
A drum placed on the floor is filled with a liquid of almost no viscosity to a height H. A small opening is made at a height h from the base. The liquid jet strikes the floor at a distance x from the wall of the drum then maximum value of x is:
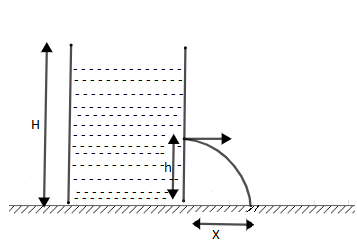
$\begin{align}
& A.\text{ }\dfrac{1}{2}\left( H-h \right) \\
& B.\text{ }H \\
& C.\text{ }\dfrac{1}{2}\left( H+h \right) \\
& D.\text{ }\dfrac{hH}{x+h} \\
\end{align}$

Answer
564.6k+ views
Hint: In order to find a solution to this question we will use ton celli’s theorem, by using the formula of celli’s theorem we will find velocity and then we put this value of velocity in the equation of the motion to find the distance x.
Formula used:
$v=\sqrt{2gh}$
$s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}$
Complete step by step solution:
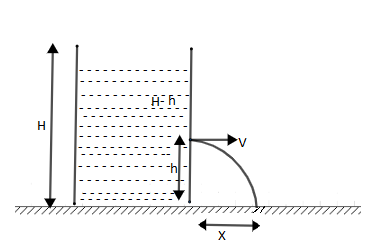
Now first we will find velocity using ton celli’s theorem which is given by
$\Rightarrow v=\sqrt{2gh}.....\left( 1 \right)$
Where, v = velocity
g = acceleration of the gravity
h = height of the water above the hole.
Here h is height of the water above the hole which (H-h) now substitute value of h in equation (1) we get,
$\Rightarrow v=\sqrt{2g\left( H-h \right)}....(2)$
Now velocity also given by,
$velocity\left( v \right)=\dfrac{displacement(x)}{time\left( t \right)}$
Time (t) will be
$t=\dfrac{x}{v}....\left( 3 \right)$
Here we can apply the equation of motion for water flowing outside in downwards direction.
$s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}$
Where, s = distance
u = initial velocity
a = acceleration
t = time
Here s = h
Initial velocity will be zero and “a” will be the acceleration at gravity g, therefore our new equation will be,
$h=\left( 0 \right)\times t\dfrac{1}{2}g{{t}^{2}}....\left( 4 \right)$
Now substitute value of equation (3) in equation (4)
$h=0+\dfrac{1}{2}g\times {{\left( \dfrac{x}{v} \right)}^{2}}$
Now substitute the value of v from the equation (1)
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow h=\dfrac{1}{2}\times g\times \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{\left( \sqrt{2g\left( H-h \right)} \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow h=\dfrac{g}{2}\times \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{2g\left( H-h \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}=2\times 2.h\left( H-h \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}=4Hh-4{{h}^{2}} \\
& \therefore x=\sqrt{4Hh-4{{h}^{2}}}.....\left( 5 \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Now to find the ${{x}_{\max }}$ we differentiate ${{x}^{2}}$ with respect to h and we will equalize with the zero.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{d\left( x_{\max }^{2} \right)}{dh}=4H-8h=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 8h=4H \\
& \therefore h=\dfrac{H}{2}......\left( 6 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now we will put the value of equation (6) into equation (5)
$\Rightarrow {{x}_{\max }}=\sqrt{4H\left( \dfrac{H}{2} \right)-4{{\left( \dfrac{H}{2} \right)}^{2}}}$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{\max }}=\sqrt{2{{H}^{2}}-{{H}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{\max }}=\sqrt{{{H}^{2}}} \\
& \therefore {{x}_{\max }}=H \\
\end{align}$
Hence, option (2) H is correct.
Note:
When we want to find the maximum distance x we have to equalize with by differentiating with respect to height h. Which is shown in the solution if we skip this step it will lead us to the wrong answer.
Formula used:
$v=\sqrt{2gh}$
$s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}$
Complete step by step solution:

Now first we will find velocity using ton celli’s theorem which is given by
$\Rightarrow v=\sqrt{2gh}.....\left( 1 \right)$
Where, v = velocity
g = acceleration of the gravity
h = height of the water above the hole.
Here h is height of the water above the hole which (H-h) now substitute value of h in equation (1) we get,
$\Rightarrow v=\sqrt{2g\left( H-h \right)}....(2)$
Now velocity also given by,
$velocity\left( v \right)=\dfrac{displacement(x)}{time\left( t \right)}$
Time (t) will be
$t=\dfrac{x}{v}....\left( 3 \right)$
Here we can apply the equation of motion for water flowing outside in downwards direction.
$s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}$
Where, s = distance
u = initial velocity
a = acceleration
t = time
Here s = h
Initial velocity will be zero and “a” will be the acceleration at gravity g, therefore our new equation will be,
$h=\left( 0 \right)\times t\dfrac{1}{2}g{{t}^{2}}....\left( 4 \right)$
Now substitute value of equation (3) in equation (4)
$h=0+\dfrac{1}{2}g\times {{\left( \dfrac{x}{v} \right)}^{2}}$
Now substitute the value of v from the equation (1)
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow h=\dfrac{1}{2}\times g\times \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{\left( \sqrt{2g\left( H-h \right)} \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow h=\dfrac{g}{2}\times \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{2g\left( H-h \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}=2\times 2.h\left( H-h \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}=4Hh-4{{h}^{2}} \\
& \therefore x=\sqrt{4Hh-4{{h}^{2}}}.....\left( 5 \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Now to find the ${{x}_{\max }}$ we differentiate ${{x}^{2}}$ with respect to h and we will equalize with the zero.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{d\left( x_{\max }^{2} \right)}{dh}=4H-8h=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 8h=4H \\
& \therefore h=\dfrac{H}{2}......\left( 6 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now we will put the value of equation (6) into equation (5)
$\Rightarrow {{x}_{\max }}=\sqrt{4H\left( \dfrac{H}{2} \right)-4{{\left( \dfrac{H}{2} \right)}^{2}}}$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{\max }}=\sqrt{2{{H}^{2}}-{{H}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{\max }}=\sqrt{{{H}^{2}}} \\
& \therefore {{x}_{\max }}=H \\
\end{align}$
Hence, option (2) H is correct.
Note:
When we want to find the maximum distance x we have to equalize with by differentiating with respect to height h. Which is shown in the solution if we skip this step it will lead us to the wrong answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




