
A DMM is placed with its arms in the N−S direction. The distance at which a short bar magnet having $ \dfrac{M}{{{B_H}}} = 80\dfrac{{A{m^2}}}{T} $ should be placed, so that the needle can stay in any position is (nearly)
(A) $ 2.5cm $ from the needle, N-pole pointing GS
(B) $ 2cm $ from the needle, N-pole pointing GN
(C) $ 4cm $ from the needle, N-pole pointing GN
(D) $ 2cm $ from the needle, N-pole pointing GS
Answer
478.2k+ views
Hint: According to the question we have to find the value of distance $ d $ at which a short bar magnet should be placed. Using the formula which gives the relation between the magnetic dipole moment ( $ M $ ) of a bar magnet and horizontal intensity ( $ {B_H} $ ) of earth’s magnetic field using a deflection magnetometer. We will answer this question.
$ \dfrac{M}{{{B_H}}} = \dfrac{{4\pi }}{{{\mu _0}}}\dfrac{{{{\left( {{d^2} - {l^2}} \right)}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}}{{2d}}\tan \theta $
Where $ M $ is the magnetic dipole moment, $ {B_H} $ is the intensity of the magnet, $ d $ is the distance at which the magnet is placed, $ l $ is the length of the magnet, $ \dfrac{{4\pi }}{{{\mu _0}}} $ is a constant, $ \theta $ is the angle.
Complete answer:
The horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field, denoted by $ {B_H} $ is the component of the earth's magnetic field along a horizontal plane whose normal vector runs through the earth's centre.
A magnetic dipole's magnetic dipole moment is the attribute of the dipole that causes it to align parallel to an external magnetic field.
Using the formula
$ \dfrac{M}{{{B_H}}} = \dfrac{{4\pi }}{{{\mu _0}}}\dfrac{{{{\left( {{d^2} - {l^2}} \right)}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}}{{2d}}\tan \theta $
For this question the angle is not considered as it is given that the needle can stay in any position so
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{M}{{{B_H}}} = \dfrac{{4\pi }}{{{\mu _0}}}\dfrac{{{{\left( {{d^2} - {l^2}} \right)}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}}{{2d}} $
Also for short bar magnet $ d > > l $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{M}{{{B_H}}} = \dfrac{{4\pi }}{{{\mu _0}}}\dfrac{{{d^3}}}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow {d^3} = \dfrac{{4\pi \times {{10}^{ - 7}} \times 80}}{{4\pi }} $
$ d = 2 \times {10^{ - 2}} = 2cm $
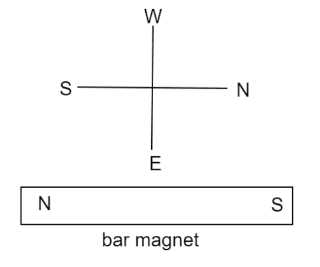
The value is positive so it is placed in the Gaussian south.
Hence option D) is the correct answer.
Note:
The deflection magnetometer is made up of a big compass box with a small magnetic needle pivoting at the centre of a circular scale so that it can rotate freely in a horizontal plane. The magnetic needle is tightly placed perpendicular to a huge aluminum pointer.
$ \dfrac{M}{{{B_H}}} = \dfrac{{4\pi }}{{{\mu _0}}}\dfrac{{{{\left( {{d^2} - {l^2}} \right)}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}}{{2d}}\tan \theta $
Where $ M $ is the magnetic dipole moment, $ {B_H} $ is the intensity of the magnet, $ d $ is the distance at which the magnet is placed, $ l $ is the length of the magnet, $ \dfrac{{4\pi }}{{{\mu _0}}} $ is a constant, $ \theta $ is the angle.
Complete answer:
The horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field, denoted by $ {B_H} $ is the component of the earth's magnetic field along a horizontal plane whose normal vector runs through the earth's centre.
A magnetic dipole's magnetic dipole moment is the attribute of the dipole that causes it to align parallel to an external magnetic field.
Using the formula
$ \dfrac{M}{{{B_H}}} = \dfrac{{4\pi }}{{{\mu _0}}}\dfrac{{{{\left( {{d^2} - {l^2}} \right)}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}}{{2d}}\tan \theta $
For this question the angle is not considered as it is given that the needle can stay in any position so
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{M}{{{B_H}}} = \dfrac{{4\pi }}{{{\mu _0}}}\dfrac{{{{\left( {{d^2} - {l^2}} \right)}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}}{{2d}} $
Also for short bar magnet $ d > > l $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{M}{{{B_H}}} = \dfrac{{4\pi }}{{{\mu _0}}}\dfrac{{{d^3}}}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow {d^3} = \dfrac{{4\pi \times {{10}^{ - 7}} \times 80}}{{4\pi }} $
$ d = 2 \times {10^{ - 2}} = 2cm $

The value is positive so it is placed in the Gaussian south.
Hence option D) is the correct answer.
Note:
The deflection magnetometer is made up of a big compass box with a small magnetic needle pivoting at the centre of a circular scale so that it can rotate freely in a horizontal plane. The magnetic needle is tightly placed perpendicular to a huge aluminum pointer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

RNA and DNA are chiral molecules their chirality is class 12 chemistry CBSE




