
A cylinder of radius R and length L is placed in a uniform electric field E parallel to the cylinder axis. The outward flux over the surface of the cylinder is given by
A. $ 2\pi {{R}^{2}}E $
B. $ \dfrac{\pi {{R}^{2}}E}{2} $
C. $ 2\pi RLE $
D. $ \pi {{R}^{2}}E $
Answer
529.9k+ views
Hint : Electric flux through an area is given as $ \phi =\int{\overrightarrow{E}.\overrightarrow{dA}}=\int{EdA\cos \theta } $ , where $ \overrightarrow{E} $ is the electric field and $ \overrightarrow{dA} $ is the area vector. $ \theta $ is the angle between E and dA.
For uniform electric field and constant value of $ \theta $ , the flux is equal to $ \phi =EA\cos \theta $ .
$ \phi =\int{\overrightarrow{E}.\overrightarrow{dA}}=\int{EdA\cos \theta } $
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Electric flux through a small area is defined as the dot product of the electric field vector and the area vector at that point.
Mathematically, electric flux through an area is given as $ \phi =\int{\overrightarrow{E}.\overrightarrow{dA}}=\int{EdA\cos \theta } $ , where $ \overrightarrow{E} $ is the electric field and $ \overrightarrow{dA} $ is the area vector. $ \theta $ is the angle between E and dA.
For uniform electric field and constant value of $ \theta $ , the flux is equal to $ \phi =EA\cos \theta $ .
It is given that a cylinder of radius R and length L is placed in a uniform electric field E parallel to the cylinder axis.
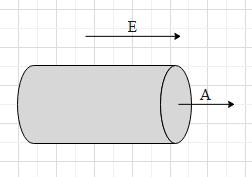
We are supposed to find the outward flux over the surface of the cylinder. As we can see in the figure, the outward flux is through the circular face of the cylinder that is at the right.
For this face, the area vector and the electric field are in the same direction. Therefore, the angle between them is zero and $ \cos 0=1 $ .
This means that outward flux is equal to $ \phi =EA\cos 0=EA $ , where A is the area of the circular face.
Here, $ A=\pi {{R}^{2}} $ .
$ \phi =EA=E(\pi {{R}^{2}})=\pi {{R}^{2}}E $ .
Therefore, the outward flux over the surface of the cylinder is given by $ \pi {{R}^{2}}E $ .
Hence, the correct option is D.
Note :
In this case, although the outward electric flux is non-zero, however the net electric flux through the cylinder is zero.
The outward flux is considered as positive flux and the inward flux is considered as negative flux.
There is a negative flux (inward flux) of the same magnitude through the circular face at the left.
And the flux through the curved surface of the cylinder is zero because the angle between the electric field and the area vector is 90 degrees and $ \cos {{90}^{\circ }}=0 $ .
Therefore, the net flux through the cylinder is zero.
For uniform electric field and constant value of $ \theta $ , the flux is equal to $ \phi =EA\cos \theta $ .
$ \phi =\int{\overrightarrow{E}.\overrightarrow{dA}}=\int{EdA\cos \theta } $
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Electric flux through a small area is defined as the dot product of the electric field vector and the area vector at that point.
Mathematically, electric flux through an area is given as $ \phi =\int{\overrightarrow{E}.\overrightarrow{dA}}=\int{EdA\cos \theta } $ , where $ \overrightarrow{E} $ is the electric field and $ \overrightarrow{dA} $ is the area vector. $ \theta $ is the angle between E and dA.
For uniform electric field and constant value of $ \theta $ , the flux is equal to $ \phi =EA\cos \theta $ .
It is given that a cylinder of radius R and length L is placed in a uniform electric field E parallel to the cylinder axis.

We are supposed to find the outward flux over the surface of the cylinder. As we can see in the figure, the outward flux is through the circular face of the cylinder that is at the right.
For this face, the area vector and the electric field are in the same direction. Therefore, the angle between them is zero and $ \cos 0=1 $ .
This means that outward flux is equal to $ \phi =EA\cos 0=EA $ , where A is the area of the circular face.
Here, $ A=\pi {{R}^{2}} $ .
$ \phi =EA=E(\pi {{R}^{2}})=\pi {{R}^{2}}E $ .
Therefore, the outward flux over the surface of the cylinder is given by $ \pi {{R}^{2}}E $ .
Hence, the correct option is D.
Note :
In this case, although the outward electric flux is non-zero, however the net electric flux through the cylinder is zero.
The outward flux is considered as positive flux and the inward flux is considered as negative flux.
There is a negative flux (inward flux) of the same magnitude through the circular face at the left.
And the flux through the curved surface of the cylinder is zero because the angle between the electric field and the area vector is 90 degrees and $ \cos {{90}^{\circ }}=0 $ .
Therefore, the net flux through the cylinder is zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




