
(a) Draw the structures of the following molecules:
(i) ${{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{5}}}$
(ii) ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$
(b) Explain the following observations:
(i) ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}$ is more acidic than ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$.
(ii) Fluorine does not exhibit any positive oxidation state.
(iii) Helium forms no real chemical compound.
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: Draw the Lewis structures using the total valence electron count. We know that the acidic character depends on the electronegativity of the bond.
Complete answer:
(a)(i) Draw the structures of ${{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{5}}}$:
Calculate the valence electrons of ${{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{5}}}$ molecule as follows:
The valence electrons of ${\text{N}}$ are ${\text{5}}$ and the valence electrons of ${\text{O}}$ are ${\text{6}}$. Thus,
Valence electrons of ${{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{5}}}$ $ = \left( {2 \times {\text{Valence electrons of N}}} \right) + \left( {5 \times {\text{Valence electrons of O}}} \right)$
$ = \left( {2 \times 5} \right) + \left( {5 \times 6} \right)$
= 10 + 30
Valence electrons of ${{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{5}}}$ $ = {\text{40}}$
Draw the Lewis structure of ${{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{5}}}$ as follows:
The structure of ${{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{5}}}$ is,
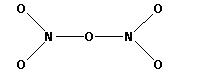
As six bonds are formed, twelve electrons are involved in bonding. Thus, the remaining electrons are,
Remaining electrons = 40 - 12 = 28
Place the remaining 28 electrons around the oxygen atoms such that all the oxygen atoms complete their octets.
Thus, the structure of ${{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{5}}}$ is as follows:
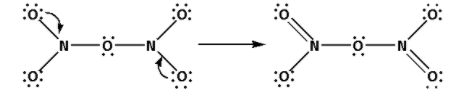
(ii) Draw the structures of ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$:
Calculate the valence electrons of ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ molecule as follows:
The valence electrons of ${\text{H}}$ are ${\text{1}}$, the valence electrons of ${\text{Cl}}$ are ${\text{7}}$ and the valence electrons of ${\text{O}}$ are ${\text{6}}$. Thus,
Valence electrons of ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$
$ = \left( {1 \times {\text{Valence electrons of H}}} \right) + \left( {1 \times {\text{Valence electrons of Cl}}} \right) + \left( {4 \times {\text{Valence electrons of O}}} \right)$
$ = \left( {1 \times 1} \right) + \left( {1 \times 7} \right) + \left( {4 \times 6} \right)$
= 1 + 7 + 24
Valence electrons of ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ $ = {\text{32}}$
Draw the Lewis structure of ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ as follows:
The structure of ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ is,
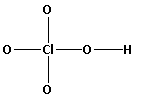
As five bonds are formed, ten electrons are involved in bonding. Thus, the remaining electrons are,
Remaining electrons = 32 - 10 = 22
Place the remaining 22 electrons around the oxygen atoms such that all the oxygen atoms complete their octets.
Thus, the structure of ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ is as follows:
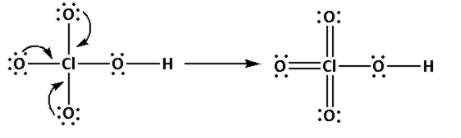
(b)(i) Explain why ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}$ is more acidic than ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$:
In ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}$, the bond is formed between hydrogen and sulphur and in ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$ bond is formed between hydrogen and oxygen.
The electronegativity of oxygen is more than that of sulphur. Thus, the bond dissociation enthalpy of the bond between hydrogen and sulphur is lower than that of the bond between hydrogen and oxygen.
Thus, ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}$ is more acidic than ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$.
(ii) Explain why fluorine does not exhibit any positive oxidation state:
The size of fluorine is very small and thus, electrons in fluorine are strongly attracted by the nuclear charge.
Thus, the removal of electrons is not possible from the atom.
Thus, fluorine does not exhibit any positive oxidation state.
(iii) Explain why helium forms no real chemical compound:
The electronic configuration of helium is $1{s^2}$.
The maximum capacity of the s orbital is 2 electrons.
Thus, the valence orbital of helium is completely filled.
Also, helium has high ionisation enthalpy and more positive electron gain enthalpy.
Thus, helium forms no real chemical compound.
Note: An atom can form chemical compounds when its valence orbital can accommodate electrons. In case of helium, valence orbital is completely filled and thus, it cannot form any chemical compounds.
Complete answer:
(a)(i) Draw the structures of ${{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{5}}}$:
Calculate the valence electrons of ${{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{5}}}$ molecule as follows:
The valence electrons of ${\text{N}}$ are ${\text{5}}$ and the valence electrons of ${\text{O}}$ are ${\text{6}}$. Thus,
Valence electrons of ${{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{5}}}$ $ = \left( {2 \times {\text{Valence electrons of N}}} \right) + \left( {5 \times {\text{Valence electrons of O}}} \right)$
$ = \left( {2 \times 5} \right) + \left( {5 \times 6} \right)$
= 10 + 30
Valence electrons of ${{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{5}}}$ $ = {\text{40}}$
Draw the Lewis structure of ${{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{5}}}$ as follows:
The structure of ${{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{5}}}$ is,

As six bonds are formed, twelve electrons are involved in bonding. Thus, the remaining electrons are,
Remaining electrons = 40 - 12 = 28
Place the remaining 28 electrons around the oxygen atoms such that all the oxygen atoms complete their octets.
Thus, the structure of ${{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{5}}}$ is as follows:

(ii) Draw the structures of ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$:
Calculate the valence electrons of ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ molecule as follows:
The valence electrons of ${\text{H}}$ are ${\text{1}}$, the valence electrons of ${\text{Cl}}$ are ${\text{7}}$ and the valence electrons of ${\text{O}}$ are ${\text{6}}$. Thus,
Valence electrons of ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$
$ = \left( {1 \times {\text{Valence electrons of H}}} \right) + \left( {1 \times {\text{Valence electrons of Cl}}} \right) + \left( {4 \times {\text{Valence electrons of O}}} \right)$
$ = \left( {1 \times 1} \right) + \left( {1 \times 7} \right) + \left( {4 \times 6} \right)$
= 1 + 7 + 24
Valence electrons of ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ $ = {\text{32}}$
Draw the Lewis structure of ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ as follows:
The structure of ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ is,

As five bonds are formed, ten electrons are involved in bonding. Thus, the remaining electrons are,
Remaining electrons = 32 - 10 = 22
Place the remaining 22 electrons around the oxygen atoms such that all the oxygen atoms complete their octets.
Thus, the structure of ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ is as follows:

(b)(i) Explain why ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}$ is more acidic than ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$:
In ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}$, the bond is formed between hydrogen and sulphur and in ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$ bond is formed between hydrogen and oxygen.
The electronegativity of oxygen is more than that of sulphur. Thus, the bond dissociation enthalpy of the bond between hydrogen and sulphur is lower than that of the bond between hydrogen and oxygen.
Thus, ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}$ is more acidic than ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$.
(ii) Explain why fluorine does not exhibit any positive oxidation state:
The size of fluorine is very small and thus, electrons in fluorine are strongly attracted by the nuclear charge.
Thus, the removal of electrons is not possible from the atom.
Thus, fluorine does not exhibit any positive oxidation state.
(iii) Explain why helium forms no real chemical compound:
The electronic configuration of helium is $1{s^2}$.
The maximum capacity of the s orbital is 2 electrons.
Thus, the valence orbital of helium is completely filled.
Also, helium has high ionisation enthalpy and more positive electron gain enthalpy.
Thus, helium forms no real chemical compound.
Note: An atom can form chemical compounds when its valence orbital can accommodate electrons. In case of helium, valence orbital is completely filled and thus, it cannot form any chemical compounds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




