
(a) Draw ray – diagrams to show the formation of image when the object is placed in front of a concave mirror (converging mirror):
(i) Between its pole and focus
(ii) Between its centre of curvature and focus. Describe the nature, size and position of the image formed in each case.
(b) State the use of a concave mirror based on the formation of images as in case above.
Answer
559.2k+ views
Hint:The image of the object placed between the focus and pole forms behind the mirror. The image of the object placed between curvature and focus forms on the same side of the object. When the image forms behind the mirror, the image is a virtual image and when the image forms on the same side of the object, the image is a real image.
Complete answer:
(a) (i) We have given that the object is placed in front of a concave mirror that is between the pole of the mirror and focus. In this case, the reflected rays from the concave mirror could not be focused at the same side of the mirror and to form the image, we have to back trace the reflected rays to form the image of the object. Let’s draw the ray – diagram for the formation of the image in this case.
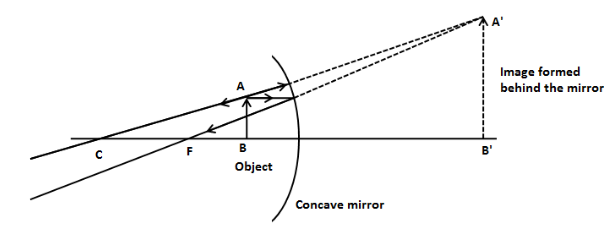
As we can see in the above figure, the image of the object is magnified, erect and virtual (since it is formed behind the mirror).
(a)(ii) We have given that the object is placed between the radius of curvature and focus of the concave mirror. In this case, the image of the object forms on the same side as the object. Let’s draw the ray-diagram for the formation of an image in this case.
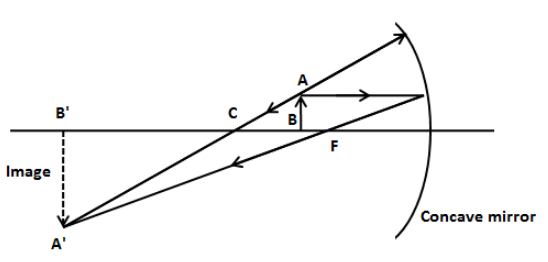
As we can see in the above figure, the image of the object is inverted, magnified and real.
(b) Let’s discuss the use of a concave mirror in the first case. In the first case, where the image forms behind the mirror, such a mirror is used as a shaving mirror. Also, the concave mirror is used in the base of a microscope as a condenser. In the headlights of vehicles, the concave mirrors are used since they collect the light coming from the bulb and emerges them as parallel rays.
Note:To draw the ray diagram for the image formation in a concave mirror, you need reflected rays to focus at a certain point. One ray from the object gets reflected from the concave mirror and goes through the focus and another ray from the object reflected from the concave mirror goes through the curvature of the mirror. The conditions for image formation are discussed in the solution. Students must remember the characteristics of the image formed by the concave mirror to draw the ray – diagram.
Complete answer:
(a) (i) We have given that the object is placed in front of a concave mirror that is between the pole of the mirror and focus. In this case, the reflected rays from the concave mirror could not be focused at the same side of the mirror and to form the image, we have to back trace the reflected rays to form the image of the object. Let’s draw the ray – diagram for the formation of the image in this case.

As we can see in the above figure, the image of the object is magnified, erect and virtual (since it is formed behind the mirror).
(a)(ii) We have given that the object is placed between the radius of curvature and focus of the concave mirror. In this case, the image of the object forms on the same side as the object. Let’s draw the ray-diagram for the formation of an image in this case.

As we can see in the above figure, the image of the object is inverted, magnified and real.
(b) Let’s discuss the use of a concave mirror in the first case. In the first case, where the image forms behind the mirror, such a mirror is used as a shaving mirror. Also, the concave mirror is used in the base of a microscope as a condenser. In the headlights of vehicles, the concave mirrors are used since they collect the light coming from the bulb and emerges them as parallel rays.
Note:To draw the ray diagram for the image formation in a concave mirror, you need reflected rays to focus at a certain point. One ray from the object gets reflected from the concave mirror and goes through the focus and another ray from the object reflected from the concave mirror goes through the curvature of the mirror. The conditions for image formation are discussed in the solution. Students must remember the characteristics of the image formed by the concave mirror to draw the ray – diagram.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




