
A decorative block shown in figure, it is made of two solids, a cube and a hemisphere. The base of the clock is a cube with an edge 5cm and the hemisphere fixed on the top has a diameter of 4.2cm. Find the total surface area of the block. (Take, \[\pi =\dfrac{22}{7}\])
Answer
612.6k+ views
Hint:Total surface area of the block will be the surface area of the cube with the surface area of the hemisphere. Subtract the base area of the hemisphere from total surface area to avoid doubling of area.
Complete step-by-step answer:
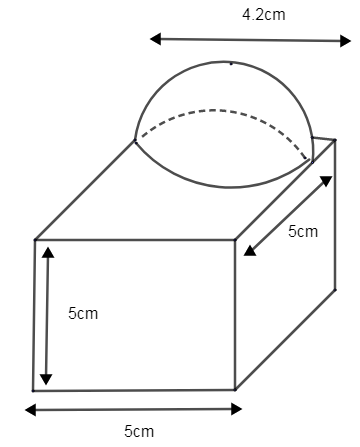
From the figure you can understand that the two solids are a cube and hemisphere. The hemisphere is placed on top of the cube.
Thus we need to find the total surface area of the block. Here the base of the hemisphere is on top of the cube. So it becomes double if we calculate both. Thus we need to subtract the base area of the hemisphere. Thus we can say that the total surface area of the block is the sum of areas of the cube and hemisphere, minus the area of the base of hemisphere.
\[\therefore \] Total surface area of block
= Total surface area of cube + curved surface area of hemisphere – base area of hemisphere - (1)
Now let us first find the area of the cube.
Given that the side of cube = 5cm
Thus total surface area of cube \[=6\times {{\left( side \right)}^{2}}\]
\[\begin{align}
& =6\times {{\left( 5 \right)}^{2}} \\
& =6\times 5\times 5=150c{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
\[\therefore \] Total surface area of cube = \[150c{{m}^{2}}-(2)\]
Let us find the curved surface area of the hemisphere.
Given diameter of hemisphere = 4.2cm
Thus radius, $r = \dfrac{diameter}{2}$ = \[\dfrac{4.2}{2}=2.1\] cm
We know that,
Curved surface area of hemisphere = \[2\pi {{r}^{2}}\]
\[\begin{align}
& =2\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times {{\left( 2.1 \right)}^{2}} \\
& =2\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 2.1\times 2.1=44\times 0.3\times 2.1 \\
& =27.72c{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
\[\therefore \] Curved surface area of hemisphere = \[27.72c{{m}^{2}}-(3)\]
Now base area of hemisphere,
Base of the hemisphere is a circle with radius 2.1 cm.
\[\therefore \] Base area of hemisphere = area of circle = \[\pi {{r}^{2}}\]
\[\begin{align}
& =\dfrac{22}{7}\times 2.1\times 2.1=22\times 0.3\times 2.1 \\
& =13.86c{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
\[\therefore \] Base area of hemisphere \[=13.86c{{m}^{2}}-(4)\]
Thus substitute the values of (2), (3) and (4) in equation (1).
\[\therefore \] Total surface area of block =
Total surface area of cube + curved surface area of hemisphere – base area of hemisphere.
\[\therefore \]Total surface area of block = 150 + 27.72 – 13.86 = \[163.86c{{m}^{2}}\]
Thus we got the total surface area of the block as \[163.86c{{m}^{2}}\].
Note: There are few points that you need to remember while solving this question. The base area of the hemisphere should be subtracted from the total surface area of the block. Or else the area gets repeated as the hemisphere is placed on top of the cube. And remember that the base of a cube is a circle.
Complete step-by-step answer:

From the figure you can understand that the two solids are a cube and hemisphere. The hemisphere is placed on top of the cube.
Thus we need to find the total surface area of the block. Here the base of the hemisphere is on top of the cube. So it becomes double if we calculate both. Thus we need to subtract the base area of the hemisphere. Thus we can say that the total surface area of the block is the sum of areas of the cube and hemisphere, minus the area of the base of hemisphere.
\[\therefore \] Total surface area of block
= Total surface area of cube + curved surface area of hemisphere – base area of hemisphere - (1)
Now let us first find the area of the cube.
Given that the side of cube = 5cm
Thus total surface area of cube \[=6\times {{\left( side \right)}^{2}}\]
\[\begin{align}
& =6\times {{\left( 5 \right)}^{2}} \\
& =6\times 5\times 5=150c{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
\[\therefore \] Total surface area of cube = \[150c{{m}^{2}}-(2)\]
Let us find the curved surface area of the hemisphere.
Given diameter of hemisphere = 4.2cm
Thus radius, $r = \dfrac{diameter}{2}$ = \[\dfrac{4.2}{2}=2.1\] cm
We know that,
Curved surface area of hemisphere = \[2\pi {{r}^{2}}\]
\[\begin{align}
& =2\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times {{\left( 2.1 \right)}^{2}} \\
& =2\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 2.1\times 2.1=44\times 0.3\times 2.1 \\
& =27.72c{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
\[\therefore \] Curved surface area of hemisphere = \[27.72c{{m}^{2}}-(3)\]
Now base area of hemisphere,
Base of the hemisphere is a circle with radius 2.1 cm.
\[\therefore \] Base area of hemisphere = area of circle = \[\pi {{r}^{2}}\]
\[\begin{align}
& =\dfrac{22}{7}\times 2.1\times 2.1=22\times 0.3\times 2.1 \\
& =13.86c{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
\[\therefore \] Base area of hemisphere \[=13.86c{{m}^{2}}-(4)\]
Thus substitute the values of (2), (3) and (4) in equation (1).
\[\therefore \] Total surface area of block =
Total surface area of cube + curved surface area of hemisphere – base area of hemisphere.
\[\therefore \]Total surface area of block = 150 + 27.72 – 13.86 = \[163.86c{{m}^{2}}\]
Thus we got the total surface area of the block as \[163.86c{{m}^{2}}\].
Note: There are few points that you need to remember while solving this question. The base area of the hemisphere should be subtracted from the total surface area of the block. Or else the area gets repeated as the hemisphere is placed on top of the cube. And remember that the base of a cube is a circle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




