
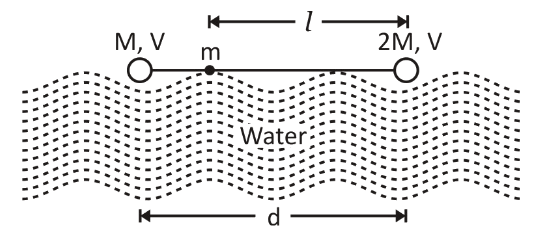
A dumbbell is placed in water of density \[\rho \]. It is observed that by attaching a mass \[m\] to the rod, the dumbbell floats with the rod horizontal on the surface of water and each sphere exactly half submerged as shown in the figure. The volume of the mass \[m\] is negligible. The value of length \[l\] is:
A. \[\dfrac{{d\left( {V\rho - 3m} \right)}}{{2\left( {V\rho - 2m} \right)}}\]
B. \[\dfrac{{d\left( {V\rho - 2m} \right)}}{{2\left( {V\rho - 3m} \right)}}\]
C. \[\dfrac{{d\left( {V\rho + 2m} \right)}}{{2\left( {V\rho - 3m} \right)}}\]
D. \[\dfrac{{d\left( {V\rho - 2m} \right)}}{{2\left( {V\rho + 2m} \right)}}\]

Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint:A body remains in equilibrium; its net upward force is equal to the net downward force acting on the body. To prevent curvilinear motion, the net torque about a point must be equal to zero.
Formula used:
Net upward force is given by the formula:
\[{F_{\text{u}}} = V \times \rho \times g\] …… (1)
Where,
\[{F_{\text{u}}}\] indicates the net upward force.
\[V\] indicates the volume submerged.
\[\rho \] indicates the density of the liquid.
\[g\] indicates acceleration due to gravity.
Net downward force is given by:
\[{F_{\text{d}}} = m \times g\] …… (2)
\[{F_{\text{d}}}\] indicates the net downward force.
\[m\] indicates the mass of the whole system.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given question, we are supplied with the following data:
There is a dumbbell which is placed in water of density \[\rho \].When we attach a mass \[m\] to the rod, the dumbbell floats with the rod horizontal on the surface of water and each sphere exactly half submerged. We are asked to assume that the volume of the mass \[m\] is negligible. We are asked to find out the length \[l\].
To begin with, we will first have to analyse the situation, as given in the diagram. It can be observed that the whole system is in equilibrium. It can be said that to maintain the position of equilibrium, the net upward force is equal to the net downward force. The dumbbells are half submerged. So, we can write:
$\left( {m + M + 2M} \right) \times g = \dfrac{V}{2}\rho g + \dfrac{V}{2}\rho g \\
\Rightarrow \left( {m + 3M} \right) \times g = V\rho g \\$
\[ \Rightarrow m + 3M = V\rho \] …… (3)
If the dumbbell needs to float, then the torque acting about the mass \[2M\] must be equal to zero. So, the two torque about that mass will be equal to one another. So, we can write the torque equation as:
$mgl = \left( {\dfrac{V}{2}\rho g - Mg} \right)d \\
\Rightarrow ml = \left( {\dfrac{V}{2}\rho - M} \right)d \\
\Rightarrow l = \dfrac{1}{m}\left( {\dfrac{V}{2}\rho - \dfrac{{V\rho - m}}{3}} \right)d \\
\therefore l = \dfrac{{d\left( {V\rho - 2m} \right)}}{{2\left( {V\rho - 3m} \right)}} \\$
Hence, the length is \[\dfrac{{d\left( {V\rho - 2m} \right)}}{{2\left( {V\rho - 3m} \right)}}\].
The correct option is B.
Note:While solving this problem, most of the students don’t really think about the torque. It is the torque, which is associated with a rotating body, under the application of opposite forces. A body undergoing a curvilinear motion can’t have torque equal to zero. Again, in the case of net upward force, the volume must be taken as half, as it is half submerged. But most of the students go wrong at this point.
Formula used:
Net upward force is given by the formula:
\[{F_{\text{u}}} = V \times \rho \times g\] …… (1)
Where,
\[{F_{\text{u}}}\] indicates the net upward force.
\[V\] indicates the volume submerged.
\[\rho \] indicates the density of the liquid.
\[g\] indicates acceleration due to gravity.
Net downward force is given by:
\[{F_{\text{d}}} = m \times g\] …… (2)
\[{F_{\text{d}}}\] indicates the net downward force.
\[m\] indicates the mass of the whole system.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given question, we are supplied with the following data:
There is a dumbbell which is placed in water of density \[\rho \].When we attach a mass \[m\] to the rod, the dumbbell floats with the rod horizontal on the surface of water and each sphere exactly half submerged. We are asked to assume that the volume of the mass \[m\] is negligible. We are asked to find out the length \[l\].
To begin with, we will first have to analyse the situation, as given in the diagram. It can be observed that the whole system is in equilibrium. It can be said that to maintain the position of equilibrium, the net upward force is equal to the net downward force. The dumbbells are half submerged. So, we can write:
$\left( {m + M + 2M} \right) \times g = \dfrac{V}{2}\rho g + \dfrac{V}{2}\rho g \\
\Rightarrow \left( {m + 3M} \right) \times g = V\rho g \\$
\[ \Rightarrow m + 3M = V\rho \] …… (3)
If the dumbbell needs to float, then the torque acting about the mass \[2M\] must be equal to zero. So, the two torque about that mass will be equal to one another. So, we can write the torque equation as:
$mgl = \left( {\dfrac{V}{2}\rho g - Mg} \right)d \\
\Rightarrow ml = \left( {\dfrac{V}{2}\rho - M} \right)d \\
\Rightarrow l = \dfrac{1}{m}\left( {\dfrac{V}{2}\rho - \dfrac{{V\rho - m}}{3}} \right)d \\
\therefore l = \dfrac{{d\left( {V\rho - 2m} \right)}}{{2\left( {V\rho - 3m} \right)}} \\$
Hence, the length is \[\dfrac{{d\left( {V\rho - 2m} \right)}}{{2\left( {V\rho - 3m} \right)}}\].
The correct option is B.
Note:While solving this problem, most of the students don’t really think about the torque. It is the torque, which is associated with a rotating body, under the application of opposite forces. A body undergoing a curvilinear motion can’t have torque equal to zero. Again, in the case of net upward force, the volume must be taken as half, as it is half submerged. But most of the students go wrong at this point.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




