\int\limits_{{{X}_{1}}}^{{{X}_{2}}}{{{F}_{H}}\cdot dx}=\dfrac{1}{2}\int\limits_{{{X}_{1}}}^{{{X}_{2}}}{k{{x}^{2}}\cdot dx}$, from the above comment $\cos ({{60}^{\circ }})=\dfrac{1}{2}$,
since integration of ${{x}^{2}}$ is given by$\int{{{x}^{2}}.dx=\dfrac{{{x}^{3}}}{3}}$|
Now by putting limit form ${{X}_{1}}$to${{X}_{2}}$
$\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ \dfrac{k{{x}^{3}}}{3} \right]\begin{matrix}
{{X}_{2}} \\
{{X}_{1}} \\
\end{matrix}=\dfrac{k}{6}\left[ {{X}_{2}}^{3}-{{X}_{1}}^{3} \right]$
So, $W=\dfrac{k}{6}\left[ {{X}_{2}}^{3}-{{X}_{1}}^{3} \right]$
So to displace an object from ${{X}_{1}}$to${{X}_{2}}$ work done will be equal to,
$W=\dfrac{k}{6}\left[ {{X}_{2}}^{3}-{{X}_{1}}^{3} \right]$.M
Additional information:
we solved this question by assuming our surface is smooth and there are no external resistance or frictional forces are there to oppose the motion of an object.
Work done is a scalar quantity, which means that it has no direction associated with it and only magnitude. Hence Work done is a quantity achieved by the dot product.
Note:
Work done is defined as a product of component of force in the direction of displacement and total displacement of a body, and dimension is same as the energy and is given by $\left[ M{{L}^{2}}{{T}^{-2}} \right]$ and the SI unit of work is joule which is defined as a work done by a force of 1 newton to displace an object by 1 metre in the direction of force.
Formula used:
$W=\int_{{{x}_{1}}}^{{{x}_{2}}}{F.ds}$
Complete Step by step solution:
In the question the force is acting on the particle with an angle of ${{60}^{\circ }}$ so we have to its horizontal component by which particle is moving towards X-axis and it is given by,

Given,$F=k{{x}^{2}}^{{}}$
Now total horizontal component of force is given by,
${{F}_{H}}=F\cdot \cos (\theta )=k{{x}^{2}}\cdot \cos ({{60}^{\circ }})=\dfrac{1}{2}k{{x}^{2}}$
$\cos ({{60}^{\circ }})=\dfrac{1}{2}$|
Now, work done = $\int\limits_{{{X}_{1}}}^{{{X}_{2}}}{{{F}_{H}}\cdot dx}=\dfrac{1}{2}\int\limits_{{{X}_{1}}}^{{{X}_{2}}}{k{{x}^{2}}\cdot dx}$, from the above comment $\cos ({{60}^{\circ }})=\dfrac{1}{2}$,
since integration of ${{x}^{2}}$ is given by$\int{{{x}^{2}}.dx=\dfrac{{{x}^{3}}}{3}}$|
Now by putting limit form ${{X}_{1}}$to${{X}_{2}}$
$\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ \dfrac{k{{x}^{3}}}{3} \right]\begin{matrix}
{{X}_{2}} \\
{{X}_{1}} \\
\end{matrix}=\dfrac{k}{6}\left[ {{X}_{2}}^{3}-{{X}_{1}}^{3} \right]$
So, $W=\dfrac{k}{6}\left[ {{X}_{2}}^{3}-{{X}_{1}}^{3} \right]$
So to displace an object from ${{X}_{1}}$to${{X}_{2}}$ work done will be equal to,
$W=\dfrac{k}{6}\left[ {{X}_{2}}^{3}-{{X}_{1}}^{3} \right]$.M
Additional information:
we solved this question by assuming our surface is smooth and there are no external resistance or frictional forces are there to oppose the motion of an object.
Work done is a scalar quantity, which means that it has no direction associated with it and only magnitude. Hence Work done is a quantity achieved by the dot product.
Note:
Work done is defined as a product of component of force in the direction of displacement and total displacement of a body, and dimension is same as the energy and is given by $\left[ M{{L}^{2}}{{T}^{-2}} \right]$ and the SI unit of work is joule which is defined as a work done by a force of 1 newton to displace an object by 1 metre in the direction of force.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




