
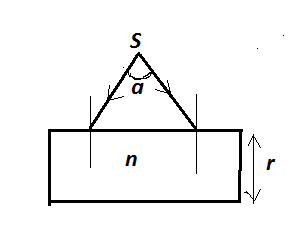
A diverging beam of light from a point source S having divergence angle$\alpha $ falls symmetrically on a glass slab as shown. The angles of incidence of the two extreme rays are equal. If the thickness of the glass slab is $t$ and the refractive index $n$, then the divergence angle of the emergent beam is,
a. Zero
b. $\alpha $
c. ${\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{1}{n}} \right)$
d. $2{\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{1}{n}} \right)$

Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: The divergence of light ray starts from the point source and it will spread them. The divergence is the angular measure of spread of light a light beam from a collimating laser or device.
Lateral shift: When light ray is incident on the parallel side of the glass slab the emergent ray shifts laterally to some distance. That distance is called the lateral shift. It depends on the thickness of the refracting surface and the refractive index of the material.
Complete answer:
Given: The divergence angle $\alpha $, the angle of incidence of two rays are equal, the thickness of the glass slab is $t$ and refractive index $n$. To find the divergence angle of the emergent beam.
The rays are passing through the glass slab. It results in change in displacement. This will not change in the direction of the emergent rays coming out of the second surface.
Due to lateral shift, the incident rays are parallel to emergent rays. The diverging angle will remain unchanged. Therefore the initial angle between incident rays will be equal to the final angle between the emergent rays. Thus the diverging divergent angle of emergent rays is the same $\alpha $.
The divergence angle of the emergent beam is $\alpha $.
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: Beam divergence is used to characterize the electromagnetic beams in the optical regime, for cases in which the aperture from which the beam emerges is large with respect to the wavelength. The refractive index is defined as the ratio between the speeds of light in medium to speed in a vacuum.
Lateral shift: When light ray is incident on the parallel side of the glass slab the emergent ray shifts laterally to some distance. That distance is called the lateral shift. It depends on the thickness of the refracting surface and the refractive index of the material.
Complete answer:
Given: The divergence angle $\alpha $, the angle of incidence of two rays are equal, the thickness of the glass slab is $t$ and refractive index $n$. To find the divergence angle of the emergent beam.
The rays are passing through the glass slab. It results in change in displacement. This will not change in the direction of the emergent rays coming out of the second surface.
Due to lateral shift, the incident rays are parallel to emergent rays. The diverging angle will remain unchanged. Therefore the initial angle between incident rays will be equal to the final angle between the emergent rays. Thus the diverging divergent angle of emergent rays is the same $\alpha $.
The divergence angle of the emergent beam is $\alpha $.
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: Beam divergence is used to characterize the electromagnetic beams in the optical regime, for cases in which the aperture from which the beam emerges is large with respect to the wavelength. The refractive index is defined as the ratio between the speeds of light in medium to speed in a vacuum.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




