
A double cone is formed by a revolving right triangle having sides 5 cm, 12 cm and 13 cm about its hypotenuse. Find T.S.A. and volume of double cons so formed.
Answer
581.4k+ views
Hint:
Firstly, find the heights of the given cones.
Then using that, find the radius of the cones.
Thus, T.S.A. of the double cone can be given by the sum of C.S.A. of both cones and volume of double cone is given by the sum of volumes of both cones.
C.S.A. of a cone $ = \pi rl$
Volume of a cone $ = \dfrac{1}{3}\pi rh$
Complete step by step solution:
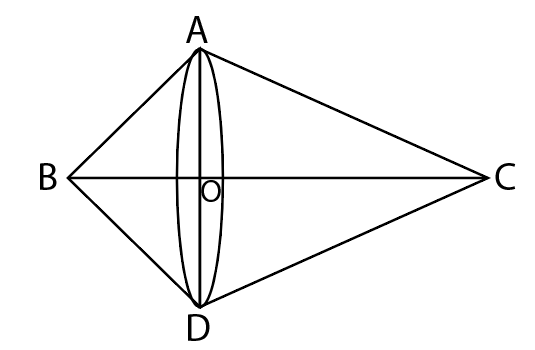
Here, a right triangle is revolved about its hypotenuse and thus the above diagram of double cone is formed.
No, in triangle ABC
Let, AB = 5 cm, AC = 12 cm and BC = 13 cm. Also, let $OB = {h_1}$ , $OC = {h_2}$ and \[OA = OD = r\] .
Thus, $OB + OC = 13$ . $\therefore {h_1} + {h_2} = 13$ . … (1)
Also, in triangle ABO, $A{B^2} = A{O^2} + O{B^2}$
$\therefore {5^2} = {h_1}^2 + {r^2}$ … (2)
And, in triangle AOC, $A{C^2} = A{O^2} + O{C^2}$
$\therefore {12^2} = {h_2}^2 + {r^2}$ … (3)
Now, subtracting equation (2) from equation (3), we get
\[
\therefore {12^2} - {5^2} = {h_2}^2 + {r^2} - {h_1}^2 - {r^2} \\
\therefore 144 - 25 = {h_2}^2 - {h_1}^2 \\
\therefore 119 = \left( {{h_2} - {h_1}} \right)\left( {{h_2} + {h_1}} \right) \\
\]
Substituting equation (1) in above equation
$\therefore 119 = \left( {{h_2} - {h_1}} \right)\left( {13} \right)$
$\therefore {h_2} - {h_1} = \dfrac{{119}}{{13}}$ … (4)
Adding equation (4) and equation (1) we get
$
{h_2} - {h_1} + {h_2} + {h_1} = \dfrac{{119}}{{13}} + 13 \\
\therefore 2{h_2} = \dfrac{{119 + 169}}{{13}} \\
\therefore 2{h_2} = \dfrac{{288}}{{13}} \\
\therefore {h_2} = \dfrac{{144}}{{13}} \\
$
Putting ${h_2} = \dfrac{{144}}{{13}}$ in equation (4) we get
$
\dfrac{{144}}{{13}} - {h_1} = \dfrac{{119}}{{13}} \\
\therefore \dfrac{{144}}{{13}} - \dfrac{{119}}{{13}} = {h_1} \\
\therefore {h_1} = \dfrac{{25}}{{13}} \\
$
Thus, we get ${h_1} = \dfrac{{25}}{{13}}$ and ${h_2} = \dfrac{{144}}{{13}}$ .
Now, substituting the value ${h_1} = \dfrac{{25}}{{13}}$ in equation (2), we get
$
{5^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{{25}}{{13}}} \right)^2} + {r^2} \\
\therefore {r^2} = 25 - \dfrac{{625}}{{169}} \\
\therefore {r^2} = \dfrac{{4226 - 625}}{{169}} \\
\therefore {r^2} = \dfrac{{3600}}{{169}} \\
\therefore r = \sqrt {\dfrac{{3600}}{{169}}} \\
\therefore r = \dfrac{{60}}{{13}} \\
$
Thus, $r = \dfrac{{69}}{{13}}$
Now, T.S.A. of the double cone can be given by the sum of C.S.A. of both cones.
$\therefore $ T.S.A. of the double cone = the sum of C.S.A. of both cones
$
= \left( {\pi \times r \times AB} \right) + \left( {\pi \times r \times AC} \right) \\
= \left( {\pi \times \dfrac{{60}}{{13}} \times 5} \right) + \left( {\pi \times \dfrac{{60}}{{13}} \times 12} \right) \\
= \pi \times \dfrac{{60}}{{13}}\left( {5 + 12} \right) \\
= \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times \dfrac{{60}}{{13}} \times 17 \\
= 246.59c{m^2} \\
$
Then, volume of double cone is given by the sum of volumes of both cones.
$\therefore $ Volume of double cone = sum of volumes of both cones
\[
= \left( {\dfrac{1}{3} \times \pi \times {r^2} \times {h_1}} \right) + \left( {\dfrac{1}{3} \times \pi \times {r^2} \times {h_2}} \right) \\
= \left( {\dfrac{1}{3} \times \pi \times {{\left( {\dfrac{{60}}{{13}}} \right)}^2} \times \dfrac{{25}}{{13}}} \right) + \left( {\dfrac{1}{3} \times \pi \times {{\left( {\dfrac{{60}}{{13}}} \right)}^2} \times \dfrac{{144}}{{13}}} \right) \\
= \dfrac{1}{3} \times \pi \times {\left( {\dfrac{{60}}{{13}}} \right)^2}\left( {\dfrac{{25}}{{13}} + \dfrac{{144}}{{13}}} \right) \\
= \dfrac{1}{3} \times \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times \dfrac{{3600}}{{169}} \times \dfrac{{169}}{{13}} \\
= 290c{m^3}
\]
Thus, we get the value of T.S.A. of the double cone as $246.59c{m^2}$ and the volume of double cone as \[290c{m^3}\].
Note:
Here, the second method to find the radius r can be
Now, substituting the value ${h_2} = \dfrac{{144}}{{13}}$ in equation (3), we get
$
{12^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{{144}}{{13}}} \right)^2} + {r^2} \\
\therefore {r^2} = 144 - \dfrac{{20736}}{{169}} \\
\therefore {r^2} = \dfrac{{24336 - 20736}}{{169}} \\
\therefore {r^2} = \dfrac{{3600}}{{169}} \\
\therefore r = \sqrt {\dfrac{{3600}}{{169}}} \\
\therefore r = \dfrac{{60}}{{13}} \\
$
Thus, $r = \dfrac{{69}}{{13}}$.
Firstly, find the heights of the given cones.
Then using that, find the radius of the cones.
Thus, T.S.A. of the double cone can be given by the sum of C.S.A. of both cones and volume of double cone is given by the sum of volumes of both cones.
C.S.A. of a cone $ = \pi rl$
Volume of a cone $ = \dfrac{1}{3}\pi rh$
Complete step by step solution:

Here, a right triangle is revolved about its hypotenuse and thus the above diagram of double cone is formed.
No, in triangle ABC
Let, AB = 5 cm, AC = 12 cm and BC = 13 cm. Also, let $OB = {h_1}$ , $OC = {h_2}$ and \[OA = OD = r\] .
Thus, $OB + OC = 13$ . $\therefore {h_1} + {h_2} = 13$ . … (1)
Also, in triangle ABO, $A{B^2} = A{O^2} + O{B^2}$
$\therefore {5^2} = {h_1}^2 + {r^2}$ … (2)
And, in triangle AOC, $A{C^2} = A{O^2} + O{C^2}$
$\therefore {12^2} = {h_2}^2 + {r^2}$ … (3)
Now, subtracting equation (2) from equation (3), we get
\[
\therefore {12^2} - {5^2} = {h_2}^2 + {r^2} - {h_1}^2 - {r^2} \\
\therefore 144 - 25 = {h_2}^2 - {h_1}^2 \\
\therefore 119 = \left( {{h_2} - {h_1}} \right)\left( {{h_2} + {h_1}} \right) \\
\]
Substituting equation (1) in above equation
$\therefore 119 = \left( {{h_2} - {h_1}} \right)\left( {13} \right)$
$\therefore {h_2} - {h_1} = \dfrac{{119}}{{13}}$ … (4)
Adding equation (4) and equation (1) we get
$
{h_2} - {h_1} + {h_2} + {h_1} = \dfrac{{119}}{{13}} + 13 \\
\therefore 2{h_2} = \dfrac{{119 + 169}}{{13}} \\
\therefore 2{h_2} = \dfrac{{288}}{{13}} \\
\therefore {h_2} = \dfrac{{144}}{{13}} \\
$
Putting ${h_2} = \dfrac{{144}}{{13}}$ in equation (4) we get
$
\dfrac{{144}}{{13}} - {h_1} = \dfrac{{119}}{{13}} \\
\therefore \dfrac{{144}}{{13}} - \dfrac{{119}}{{13}} = {h_1} \\
\therefore {h_1} = \dfrac{{25}}{{13}} \\
$
Thus, we get ${h_1} = \dfrac{{25}}{{13}}$ and ${h_2} = \dfrac{{144}}{{13}}$ .
Now, substituting the value ${h_1} = \dfrac{{25}}{{13}}$ in equation (2), we get
$
{5^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{{25}}{{13}}} \right)^2} + {r^2} \\
\therefore {r^2} = 25 - \dfrac{{625}}{{169}} \\
\therefore {r^2} = \dfrac{{4226 - 625}}{{169}} \\
\therefore {r^2} = \dfrac{{3600}}{{169}} \\
\therefore r = \sqrt {\dfrac{{3600}}{{169}}} \\
\therefore r = \dfrac{{60}}{{13}} \\
$
Thus, $r = \dfrac{{69}}{{13}}$
Now, T.S.A. of the double cone can be given by the sum of C.S.A. of both cones.
$\therefore $ T.S.A. of the double cone = the sum of C.S.A. of both cones
$
= \left( {\pi \times r \times AB} \right) + \left( {\pi \times r \times AC} \right) \\
= \left( {\pi \times \dfrac{{60}}{{13}} \times 5} \right) + \left( {\pi \times \dfrac{{60}}{{13}} \times 12} \right) \\
= \pi \times \dfrac{{60}}{{13}}\left( {5 + 12} \right) \\
= \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times \dfrac{{60}}{{13}} \times 17 \\
= 246.59c{m^2} \\
$
Then, volume of double cone is given by the sum of volumes of both cones.
$\therefore $ Volume of double cone = sum of volumes of both cones
\[
= \left( {\dfrac{1}{3} \times \pi \times {r^2} \times {h_1}} \right) + \left( {\dfrac{1}{3} \times \pi \times {r^2} \times {h_2}} \right) \\
= \left( {\dfrac{1}{3} \times \pi \times {{\left( {\dfrac{{60}}{{13}}} \right)}^2} \times \dfrac{{25}}{{13}}} \right) + \left( {\dfrac{1}{3} \times \pi \times {{\left( {\dfrac{{60}}{{13}}} \right)}^2} \times \dfrac{{144}}{{13}}} \right) \\
= \dfrac{1}{3} \times \pi \times {\left( {\dfrac{{60}}{{13}}} \right)^2}\left( {\dfrac{{25}}{{13}} + \dfrac{{144}}{{13}}} \right) \\
= \dfrac{1}{3} \times \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times \dfrac{{3600}}{{169}} \times \dfrac{{169}}{{13}} \\
= 290c{m^3}
\]
Thus, we get the value of T.S.A. of the double cone as $246.59c{m^2}$ and the volume of double cone as \[290c{m^3}\].
Note:
Here, the second method to find the radius r can be
Now, substituting the value ${h_2} = \dfrac{{144}}{{13}}$ in equation (3), we get
$
{12^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{{144}}{{13}}} \right)^2} + {r^2} \\
\therefore {r^2} = 144 - \dfrac{{20736}}{{169}} \\
\therefore {r^2} = \dfrac{{24336 - 20736}}{{169}} \\
\therefore {r^2} = \dfrac{{3600}}{{169}} \\
\therefore r = \sqrt {\dfrac{{3600}}{{169}}} \\
\therefore r = \dfrac{{60}}{{13}} \\
$
Thus, $r = \dfrac{{69}}{{13}}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




