
(a)- Define racemic mixture.
(b)- Give IUPAC name of $C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-CH(C{{H}_{3}})-CHO$.
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: A racemic mixture is defined on the basis of enantiomers. In IUPAC name of $C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-CH(C{{H}_{3}})-CHO$, the numbering of carbon starts from the aldehyde group because it is a functional group.
Complete step by step answer:
(a)- The optical activity of the compound is the ability of the compound to rotate the plane of polarized light. And optically active compounds are those which rotate the plane of polarized light.
So those compounds which have a carbon atom on which the attached groups are different can rotate the plane of polarized light. This means that the compound must be asymmetric. If the compound is symmetric then it will not show optical activity or it is an optically inactive compound. The carbon which has all 4 groups attached differently is termed as chiral carbon atom in that molecule.
So, the optically active compounds which are non-superimposable mirror images of each other are called enantiomers and the phenomenon is called enantiomerism.
An example of an optically active compound is bromochloroiodomethane. It is asymmetric and has a non-superimposable mirror image.
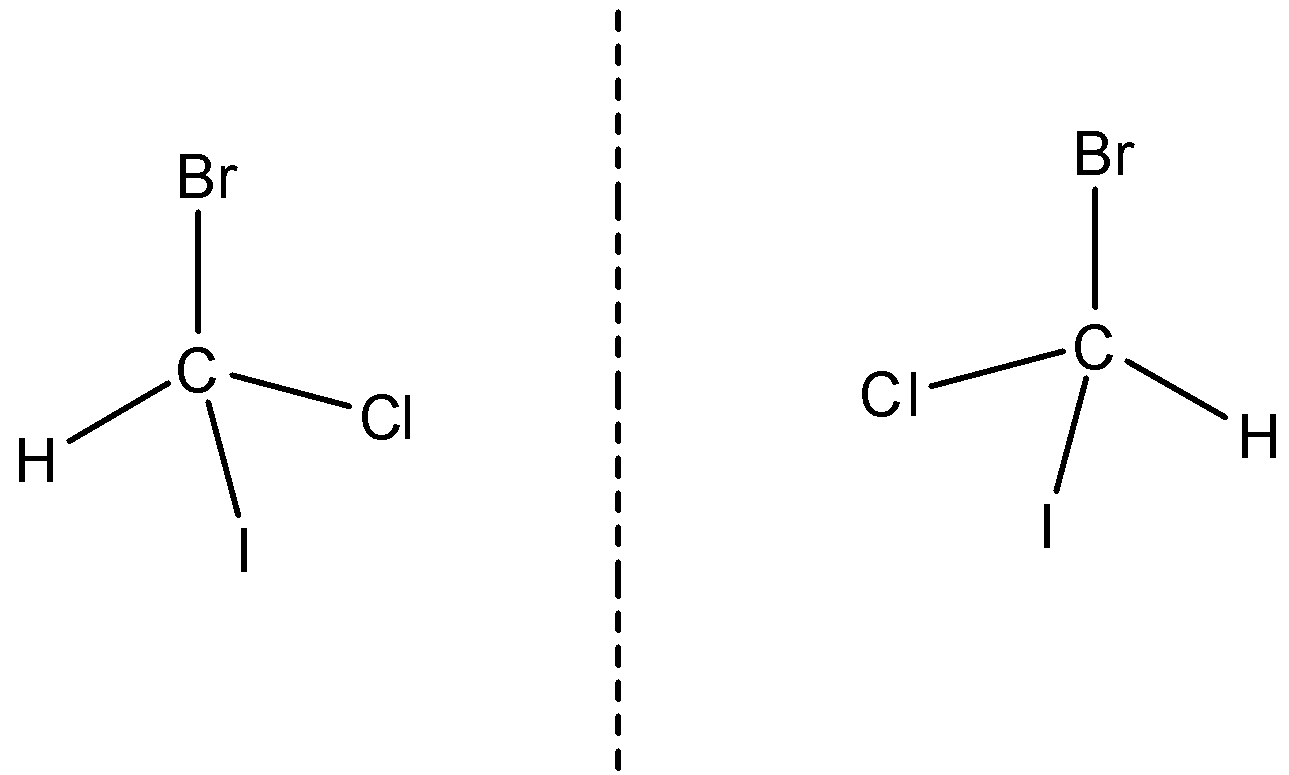
So a mixture containing an equal amount of two enantiomers is known as a racemic mixture or racemic modification.
(b)- For the IUPAC name of $C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-CH(C{{H}_{3}})-CHO$:
The numbering will start from the aldehyde group because it is a functional group. So, the longest chain is of four carbon atoms, and the second carbon atom has a methyl group. So the name will be:
2-Methylbutan-1-al or 2-Methylbutanal.
Note: It must be noted that a racemic mixture is always optically inactive because the rotation of one molecule is exactly opposite of the other molecule, hence cancel each other and remain optically inactive. The numbering of the chain must be done in such a way that the functional group and substituents attached get the lowest possible numbering.
Complete step by step answer:
(a)- The optical activity of the compound is the ability of the compound to rotate the plane of polarized light. And optically active compounds are those which rotate the plane of polarized light.
So those compounds which have a carbon atom on which the attached groups are different can rotate the plane of polarized light. This means that the compound must be asymmetric. If the compound is symmetric then it will not show optical activity or it is an optically inactive compound. The carbon which has all 4 groups attached differently is termed as chiral carbon atom in that molecule.
So, the optically active compounds which are non-superimposable mirror images of each other are called enantiomers and the phenomenon is called enantiomerism.
An example of an optically active compound is bromochloroiodomethane. It is asymmetric and has a non-superimposable mirror image.

So a mixture containing an equal amount of two enantiomers is known as a racemic mixture or racemic modification.
(b)- For the IUPAC name of $C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-CH(C{{H}_{3}})-CHO$:
The numbering will start from the aldehyde group because it is a functional group. So, the longest chain is of four carbon atoms, and the second carbon atom has a methyl group. So the name will be:
2-Methylbutan-1-al or 2-Methylbutanal.
Note: It must be noted that a racemic mixture is always optically inactive because the rotation of one molecule is exactly opposite of the other molecule, hence cancel each other and remain optically inactive. The numbering of the chain must be done in such a way that the functional group and substituents attached get the lowest possible numbering.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




