
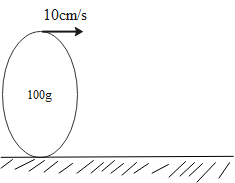
A disc of mass $100g$ is rolling without slipping on a horizontal surface with a velocity of $10cm/s$. Calculate its total energy.
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: When an object performs a rolling motion it means the object is performing two motions simultaneously. The rolling motion is constituted by the performance of rotational and translational motion by an object at the same time. The total energy of such a system is the total sum of the energy for both kinds of motion.
Formula to be used:
${{E}_{total}}={{R}_{E}}+{{T}_{E}}$
Complete step by step answer:
As per the given data,
The mass ($m$) of the disc is $100g=0.1kg$
The velocity (${{v}_{0}}$) of the body is $10cm/s=10\times {{10}^{-2}}m/s$
When an object is rolling on a horizontal surface without slipping the energy is divided into performing two kinds of motion at a time. Rotational motion and other is the translational motion.
Energy for the rotational motion is known as the rotational kinetic energy. It is dependent on the moment of inertia of the object and the angular velocity by which it is rotating on its axis.
The rotational energy of a system is given by,
${{R}_{E}}=\dfrac{1}{2}I{{\omega }^{2}}$
Where,
$I$ is the moment of inertia of the body
$\omega $ is the angular velocity of the object
This can be also written as,
$\begin{align}
& {{R}_{E}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{m{{r}^{2}}}{2}\dfrac{{{v}^{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{R}_{E}}=\dfrac{1}{4}m{{v}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
The energy for the translational motion is known as the translational kinetic energy. It is dependent on the mass of the object and the velocity by which it is moving over a particular path. (Horizontal path for this case)
The translational kinetic energy is given as,
${{T}_{E}}=\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}$
So here from the values of rotational and translational kinetic energy we can say that the total energy of the disc is,
$\begin{align}
& {{E}_{total}}={{R}_{E}}+{{T}_{E}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{E}_{total}}=\dfrac{1}{4}m{{v}^{2}}+\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}} \\
& \therefore {{E}_{total}}=\dfrac{3}{4}m{{v}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
By putting the values as per the data given,
$\begin{align}
& {{E}_{total}}=\dfrac{3}{4}(0.1){{\left( 10\times {{10}^{-2}} \right)}^{2}} \\
& {{E}_{total}}=0.00075 \\
& {{E}_{total}}=7.5\times {{10}^{-4}}J \\
\end{align}$
Thus, the total energy of the disc will be $7.5\times {{10}^{-4}}J$. And this is the required answer.
Note:
The rotational kinetic energy is also known as the angular kinetic energy of the body. When an object performs a rolling motion only a small section of the surface of the body comes in contact with the surface on which it is moving. As a result, a very small amount of frictional force acts on the body and it is easy to displace the object easily.
Formula to be used:
${{E}_{total}}={{R}_{E}}+{{T}_{E}}$
Complete step by step answer:
As per the given data,
The mass ($m$) of the disc is $100g=0.1kg$
The velocity (${{v}_{0}}$) of the body is $10cm/s=10\times {{10}^{-2}}m/s$
When an object is rolling on a horizontal surface without slipping the energy is divided into performing two kinds of motion at a time. Rotational motion and other is the translational motion.

Energy for the rotational motion is known as the rotational kinetic energy. It is dependent on the moment of inertia of the object and the angular velocity by which it is rotating on its axis.
The rotational energy of a system is given by,
${{R}_{E}}=\dfrac{1}{2}I{{\omega }^{2}}$
Where,
$I$ is the moment of inertia of the body
$\omega $ is the angular velocity of the object
This can be also written as,
$\begin{align}
& {{R}_{E}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{m{{r}^{2}}}{2}\dfrac{{{v}^{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{R}_{E}}=\dfrac{1}{4}m{{v}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
The energy for the translational motion is known as the translational kinetic energy. It is dependent on the mass of the object and the velocity by which it is moving over a particular path. (Horizontal path for this case)
The translational kinetic energy is given as,
${{T}_{E}}=\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}$
So here from the values of rotational and translational kinetic energy we can say that the total energy of the disc is,
$\begin{align}
& {{E}_{total}}={{R}_{E}}+{{T}_{E}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{E}_{total}}=\dfrac{1}{4}m{{v}^{2}}+\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}} \\
& \therefore {{E}_{total}}=\dfrac{3}{4}m{{v}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
By putting the values as per the data given,
$\begin{align}
& {{E}_{total}}=\dfrac{3}{4}(0.1){{\left( 10\times {{10}^{-2}} \right)}^{2}} \\
& {{E}_{total}}=0.00075 \\
& {{E}_{total}}=7.5\times {{10}^{-4}}J \\
\end{align}$
Thus, the total energy of the disc will be $7.5\times {{10}^{-4}}J$. And this is the required answer.
Note:
The rotational kinetic energy is also known as the angular kinetic energy of the body. When an object performs a rolling motion only a small section of the surface of the body comes in contact with the surface on which it is moving. As a result, a very small amount of frictional force acts on the body and it is easy to displace the object easily.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




