
A current of 1 ampere is passed through a straight wire of length $2.0m$. What will be the magnetic field at a point in air at a distance of $0.3m$ from either end of the wire and lying on the axis of wire ?
(A) $\dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{2\pi }}$
(B) $\dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }}$
(C) $\dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{8\pi }}$
(D) zero
Answer
581.7k+ views
Hint:In order to solve this problem first draw a diagram in which point P is shown perfectly with wire.
After that use the formula of the magnetic field due to wire derived with the help of Biot – Savart law which is :
$d\vec B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }}\dfrac{{I(d\vec \ell \times \vec r)}}{{{r^3}}}$
Now put the angle between $\vec d\ell $ and $\vec r$ zero because the P point is situated at the axis of the wire.
Finally we get a magnetic field at point P.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the magnetic field due to wire is given as
$d\vec B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }}\dfrac{{I(d\vec \ell \times \vec r)}}{{{r^3}}}$ …..(1)
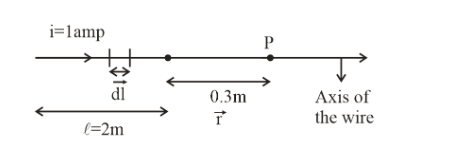
Here direction of $\vec d\ell $ and $\vec r$ is same i.e., angle between then is zero, so, the cross product of them is zero i.e., $\vec d\ell \times \vec r = |\vec d\ell ||\vec r|\sin \theta $
$ = |\vec d\ell ||\vec r|\sin 0$
$\vec d\ell \times \vec r = 0$ …..(2)
So, from equation 1 & 2, we get
$dB = 0$
$\therefore B = 0$
Hence, the magnetic field at point P i.e., at the axis of the wire is zero.
So, option D is the correct answer zero.
Note:Here students may get confused between methods of calculating magnetic fields due to wire.
There are 2 laws :
(1) Biot – Savart law
(2) Ampere’s Circuital law
-The second point at which student may get confused is that where the point is situated i.e.
-If point is situated at the axial line then magnetic field $B = 0$ because \[\theta = {0^ \circ }\]
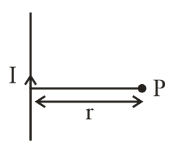
-If point is not at the axis of wire then magnetic field due to wire at any point is given as
${B_P} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{2\pi r}}$ because \[\theta = {90^ \circ }\]
After that use the formula of the magnetic field due to wire derived with the help of Biot – Savart law which is :
$d\vec B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }}\dfrac{{I(d\vec \ell \times \vec r)}}{{{r^3}}}$
Now put the angle between $\vec d\ell $ and $\vec r$ zero because the P point is situated at the axis of the wire.
Finally we get a magnetic field at point P.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the magnetic field due to wire is given as
$d\vec B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }}\dfrac{{I(d\vec \ell \times \vec r)}}{{{r^3}}}$ …..(1)

Here direction of $\vec d\ell $ and $\vec r$ is same i.e., angle between then is zero, so, the cross product of them is zero i.e., $\vec d\ell \times \vec r = |\vec d\ell ||\vec r|\sin \theta $
$ = |\vec d\ell ||\vec r|\sin 0$
$\vec d\ell \times \vec r = 0$ …..(2)
So, from equation 1 & 2, we get
$dB = 0$
$\therefore B = 0$
Hence, the magnetic field at point P i.e., at the axis of the wire is zero.
So, option D is the correct answer zero.
Note:Here students may get confused between methods of calculating magnetic fields due to wire.
There are 2 laws :
(1) Biot – Savart law
(2) Ampere’s Circuital law
-The second point at which student may get confused is that where the point is situated i.e.
-If point is situated at the axial line then magnetic field $B = 0$ because \[\theta = {0^ \circ }\]
-If point is not at the axis of wire then magnetic field due to wire at any point is given as
${B_P} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{2\pi r}}$ because \[\theta = {90^ \circ }\]

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




