
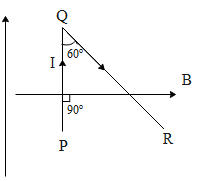
A current ‘I’ is flowing through a wire PQR. This wire is bent in the form of an angle and is placed in uniform magnetic field ‘B’ according to the figure. If PQ =$l$ and $\angle PQR={{60}^{\circ }}$ . The ratio of magnetic forces on the PQ and QR respectively.
a) 1:2
b) $\sqrt{3}:2$
c) $2:\sqrt{3}$
d) 1: 1

Answer
534.3k+ views
Hint: If a current carrying wire is placed in a magnetic field, it experiences a force. The force is proportional to the length of the wire, the magnitude of the field and the angle between the field and the current carrying element of the wire. The magnetic field is uniform, and hence using the expression for force on a current carrying wire and comparing the two forces on the respective sections will enable us to select the appropriate answer.
Formula used:
$F=ilB\sin \theta $
Complete answer:
Let us say we have a wire of length ‘l’ carrying current ‘i’ placed in a uniform magnetic field ‘B’. If the angle between the wire and filed is equal to$\theta $ , then the force (F) on the current carrying wire is equal to,
$F=ilB\sin \theta $
The section PQ of the wire carries current ‘I’ and is perpendicular to the magnetic field. Hence the force on the section PQ is equal to,
$\begin{align}
& {{F}_{PQ}}=IlB\sin {{90}^{\circ }} \\
& \because \sin {{90}^{\circ }}=1 \\
& \therefore {{F}_{PQ}}=IlB \\
\end{align}$
If we observe the above figure, the points PQR form a right-angled triangle right angled at P. Hence segment QR of the wire forms the hypotenuse of length x. Since QR makes an angle of 60 degrees with the segment PQ of length ‘l’, the length of the QR is,
$\begin{align}
& \cos {{60}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{PQ}{QR} \\
& \because PQ=l,\text{ }\cos {{60}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{l}{QR} \\
& \therefore QR=2l \\
\end{align}$
The segment QR makes an angle of 30 degrees with the external magnetic field. Hence the force experienced by wire QR is,
$\begin{align}
& {{F}_{QR}}=I(2l)B\sin {{30}^{\circ }} \\
& \because \sin {{30}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
& \therefore {{F}_{PQ}}=\dfrac{2IlB}{2}=IlB \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the ratio of the force on the wire PQ and QR is equal to,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{{{F}_{PQ}}}{{{F}_{QR}}}=\dfrac{IlB}{IlB} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{F}_{PQ}}}{{{F}_{QR}}}=1 \\
& \therefore {{F}_{PQ}}:{{F}_{QR}}=1:1 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the correct answer of the above question is option d.
Note:
The segment of wire QR is joined to the wire PQ hence both wires are to be considered to be in series. Therefore, the same current flows in both the segments of the wires. In order to determine direction of the force on the above current carrying conductors can be obtained from Fleming’s left hand rule which says that stretch the thumb, middle singer and the index finger of your left hand such that all of them are mutually perpendicular to each other. If the magnetic field is in the direction of the index finger and the current in the direction of the middle finger, then the force on the conductor is in the direction of the thumb.
Formula used:
$F=ilB\sin \theta $
Complete answer:
Let us say we have a wire of length ‘l’ carrying current ‘i’ placed in a uniform magnetic field ‘B’. If the angle between the wire and filed is equal to$\theta $ , then the force (F) on the current carrying wire is equal to,
$F=ilB\sin \theta $
The section PQ of the wire carries current ‘I’ and is perpendicular to the magnetic field. Hence the force on the section PQ is equal to,
$\begin{align}
& {{F}_{PQ}}=IlB\sin {{90}^{\circ }} \\
& \because \sin {{90}^{\circ }}=1 \\
& \therefore {{F}_{PQ}}=IlB \\
\end{align}$
If we observe the above figure, the points PQR form a right-angled triangle right angled at P. Hence segment QR of the wire forms the hypotenuse of length x. Since QR makes an angle of 60 degrees with the segment PQ of length ‘l’, the length of the QR is,
$\begin{align}
& \cos {{60}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{PQ}{QR} \\
& \because PQ=l,\text{ }\cos {{60}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{l}{QR} \\
& \therefore QR=2l \\
\end{align}$
The segment QR makes an angle of 30 degrees with the external magnetic field. Hence the force experienced by wire QR is,
$\begin{align}
& {{F}_{QR}}=I(2l)B\sin {{30}^{\circ }} \\
& \because \sin {{30}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
& \therefore {{F}_{PQ}}=\dfrac{2IlB}{2}=IlB \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the ratio of the force on the wire PQ and QR is equal to,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{{{F}_{PQ}}}{{{F}_{QR}}}=\dfrac{IlB}{IlB} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{F}_{PQ}}}{{{F}_{QR}}}=1 \\
& \therefore {{F}_{PQ}}:{{F}_{QR}}=1:1 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the correct answer of the above question is option d.
Note:
The segment of wire QR is joined to the wire PQ hence both wires are to be considered to be in series. Therefore, the same current flows in both the segments of the wires. In order to determine direction of the force on the above current carrying conductors can be obtained from Fleming’s left hand rule which says that stretch the thumb, middle singer and the index finger of your left hand such that all of them are mutually perpendicular to each other. If the magnetic field is in the direction of the index finger and the current in the direction of the middle finger, then the force on the conductor is in the direction of the thumb.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




