
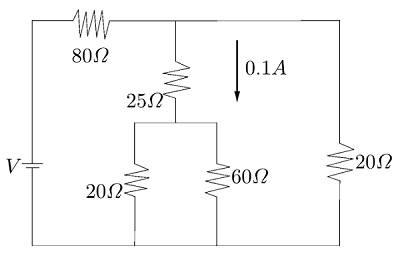
A current of $0.1{\text{ }}A$. flows through a $25{\text{ }}\Omega $ resistor represented by the circuit diagram. The current in the $80{\text{ }}\Omega $ resistor is
A. $0.1{\text{ }}A\:$
B. $0.2{\text{ }}A\:$
C. $0.3{\text{ }}A\:$
D. $0.4{\text{ }}A\:$

Answer
510.6k+ views
Hint:Firstly, we will evaluate the potential of the cell from the given diagram. We will first evaluate the equivalent resistance of the whole circuit and then use ohm's law to evaluate the current through the targeted resistor.
Formulae Used:
${R_{Series}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}{R_1}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}{R_2}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}...{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}{R_n}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{R_{Parallel}}}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}...{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{{R_n}}}$
$\Rightarrow V{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}IR$
$\Rightarrow I{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{V}{R}$
Complete step by step answer:
In the diagram, it is given that $0.1{\text{ }}A$ of current through the $25{\text{ }}\Omega $ resistor and this resistor lies in an arm parallel to the cell and thus the potential of the cell can be calculated as
$V{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}(0.1{\text{ }}A){\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}(25{\text{ }}\Omega )$
Thus, we get
$V{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}2.5{\text{ }}V$
Now, the net resistance in the secondary circuit in the middle arm can be calculated through the formula of parallel circuits.Thus,
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{ne{t_{\sec }}}}}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{20}}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{60}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{15}}$
Thus,
${R_{ne{t_{\sec }}}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}15{\text{ }}\Omega $
Now, for the net resistance in the middle arm, we would use the formula of the series combination.
${R_{Mid}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}25{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}15{\text{ }} \\
\Rightarrow {R_{Mid}}{\text{ }}= {\text{ }}40{\text{ }}\Omega $
Now, we know that current varies inversely with resistance.Let us consider that current $I$ flows out from the cell.Thus,
$\dfrac{{0.1}}{I}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{20}}{{40}}$
Further, we get
$I{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}0.2{\text{ }}A$
Thus, the current flowing through the targeted resistor is
$0.2{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}0.1{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}0.3{\text{ }}A$
Hence, the correct answer is C.
Note:Students should be very much cautious while evaluating the net resistance as students often make mistakes while judging the type of combination of the resistors. We have used the concept of variance of current with respect to resistance as there are two arms parallel to each other as well as to the arm containing the cell. If we observe carefully, we can see that we have not used the resistance of the resistor in series as it will be of no use if we compare its variance with that of the parallel arm as the potentials are different for both. Thus, students should be considerate while using this process.
Formulae Used:
${R_{Series}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}{R_1}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}{R_2}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}...{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}{R_n}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{R_{Parallel}}}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}...{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{{R_n}}}$
$\Rightarrow V{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}IR$
$\Rightarrow I{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{V}{R}$
Complete step by step answer:
In the diagram, it is given that $0.1{\text{ }}A$ of current through the $25{\text{ }}\Omega $ resistor and this resistor lies in an arm parallel to the cell and thus the potential of the cell can be calculated as
$V{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}(0.1{\text{ }}A){\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}(25{\text{ }}\Omega )$
Thus, we get
$V{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}2.5{\text{ }}V$
Now, the net resistance in the secondary circuit in the middle arm can be calculated through the formula of parallel circuits.Thus,
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{ne{t_{\sec }}}}}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{20}}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{60}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{15}}$
Thus,
${R_{ne{t_{\sec }}}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}15{\text{ }}\Omega $
Now, for the net resistance in the middle arm, we would use the formula of the series combination.
${R_{Mid}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}25{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}15{\text{ }} \\
\Rightarrow {R_{Mid}}{\text{ }}= {\text{ }}40{\text{ }}\Omega $
Now, we know that current varies inversely with resistance.Let us consider that current $I$ flows out from the cell.Thus,
$\dfrac{{0.1}}{I}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{20}}{{40}}$
Further, we get
$I{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}0.2{\text{ }}A$
Thus, the current flowing through the targeted resistor is
$0.2{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}0.1{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}0.3{\text{ }}A$
Hence, the correct answer is C.
Note:Students should be very much cautious while evaluating the net resistance as students often make mistakes while judging the type of combination of the resistors. We have used the concept of variance of current with respect to resistance as there are two arms parallel to each other as well as to the arm containing the cell. If we observe carefully, we can see that we have not used the resistance of the resistor in series as it will be of no use if we compare its variance with that of the parallel arm as the potentials are different for both. Thus, students should be considerate while using this process.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

RNA and DNA are chiral molecules their chirality is class 12 chemistry CBSE




