
A ferromagnetic material heated above its Curie temperature. Which one is the correct statement?
A. Ferromagnetic domains are perfectly arranged
B. Ferromagnetic domains become random
C. Ferromagnetic domains are not influenced
D. Ferromagnetic material changes into diamagnetic material
Answer
599.7k+ views
Hint: When we heat some element, molecules inside it get thermal energy and start to move here and there. This same thing happens with magnetic materials too, increasing the temperature makes the domains inside it chaotic, which reduces the magnetic strength.
Complete step by step answer:
To know the effect of temperature on ferromagnetic material we have to know what ferromagnetic materials are.
Ferromagnetic Material: Ferromagnetic materials are those which get strongly magnetised when placed in an external magnetic field. They have a strong tendency to move from weak magnetic field to strong magnetic field.
In simple language, these types of material get strongly attracted to a magnet.
Examples of ferromagnetic materials are: Iron, Cobalt, nickel, gadolinium, etc.
Let us see the structure of ferromagnetic material,
Individual atoms (or ions or molecules) in a ferromagnetic material possess a dipole moment. However these atoms arranged themselves in a common direction over a macroscopic volume called domains. When we place ferromagnetic materials in the external magnetic field. The domain gets aligned in the direction of the magnetic field. And when we remove the external magnetic field, the domains are still aligned in the same direction. This is only observed under a microscope.
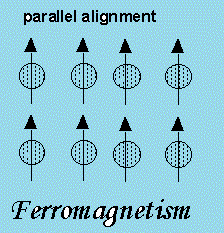
Effect of temperature on ferromagnetic material
The ferromagnetic material depends on temperature. At high temperature, a ferromagnetic material becomes paramagnetic material. The domain structure disintegrates with temperature.
The temperature of transition from ferromagnetic material to paramagnetic material is known as Curie temperature ${{T}_{c}}$ .
Answer is option B. Ferromagnetic domains become random.
Additional Information:
Curie temperature of some ferromagnetic materials are below, so that you get an Idea of Curie temperature.
Cobalt - 1394 K
Iron - 1043 K
Nickel – 631 K
Note: There is a term magnetic susceptibility which shows how easily the substance can get magnetised when placed in the magnetising field. Therefore when the temperature gradually increases then its magnetic susceptibility decreases and at a stage the substance changes into paramagnetic.
Complete step by step answer:
To know the effect of temperature on ferromagnetic material we have to know what ferromagnetic materials are.
Ferromagnetic Material: Ferromagnetic materials are those which get strongly magnetised when placed in an external magnetic field. They have a strong tendency to move from weak magnetic field to strong magnetic field.
In simple language, these types of material get strongly attracted to a magnet.
Examples of ferromagnetic materials are: Iron, Cobalt, nickel, gadolinium, etc.
Let us see the structure of ferromagnetic material,
Individual atoms (or ions or molecules) in a ferromagnetic material possess a dipole moment. However these atoms arranged themselves in a common direction over a macroscopic volume called domains. When we place ferromagnetic materials in the external magnetic field. The domain gets aligned in the direction of the magnetic field. And when we remove the external magnetic field, the domains are still aligned in the same direction. This is only observed under a microscope.

Effect of temperature on ferromagnetic material
The ferromagnetic material depends on temperature. At high temperature, a ferromagnetic material becomes paramagnetic material. The domain structure disintegrates with temperature.
The temperature of transition from ferromagnetic material to paramagnetic material is known as Curie temperature ${{T}_{c}}$ .
Answer is option B. Ferromagnetic domains become random.
Additional Information:
Curie temperature of some ferromagnetic materials are below, so that you get an Idea of Curie temperature.
Cobalt - 1394 K
Iron - 1043 K
Nickel – 631 K
Note: There is a term magnetic susceptibility which shows how easily the substance can get magnetised when placed in the magnetising field. Therefore when the temperature gradually increases then its magnetic susceptibility decreases and at a stage the substance changes into paramagnetic.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




