
A cylinder has a surface area of $360\pi $ units square, and is 3 units tall. What is the diameter of the cylinder’s circular base?
(a) 24 units
(b) 36 units
(c) 32 units
(d) 18 units
Answer
598.5k+ views
Hint: We will substitute the given surface area and height in the formula of surface area of a cylinder. The formula is $S=2\pi r\left( r+h \right)$, where S is the surface area, r is the base radius and h is the height of the cylinder. From this equation we will find the radius of the base circle. We will get the diameter of the base circle as $2\times r$.
Complete step by step solution:
The total surface area is given as $360\pi $ units square and the cylinder is 3 units tall. The tallness is also known as the height of the cylinder.
The figure will be as follows:
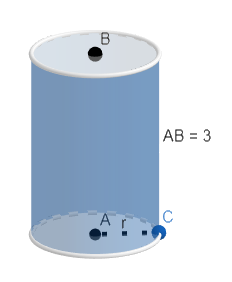
We will substitute S = $360\pi $ and h = 3 in the formula $S=2\pi r\left( r+h \right)$.
$360\pi =2\pi r\left( r+3 \right)$
$\pi $ will get divided by itself. We will divide both sides by 2.
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 360\pi =2\pi r\left( r+3 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{360}{2}=\dfrac{2}{2}r\left( r+3 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 180=r\left( r+3 \right)
\end{align}\]
Now, we will solve the parenthesis. After solving we will get a quadratic equation in r.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{r}^{2}}+3r=180 \\
& \Rightarrow {{r}^{2}}+3r-180=0
\end{align}$
We will solve the quadratic equation by factorisation method. The sum of the two factors should be 3 and product should be -180. Thus, the two factors will be -12 and 15.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{r}^{2}}-12r+15r-180=0 \\
& \Rightarrow r\left( r-12 \right)+15\left( r-12 \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \left( r-12 \right)\left( r+15 \right)=0
\end{align}$
Therefore, r is either 12 or -15, but radius cannot be negative, so radius is 12 units.
Hence, diameter will be $12\times 2=24\ \text{units}$.
Note: It is advisable to be careful while solving the quadratic equation. Another method is to verify the options by substituting the half of the options in the derived quadratic equation as diameters are given in the options. We can also verify the options by substituting the radius derived from the options into the formula of surface area and verify which option gives the surface area as $360\pi $.
Complete step by step solution:
The total surface area is given as $360\pi $ units square and the cylinder is 3 units tall. The tallness is also known as the height of the cylinder.
The figure will be as follows:

We will substitute S = $360\pi $ and h = 3 in the formula $S=2\pi r\left( r+h \right)$.
$360\pi =2\pi r\left( r+3 \right)$
$\pi $ will get divided by itself. We will divide both sides by 2.
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 360\pi =2\pi r\left( r+3 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{360}{2}=\dfrac{2}{2}r\left( r+3 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 180=r\left( r+3 \right)
\end{align}\]
Now, we will solve the parenthesis. After solving we will get a quadratic equation in r.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{r}^{2}}+3r=180 \\
& \Rightarrow {{r}^{2}}+3r-180=0
\end{align}$
We will solve the quadratic equation by factorisation method. The sum of the two factors should be 3 and product should be -180. Thus, the two factors will be -12 and 15.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{r}^{2}}-12r+15r-180=0 \\
& \Rightarrow r\left( r-12 \right)+15\left( r-12 \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \left( r-12 \right)\left( r+15 \right)=0
\end{align}$
Therefore, r is either 12 or -15, but radius cannot be negative, so radius is 12 units.
Hence, diameter will be $12\times 2=24\ \text{units}$.
Note: It is advisable to be careful while solving the quadratic equation. Another method is to verify the options by substituting the half of the options in the derived quadratic equation as diameters are given in the options. We can also verify the options by substituting the radius derived from the options into the formula of surface area and verify which option gives the surface area as $360\pi $.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




