
A diver is hunting a fish with a water gun. He accidentally fires the gun, so that bullet punctures the side of the ship. The hole is located at a depth of $10m$ below the water surface. The speed with which water enters the ship is:
(A) $18m{\sec ^{ - 1}}$
(B) $14m{\sec ^{ - 1}}$
(C) $25m{\sec ^{ - 1}}$
(D) Can’t be determined
Answer
504.3k+ views
Hint:In order to solve this question, we will use the concept of Law of conservation of energy which states that the total energy of the system remains constant which means either Kinetic energy will convert into potential energy or Potential energy will convert into Kinetic energy Keeping total energy of a system at a point is constant. Here, we will use the equilibrium of these energies at a whole point and will find the magnitude of velocity at which water will enter into the ship.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Let A be the topmost point of the water surface and B be the point $10m$ below the water surface from where water will enter through the hole.
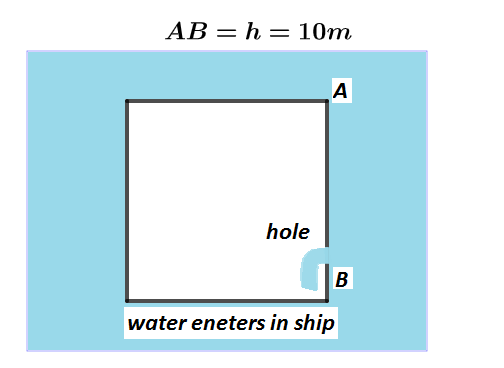
Now, at topmost point A of the water surface there is no Kinetic energy and hence water only possesses the Gravitational potential energy, so, Gravitational potential energy per unit volume of the water at a height of $h = 10m$ can be written as:
$P.E = \rho gh$ Where,
$\rho $ Is the density of the water
$g$ Is the acceleration due to gravity.
Now, as soon as the hole is made, this Gravitational potential energy of water at point A will convert into Kinetic energy at point B which can be calculated as:
Since, \[KE = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}\] but we need to find K.E per unit volume so $\rho = \dfrac{m}{V}$ Hence,
$K.E = \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v^2}$
Where, $v$ is the velocity with which water will enter into the ship.
Now, according to conservation of energy, Gravitational potential energy will equal to Kinetic energy so, we have
$\rho gh = \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v^2}$
Or
$v = \sqrt {2gh} $
Put the values of $h = 10m$ and $g = 9.8m{\sec ^{ - 2}}$ we get,
$v = \sqrt {20 \times 9.8} $
$v = 14m{\sec ^{ - 1}}$
So, the water will enter into the ship with a velocity of $v = 14m{\sec ^{ - 1}}$
Hence, the correct option is (B) $14m{\sec ^{ - 1}}$.
Note: It should be remembered that, the gravitational potential energy and Kinetic energy are calculated in per unit volume of their respective magnitudes, in fluid mechanics we can’t simply use mass form of energy. In fluid mechanics, We have to convert all energies in density form through dividing the mass by volume.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Let A be the topmost point of the water surface and B be the point $10m$ below the water surface from where water will enter through the hole.

Now, at topmost point A of the water surface there is no Kinetic energy and hence water only possesses the Gravitational potential energy, so, Gravitational potential energy per unit volume of the water at a height of $h = 10m$ can be written as:
$P.E = \rho gh$ Where,
$\rho $ Is the density of the water
$g$ Is the acceleration due to gravity.
Now, as soon as the hole is made, this Gravitational potential energy of water at point A will convert into Kinetic energy at point B which can be calculated as:
Since, \[KE = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}\] but we need to find K.E per unit volume so $\rho = \dfrac{m}{V}$ Hence,
$K.E = \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v^2}$
Where, $v$ is the velocity with which water will enter into the ship.
Now, according to conservation of energy, Gravitational potential energy will equal to Kinetic energy so, we have
$\rho gh = \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v^2}$
Or
$v = \sqrt {2gh} $
Put the values of $h = 10m$ and $g = 9.8m{\sec ^{ - 2}}$ we get,
$v = \sqrt {20 \times 9.8} $
$v = 14m{\sec ^{ - 1}}$
So, the water will enter into the ship with a velocity of $v = 14m{\sec ^{ - 1}}$
Hence, the correct option is (B) $14m{\sec ^{ - 1}}$.
Note: It should be remembered that, the gravitational potential energy and Kinetic energy are calculated in per unit volume of their respective magnitudes, in fluid mechanics we can’t simply use mass form of energy. In fluid mechanics, We have to convert all energies in density form through dividing the mass by volume.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




