
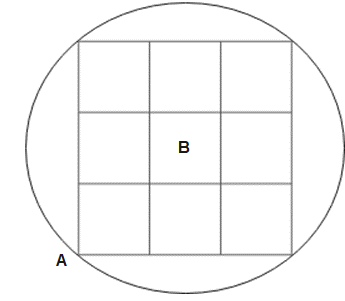
A finite square grid, each link having resistance $r$, is fitted in a resistance-less conducting circular wire. Determine the equivalent resistance between $\mathrm{A}$ and $\mathrm{B}$ (in $\Omega$ ) if $\text{r}=(\dfrac{80}{7})\Omega $

Answer
555k+ views
Hint: The equivalent resistance is where either parallel or series-connected aggregate resistance is calculated. Basically, either in series or parallel, the circuit is designed. When you move the charges/current through your devices, electrical resistance shows how much energy one needs. Calculate The resultant resistance between A to B.
Complete answer:
For each type of circuit, the method we use for calculating equivalent resistance is different. For a series circuit, the resistances of each element are simply added up. However, in a parallel circuit, the total reciprocal resistance is equal to the sum of each branch's reciprocal resistance. Basically, either in series or parallel, the circuit is designed. When you move the charges/current through your devices, electrical resistance shows how much energy one needs.
If we connect battery between $\mathrm{A}$ and $\mathrm{B}$, then different points will be at the same potentials. $(1,2,3,4),(5,6,7,8),(9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16),$ and (17,18,19,20)
The resulting circuit can be:
${{\text{R}}_{\text{AB}}}=\dfrac{21}{40}\text{r}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{R}}_{\text{AB}}}=\dfrac{21}{40}\times \dfrac{80}{7}$
$\therefore {{\text{R}}_{\text{AB}}}=6\Omega $
The equivalent resistance between $\mathrm{A}$ and $\mathrm{B}$ is $6\Omega $
Note:
The equivalent resistance is where either parallel or series-connected aggregate resistance is calculated. Basically, either in series or parallel, the circuit is designed. As used in electrical circuits, practical capacitors and inductors are not ideal components with only capacitance or inductance. Equivalent resistance is a purely resistive property that changes with no other variable. An additional name given to the impedance is effective resistance. A set of resistors or components that only have resistance is defined as equivalent resistance.
Complete answer:
For each type of circuit, the method we use for calculating equivalent resistance is different. For a series circuit, the resistances of each element are simply added up. However, in a parallel circuit, the total reciprocal resistance is equal to the sum of each branch's reciprocal resistance. Basically, either in series or parallel, the circuit is designed. When you move the charges/current through your devices, electrical resistance shows how much energy one needs.
If we connect battery between $\mathrm{A}$ and $\mathrm{B}$, then different points will be at the same potentials. $(1,2,3,4),(5,6,7,8),(9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16),$ and (17,18,19,20)
The resulting circuit can be:
${{\text{R}}_{\text{AB}}}=\dfrac{21}{40}\text{r}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{R}}_{\text{AB}}}=\dfrac{21}{40}\times \dfrac{80}{7}$
$\therefore {{\text{R}}_{\text{AB}}}=6\Omega $
The equivalent resistance between $\mathrm{A}$ and $\mathrm{B}$ is $6\Omega $
Note:
The equivalent resistance is where either parallel or series-connected aggregate resistance is calculated. Basically, either in series or parallel, the circuit is designed. As used in electrical circuits, practical capacitors and inductors are not ideal components with only capacitance or inductance. Equivalent resistance is a purely resistive property that changes with no other variable. An additional name given to the impedance is effective resistance. A set of resistors or components that only have resistance is defined as equivalent resistance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




