
A food chain consists of
A. Producers
B. Consumers
C. Decomposers
D. Producers and consumers
Answer
577.2k+ views
Hint: Food chain, in nature, the cycle of transferring matter and energy in the form of food from the species to the species. Food chains are locally entangled in a food web since most species eat more than one form of animal or plant.
Complete answer:
Chain species are categorised into these levels on the basis of their feeding behaviour. The first and the lowest level are the producers, the green trees. Plants or their products are eaten by second-level organisms — herbivores or plant eaters. At the level 3, primary carnivores or meat eaters consume herbivores; at the 4th level, secondary carnivores consume primary carnivores. These types are not specifically defined, since several species eat on many trophic levels; for eg, some carnivores often consume plant material or carrion and are considered omnivores, and some herbivores sometimes consume animal matter. A separate trophic stage, decomposers or transformers, comprises organisms like bacteria and fungi that break down dead organisms and waste materials into nutrients that can be used by producers.
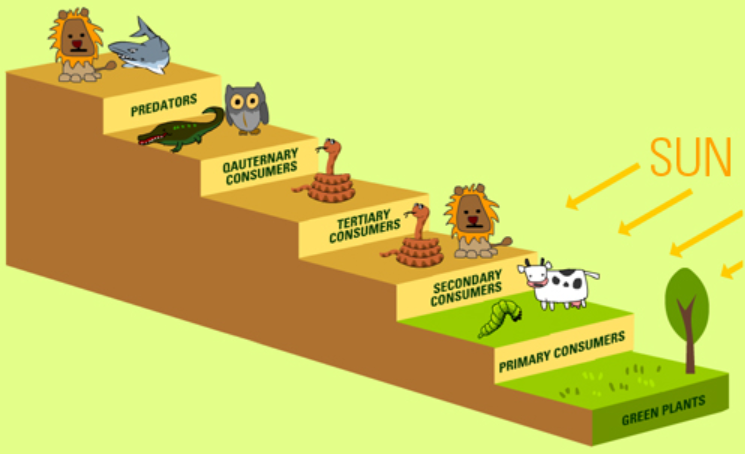
Fig: Food chain from lower level to higher level.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Additional Information: Food chains give an accurate picture about who eats whom. However, certain issues occur when we try to use them to characterise the entire ecological community. For example, an organism may often consume multiple types of prey or consume multiple predators, even those at different trophic levels. To better represent these relationships, we can also use a food web, a chart that indicates all the trophic — eating-related — interactions between different species in an ecosystem.
Note:
The main additional advantage of the food chain is it is simple and straightforward. It shows what organisms eat and what energy flows between them. It is very simple and generally only 3-4 chains long. But, with regard to the food web, which shows the collection of food chains connected together, therefore gives a broader and more complete picture of the feeding relationship among organisms.
Complete answer:
Chain species are categorised into these levels on the basis of their feeding behaviour. The first and the lowest level are the producers, the green trees. Plants or their products are eaten by second-level organisms — herbivores or plant eaters. At the level 3, primary carnivores or meat eaters consume herbivores; at the 4th level, secondary carnivores consume primary carnivores. These types are not specifically defined, since several species eat on many trophic levels; for eg, some carnivores often consume plant material or carrion and are considered omnivores, and some herbivores sometimes consume animal matter. A separate trophic stage, decomposers or transformers, comprises organisms like bacteria and fungi that break down dead organisms and waste materials into nutrients that can be used by producers.

Fig: Food chain from lower level to higher level.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Additional Information: Food chains give an accurate picture about who eats whom. However, certain issues occur when we try to use them to characterise the entire ecological community. For example, an organism may often consume multiple types of prey or consume multiple predators, even those at different trophic levels. To better represent these relationships, we can also use a food web, a chart that indicates all the trophic — eating-related — interactions between different species in an ecosystem.
Note:
The main additional advantage of the food chain is it is simple and straightforward. It shows what organisms eat and what energy flows between them. It is very simple and generally only 3-4 chains long. But, with regard to the food web, which shows the collection of food chains connected together, therefore gives a broader and more complete picture of the feeding relationship among organisms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




