
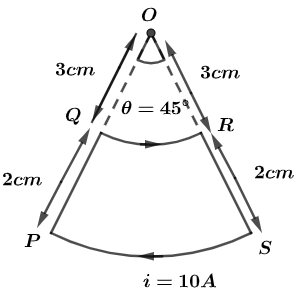
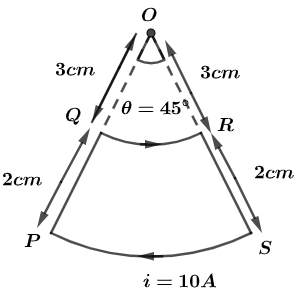
A current loop, having two circular arcs joined by two radial lines is shown in the figure. It carries a current of $10A$. The magnetic field at the point O will be close to:
A. $1.0\times {{10}^{-5}}T$
B. $1.5\times {{10}^{-5}}T$
C. $1.0\times {{10}^{-7}}T$
D. $2.0\times {{10}^{-7}}T$

Answer
600k+ views
Hint: We know that the formula for magnetic field for an arc subtended by an angle theta can be given by Biot-Savart's law as, $B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}}{4\pi }\cdot \dfrac{\theta i}{r}$, using this formula we will find the magnetic field by arc at distance OQ from the centre and then at distance OP from the centre and then we will take their difference to find the over all magnetic field acting at centre O.
Formula used: $B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}}{4\pi }\cdot \dfrac{\theta i}{r}$
Complete step by step answer:
In question we have given that a current loop, having two circular arcs joined by two radial lines is shown in the figure and it carries a current of $10A$.
Now we have been asked to find the magnetic field at centre O, so, now the magnetic field at centre due to circular arc can be given by the formula,
$B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}}{4\pi }\cdot \dfrac{\theta i}{r}$
Where, B is magnitude of magnetic field, $\theta $ is angle subtended by the arc, r is radius of arc and ${{\mu }_{0}}$ is coefficient of magnetic field.
Now, the arc QR is at the distance OQ from the centre so the radius can be given by,
$OQ={{r}_{1}}=3\ cm=3\times {{10}^{-2}}m$ ………………….(i)
In the same way, arc PS is at distance OP from the centre so, the radius can be given by,
$OP={{r}_{2}}=\left( 3+2 \right)\ cm=5cm=5\times {{10}^{-2}}m$ ……………….(ii)
Now, the magnetic field at centre O by arc QR can be given as,
${{B}_{OQ}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}}{4\pi }\cdot \dfrac{\theta i}{{{r}_{1}}}$ …………..(iii)
Where,$i=10A$, $\theta =45{}^\circ $, ${{\mu }_{0}}=4\pi \times {{10}^{-7}}$ and ${{r}_{1}}=3\times {{10}^{-2}}m$
Now, we will convert $\theta $ from degree to radian using the formula,
$rad=\deg \times \dfrac{\pi }{180}$
$\Rightarrow rad=45\times \dfrac{\pi }{180}\Rightarrow \dfrac{\pi }{4}rad$
Substituting all these values in equation (iii) we will get,
${{B}_{OP}}=\dfrac{4\pi \times {{10}^{-7}}}{4\pi }\times \dfrac{\pi }{4}\times \dfrac{10}{3\times {{10}^{-2}}}$ ……………………(iv)
In the same way we can find the magnetic field at centre O by arc PS as,
${{B}_{PS}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}}{4\pi }\cdot \dfrac{\theta i}{{{r}_{2}}}$
Again, substituting the values we will get,
${{B}_{PS}}=\dfrac{4\pi \times {{10}^{-7}}}{4\pi }\times \dfrac{\pi }{4}\times \dfrac{10}{5\times {{10}^{-2}}}$ ………………………(v)
Now, we will consider the directions of current and on the basis of that we will decide the signs, as the currents are in opposite directions to each other it will be a negative sign.
So, the overall magnetic field can be given as,
$B={{B}_{OP}}-{{B}_{PS}}=\dfrac{4\pi \times {{10}^{-7}}}{4\pi }\times \dfrac{\pi }{4}\times \dfrac{10}{3\times {{10}^{-2}}}-\dfrac{4\pi \times {{10}^{-7}}}{4\pi }\times \dfrac{\pi }{4}\times \dfrac{10}{5\times {{10}^{-2}}}$
Further, simplifying the equation we will get,
$\Rightarrow B=\dfrac{4\pi \times {{10}^{-7}}}{4\pi }\times \dfrac{\pi }{4}\times 10\times \left[ \dfrac{1}{3\times {{10}^{-2}}}-\dfrac{1}{5\times {{10}^{-2}}} \right]$
$\Rightarrow B={{10}^{-6}}\times \dfrac{\pi }{4}\left[ \dfrac{5\times {{10}^{-2}}-3\times {{10}^{-2}}}{3\times {{10}^{-2}}\times 5\times {{10}^{-2}}} \right]$
$\Rightarrow B={{10}^{-6}}\times \dfrac{\pi }{4}\left[ \dfrac{2\times {{10}^{-2}}}{15\times {{10}^{-4}}} \right]$
$\Rightarrow B={{10}^{-6}}\times \dfrac{\pi }{4}\left[ \dfrac{2}{15\times {{10}^{-2}}} \right]$
$\Rightarrow B={{10}^{-6}}\times \dfrac{\pi }{4}\left[ \dfrac{2}{15\times {{10}^{-2}}} \right]={{10}^{-4}}\times \dfrac{\pi }{4}\left[ \dfrac{2}{15} \right]$
$\Rightarrow B={{10}^{-4}}\times \dfrac{\pi }{3}=1\times {{10}^{-5}}T$
Hence, the magnetic field at centre O is $1.0\times {{10}^{-5}}T$.
Thus, option (a) is correct.
Note: This sum can also be solved directly by using the formula $B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}\theta i}{4\pi }\cdot \left[ \dfrac{1}{{{r}_{1}}}-\dfrac{1}{{{r}_{2}}} \right]$ instead of calculating the magnetic fields at ${{r}_{1}}$ and ${{r}_{2}}$ separately and then find the difference to find the overall magnetic field. Students should also take care of the direction of current flow as considering the directions of flow positive or negative signs are decided.
Formula used: $B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}}{4\pi }\cdot \dfrac{\theta i}{r}$
Complete step by step answer:
In question we have given that a current loop, having two circular arcs joined by two radial lines is shown in the figure and it carries a current of $10A$.

Now we have been asked to find the magnetic field at centre O, so, now the magnetic field at centre due to circular arc can be given by the formula,
$B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}}{4\pi }\cdot \dfrac{\theta i}{r}$
Where, B is magnitude of magnetic field, $\theta $ is angle subtended by the arc, r is radius of arc and ${{\mu }_{0}}$ is coefficient of magnetic field.
Now, the arc QR is at the distance OQ from the centre so the radius can be given by,
$OQ={{r}_{1}}=3\ cm=3\times {{10}^{-2}}m$ ………………….(i)
In the same way, arc PS is at distance OP from the centre so, the radius can be given by,
$OP={{r}_{2}}=\left( 3+2 \right)\ cm=5cm=5\times {{10}^{-2}}m$ ……………….(ii)
Now, the magnetic field at centre O by arc QR can be given as,
${{B}_{OQ}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}}{4\pi }\cdot \dfrac{\theta i}{{{r}_{1}}}$ …………..(iii)
Where,$i=10A$, $\theta =45{}^\circ $, ${{\mu }_{0}}=4\pi \times {{10}^{-7}}$ and ${{r}_{1}}=3\times {{10}^{-2}}m$
Now, we will convert $\theta $ from degree to radian using the formula,
$rad=\deg \times \dfrac{\pi }{180}$
$\Rightarrow rad=45\times \dfrac{\pi }{180}\Rightarrow \dfrac{\pi }{4}rad$
Substituting all these values in equation (iii) we will get,
${{B}_{OP}}=\dfrac{4\pi \times {{10}^{-7}}}{4\pi }\times \dfrac{\pi }{4}\times \dfrac{10}{3\times {{10}^{-2}}}$ ……………………(iv)
In the same way we can find the magnetic field at centre O by arc PS as,
${{B}_{PS}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}}{4\pi }\cdot \dfrac{\theta i}{{{r}_{2}}}$
Again, substituting the values we will get,
${{B}_{PS}}=\dfrac{4\pi \times {{10}^{-7}}}{4\pi }\times \dfrac{\pi }{4}\times \dfrac{10}{5\times {{10}^{-2}}}$ ………………………(v)
Now, we will consider the directions of current and on the basis of that we will decide the signs, as the currents are in opposite directions to each other it will be a negative sign.
So, the overall magnetic field can be given as,
$B={{B}_{OP}}-{{B}_{PS}}=\dfrac{4\pi \times {{10}^{-7}}}{4\pi }\times \dfrac{\pi }{4}\times \dfrac{10}{3\times {{10}^{-2}}}-\dfrac{4\pi \times {{10}^{-7}}}{4\pi }\times \dfrac{\pi }{4}\times \dfrac{10}{5\times {{10}^{-2}}}$
Further, simplifying the equation we will get,
$\Rightarrow B=\dfrac{4\pi \times {{10}^{-7}}}{4\pi }\times \dfrac{\pi }{4}\times 10\times \left[ \dfrac{1}{3\times {{10}^{-2}}}-\dfrac{1}{5\times {{10}^{-2}}} \right]$
$\Rightarrow B={{10}^{-6}}\times \dfrac{\pi }{4}\left[ \dfrac{5\times {{10}^{-2}}-3\times {{10}^{-2}}}{3\times {{10}^{-2}}\times 5\times {{10}^{-2}}} \right]$
$\Rightarrow B={{10}^{-6}}\times \dfrac{\pi }{4}\left[ \dfrac{2\times {{10}^{-2}}}{15\times {{10}^{-4}}} \right]$
$\Rightarrow B={{10}^{-6}}\times \dfrac{\pi }{4}\left[ \dfrac{2}{15\times {{10}^{-2}}} \right]$
$\Rightarrow B={{10}^{-6}}\times \dfrac{\pi }{4}\left[ \dfrac{2}{15\times {{10}^{-2}}} \right]={{10}^{-4}}\times \dfrac{\pi }{4}\left[ \dfrac{2}{15} \right]$
$\Rightarrow B={{10}^{-4}}\times \dfrac{\pi }{3}=1\times {{10}^{-5}}T$
Hence, the magnetic field at centre O is $1.0\times {{10}^{-5}}T$.
Thus, option (a) is correct.
Note: This sum can also be solved directly by using the formula $B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}\theta i}{4\pi }\cdot \left[ \dfrac{1}{{{r}_{1}}}-\dfrac{1}{{{r}_{2}}} \right]$ instead of calculating the magnetic fields at ${{r}_{1}}$ and ${{r}_{2}}$ separately and then find the difference to find the overall magnetic field. Students should also take care of the direction of current flow as considering the directions of flow positive or negative signs are decided.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




