
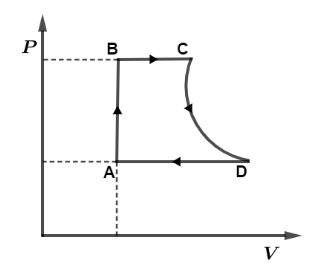
A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of an ideal gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown in figure. The heat exchanged by the engine with the surroundings at constant volume is: Take $({C_V} = \dfrac{3}{2}R)$
A. $({P_B} - {P_A}){V_A}$
B. $\dfrac{1}{2}({P_B} - {P_A}){V_A}$
C. $\dfrac{3}{2}[{P_B}{V_B} - {P_A}{V_A}]$
D. $\dfrac{5}{2}[{P_B}{V_B} - {P_A}{V_A}]$

Answer
514.8k+ views
Hint: In thermodynamics, we know that a cyclic process is one in which total internal energy is zero and work done is the area under $P - V$ curve. Isobaric process is one in which pressure remains constant whereas an isochoric process is one in which volume remains constant. We will use these parameters on $P - V$ to find the heat exchanged with the surrounding.
Formula used:
First law of thermodynamics can be written mathematically as $dQ = dU + dW$ and $dQ = {C_V}dT$ where ${C_V}$ is known as specific heat at constant volume.
$dW = PdV$ Is the work done by the gas.
Complete step by step answer:
From the given $P - V$ curve we have, process AB is isochoric which is at constant volume so, $dV = 0$ which means $dW = 0$ then by using relation, $dQ = dU + dW$
$d{Q_{AB}} = d{U_{AB}} \to (i)$
Now, again we can use the relation of $dQ = {C_V}dT$ in order to find heat exchange in process AB
$Q = \int\limits_{{T_A}}^{{T_B}} {{C_V}dT} $
$\Rightarrow Q = {C_V}[{T_B} - {T_A}]$
Now, it points of A and B use the ideal gas equation which is $PV = nRT$ given that, $n = 1mole$ so
For point A we have, ${P_A}{V_A}(\dfrac{1}{R}) = {T_A}$
For point B we have, ${P_B}{V_B}(\dfrac{1}{R}) = {T_{_B}}$ put these values in equation $Q = {C_V}[{T_B} - {T_A}]$ we get,
$Q = {C_V}[{P_B}{V_B} - {P_A}{V_A}](\dfrac{1}{R})$
Put $({C_V} = \dfrac{3}{2}R)$ as given in the question
$Q = \dfrac{{3R}}{2}[{P_B}{V_B} - {P_A}{V_A}](\dfrac{1}{R})$
$\therefore Q = \dfrac{3}{2}[{P_B}{V_B} - {P_A}{V_A}]$
So, the heat exchanged by the gas with surrounding at constant volume is $Q = \dfrac{3}{2}[{P_B}{V_B} - {P_A}{V_A}]$
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note: It should be remembered that, an ideal gas is one which obeys the ideal gas equation perfectly which is written as $PV = nRT$ where $R$ is known as the universal gas constant and it’s a fixed constant having a value of $8.314\,J{K^{ - 1}}mo{l^{ - 1}}$ . Also work done in an isochoric process is always zero while in an isobaric process it’s written as ${W_{isobaric}} = P({V_2} - {V_1})$ .
Formula used:
First law of thermodynamics can be written mathematically as $dQ = dU + dW$ and $dQ = {C_V}dT$ where ${C_V}$ is known as specific heat at constant volume.
$dW = PdV$ Is the work done by the gas.
Complete step by step answer:
From the given $P - V$ curve we have, process AB is isochoric which is at constant volume so, $dV = 0$ which means $dW = 0$ then by using relation, $dQ = dU + dW$
$d{Q_{AB}} = d{U_{AB}} \to (i)$
Now, again we can use the relation of $dQ = {C_V}dT$ in order to find heat exchange in process AB
$Q = \int\limits_{{T_A}}^{{T_B}} {{C_V}dT} $
$\Rightarrow Q = {C_V}[{T_B} - {T_A}]$
Now, it points of A and B use the ideal gas equation which is $PV = nRT$ given that, $n = 1mole$ so
For point A we have, ${P_A}{V_A}(\dfrac{1}{R}) = {T_A}$
For point B we have, ${P_B}{V_B}(\dfrac{1}{R}) = {T_{_B}}$ put these values in equation $Q = {C_V}[{T_B} - {T_A}]$ we get,
$Q = {C_V}[{P_B}{V_B} - {P_A}{V_A}](\dfrac{1}{R})$
Put $({C_V} = \dfrac{3}{2}R)$ as given in the question
$Q = \dfrac{{3R}}{2}[{P_B}{V_B} - {P_A}{V_A}](\dfrac{1}{R})$
$\therefore Q = \dfrac{3}{2}[{P_B}{V_B} - {P_A}{V_A}]$
So, the heat exchanged by the gas with surrounding at constant volume is $Q = \dfrac{3}{2}[{P_B}{V_B} - {P_A}{V_A}]$
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note: It should be remembered that, an ideal gas is one which obeys the ideal gas equation perfectly which is written as $PV = nRT$ where $R$ is known as the universal gas constant and it’s a fixed constant having a value of $8.314\,J{K^{ - 1}}mo{l^{ - 1}}$ . Also work done in an isochoric process is always zero while in an isobaric process it’s written as ${W_{isobaric}} = P({V_2} - {V_1})$ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




