
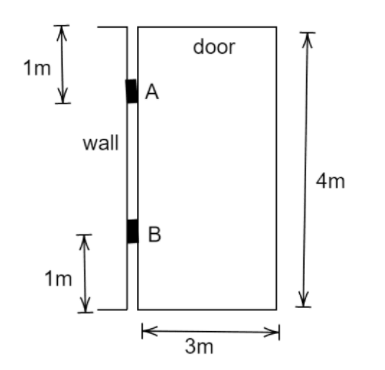
A door of $100\,kg$ mass which is supported by two hinges $A$ and $B$ on a wall is of size $4\,m \times 3\,m$ as shown. If the force by hinges on the door are equal, find these forces exerted by hinges.

Answer
476.1k+ views
Hint: Find all the forces acting on the door, that is, due to gravity and then the force to balance that. There will be some horizontal force also on the hinges which will be equal and opposite. Finally, find the values of these forces and their sum will give us the required force exerted by hinges.
Complete step by step answer:
Forces acting on the door are $mg$ in a downward direction because of its weight. An upward force ${F_V}$ on both the hinges to balance the downward force. If the door is rotated then a ${F_H}$ force is acted towards the left and to balance that same force is acted towards the right.
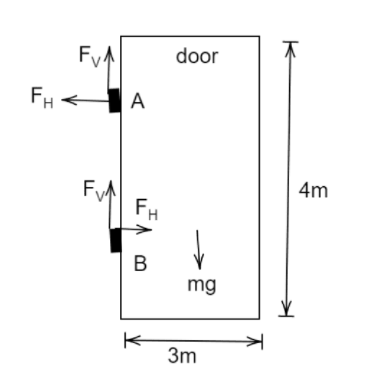
Therefore for this equilibrium position of the door we get,
$2{F_V} = mg$
$ \Rightarrow {F_V} = \dfrac{{mg}}{2} = \dfrac{{100 \times 10}}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow {F_V} = 500\,N$
To calculate the horizontal force by the hinges we use the rotational equilibrium situation of the door that is net torque on the door will be zero
$\tau = 2{F_V} \times 1.5 - 2{F_H} \times 1 = 0$
Therefore we get,
${F_H} = \dfrac{{3{F_V}}}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow {F_H} = \dfrac{{3 \times 500}}{2} = 750N$
Hence, the forces exerted by either hinge in magnitude is
$F' = \sqrt {{F_V}^2 + {F_H}^2} $
$ \Rightarrow F' = \sqrt {{{(500)}^2} + {{(750)}^2}} $
$ \therefore F' = 250\sqrt {13} N$
Hence,the force by hinges on the door is $250\sqrt {13} N$.
Note: Torque is a measurement of how much a force exerted on an object rotates it.The state of a system in which the total angular acceleration is zero is known as rotational equilibrium. Two conditions must be met for an object to remain in equilibrium: both the net force and the net torque must be zero.
Complete step by step answer:
Forces acting on the door are $mg$ in a downward direction because of its weight. An upward force ${F_V}$ on both the hinges to balance the downward force. If the door is rotated then a ${F_H}$ force is acted towards the left and to balance that same force is acted towards the right.

Therefore for this equilibrium position of the door we get,
$2{F_V} = mg$
$ \Rightarrow {F_V} = \dfrac{{mg}}{2} = \dfrac{{100 \times 10}}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow {F_V} = 500\,N$
To calculate the horizontal force by the hinges we use the rotational equilibrium situation of the door that is net torque on the door will be zero
$\tau = 2{F_V} \times 1.5 - 2{F_H} \times 1 = 0$
Therefore we get,
${F_H} = \dfrac{{3{F_V}}}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow {F_H} = \dfrac{{3 \times 500}}{2} = 750N$
Hence, the forces exerted by either hinge in magnitude is
$F' = \sqrt {{F_V}^2 + {F_H}^2} $
$ \Rightarrow F' = \sqrt {{{(500)}^2} + {{(750)}^2}} $
$ \therefore F' = 250\sqrt {13} N$
Hence,the force by hinges on the door is $250\sqrt {13} N$.
Note: Torque is a measurement of how much a force exerted on an object rotates it.The state of a system in which the total angular acceleration is zero is known as rotational equilibrium. Two conditions must be met for an object to remain in equilibrium: both the net force and the net torque must be zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




